Armon Shariati
Simultaneous Localization and Layout Model Selection in Manhattan Worlds
Dec 13, 2018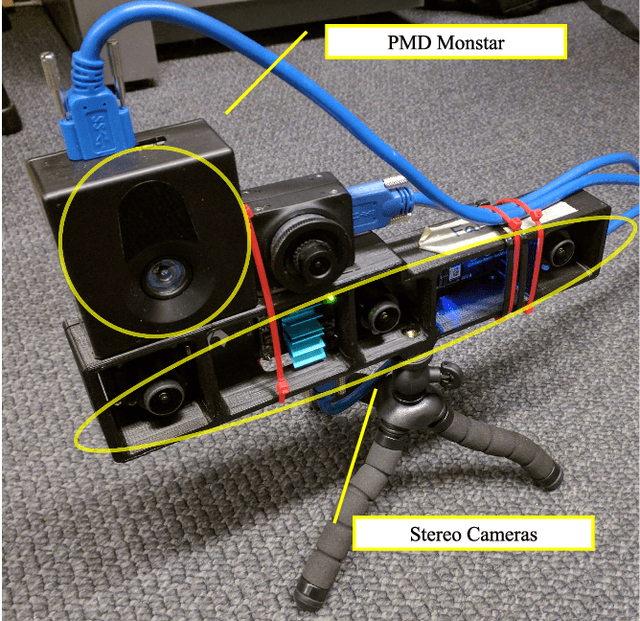
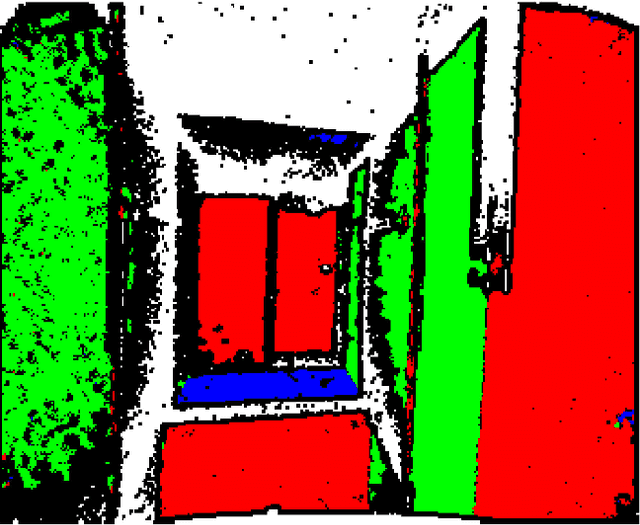

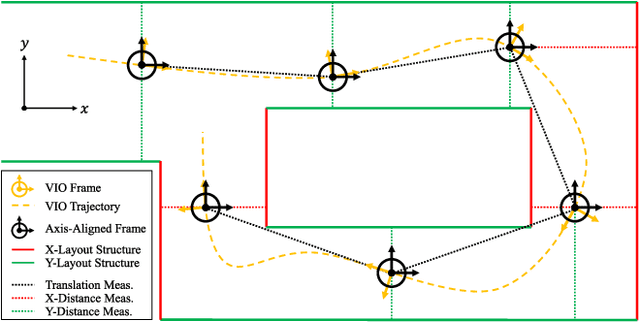
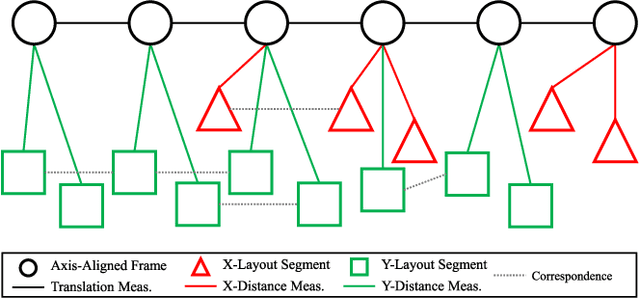
Abstract:In this paper, we will demonstrate how Manhattan structure can be exploited to transform the Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) problem, which is typically solved by a nonlinear optimization over feature positions, into a model selection problem solved by a convex optimization over higher order layout structures, namely walls, floors, and ceilings. Furthermore, we show how our novel formulation leads to an optimization procedure that automatically performs data association and loop closure and which ultimately produces the simplest model of the environment that is consistent with the available measurements. We verify our method on real world data sets collected with various sensing modalities.
Predictive and Semantic Layout Estimation for Robotic Applications in Manhattan Worlds
Nov 19, 2018
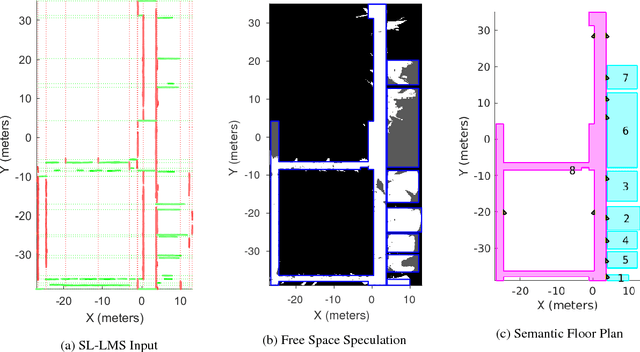
Abstract:This paper describes an approach to automatically extracting floor plans from the kinds of incomplete measurements that could be acquired by an autonomous mobile robot. The approach proceeds by reasoning about extended structural layout surfaces which are automatically extracted from the available data. The scheme can be run in an online manner to build water tight representations of the environment. The system effectively speculates about room boundaries and free space regions which provides useful guidance to subsequent motion planning systems. Experimental results are presented on multiple data sets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge