Armand Stricker
Chitchat as Interference: Adding User Backstories to Task-Oriented Dialogues
Feb 23, 2024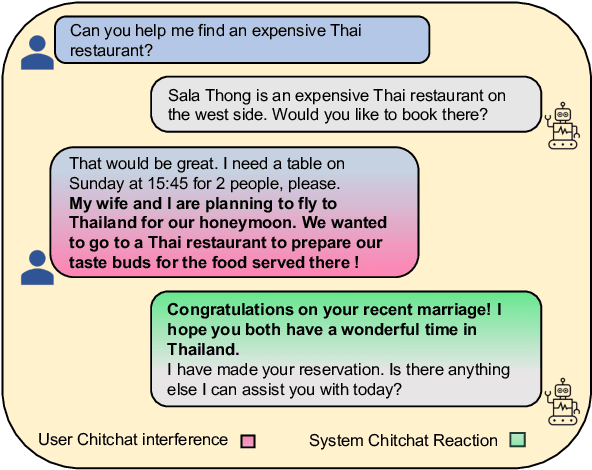
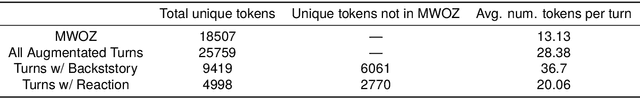
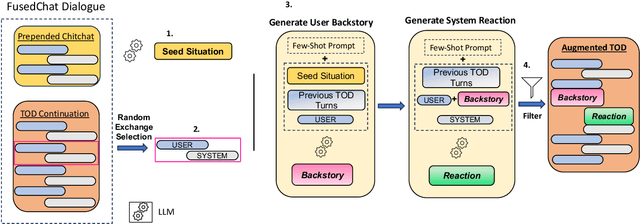

Abstract:During task-oriented dialogues (TODs), human users naturally introduce chitchat that is beyond the immediate scope of the task, interfering with the flow of the conversation. To address this issue without the need for expensive manual data creation, we use few-shot prompting with Llama-2-70B to enhance the MultiWOZ dataset with user backstories, a typical example of chitchat interference in TODs. We assess the impact of this addition by testing two models: one trained solely on TODs and another trained on TODs with a preliminary chitchat interaction. Our analysis reveals that our enriched dataset poses a significant challenge to these systems. Moreover, we demonstrate that our dataset can be effectively used for training purposes, enabling a system to consistently acknowledge the user's backstory while also successfully moving the task forward in the same turn, as confirmed by human evaluation. These findings highlight the benefits of generating novel chitchat-TOD scenarios to test TOD systems more thoroughly and improve their resilience to natural user interferences.
A Unified Approach to Emotion Detection and Task-Oriented Dialogue Modeling
Jan 24, 2024Abstract:In current text-based task-oriented dialogue (TOD) systems, user emotion detection (ED) is often overlooked or is typically treated as a separate and independent task, requiring additional training. In contrast, our work demonstrates that seamlessly unifying ED and TOD modeling brings about mutual benefits, and is therefore an alternative to be considered. Our method consists in augmenting SimpleToD, an end-to-end TOD system, by extending belief state tracking to include ED, relying on a single language model. We evaluate our approach using GPT-2 and Llama-2 on the EmoWOZ benchmark, a version of MultiWOZ annotated with emotions. Our results reveal a general increase in performance for ED and task results. Our findings also indicate that user emotions provide useful contextual conditioning for system responses, and can be leveraged to further refine responses in terms of empathy.
Enhancing Task-Oriented Dialogues with Chitchat: a Comparative Study Based on Lexical Diversity and Divergence
Nov 23, 2023



Abstract:As a recent development, task-oriented dialogues (TODs) have been enriched with chitchat in an effort to make dialogues more diverse and engaging. This enhancement is particularly valuable as TODs are often confined to narrow domains, making the mitigation of repetitive and predictable responses a significant challenge. This paper presents a comparative analysis of three chitchat enhancements, aiming to identify the most effective approach in terms of diversity. Additionally, we quantify the divergence between the added chitchat, the original task-oriented language, and chitchat typically found in chitchat datasets, highlighting the top 20 divergent keywords for each comparison. Our findings drive a discussion on future enhancements for augmenting TODs, emphasizing the importance of grounding dialogues beyond the task to achieve more diverse and natural exchanges.
Searching for Snippets of Open-Domain Dialogue in Task-Oriented Dialogue Datasets
Nov 23, 2023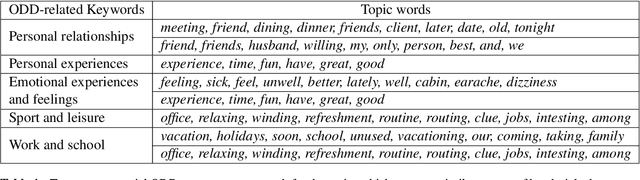
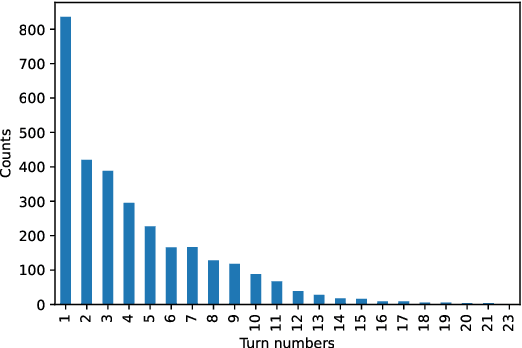
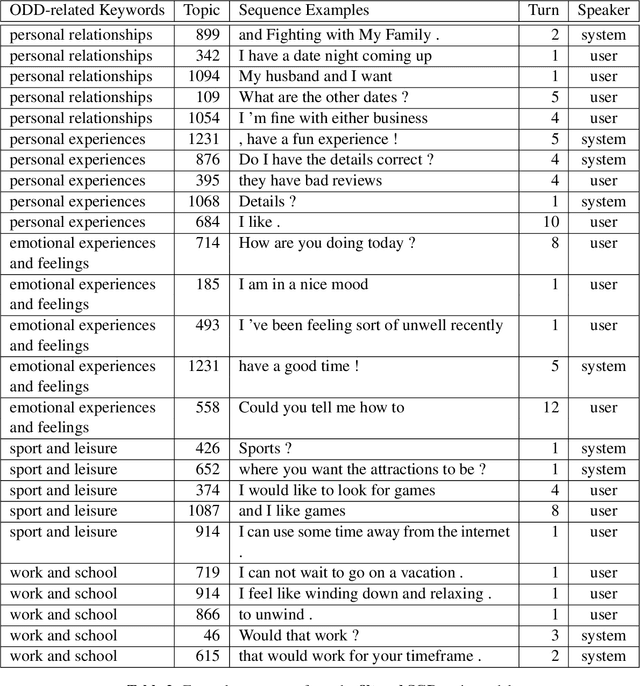
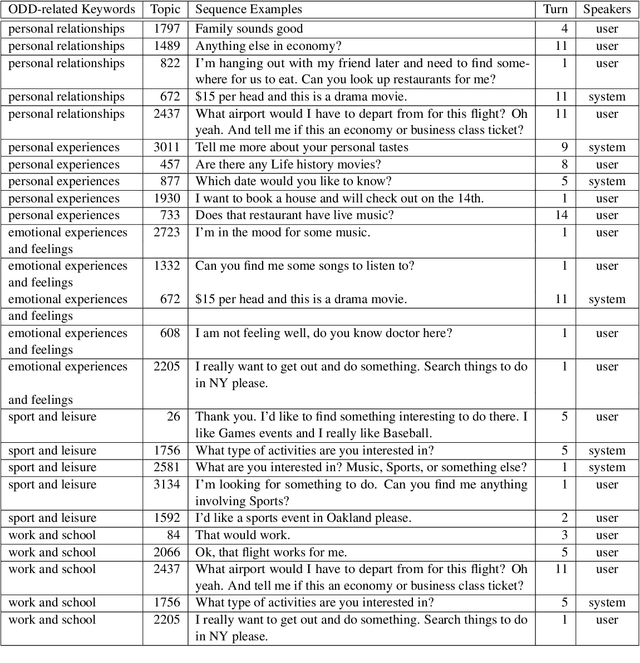
Abstract:Most existing dialogue corpora and models have been designed to fit into 2 predominant categories : task-oriented dialogues portray functional goals, such as making a restaurant reservation or booking a plane ticket, while chit-chat/open-domain dialogues focus on holding a socially engaging talk with a user. However, humans tend to seamlessly switch between modes and even use chitchat to enhance task-oriented conversations. To bridge this gap, new datasets have recently been created, blending both communication modes into conversation examples. The approaches used tend to rely on adding chit-chat snippets to pre-existing, human-generated task-oriented datasets. Given the tendencies observed in humans, we wonder however if the latter do not \textit{already} hold chit-chat sequences. By using topic modeling and searching for topics which are most similar to a set of keywords related to social talk, we explore the training sets of Schema-Guided Dialogues and MultiWOZ. Our study shows that sequences related to social talk are indeed naturally present, motivating further research on ways chitchat is combined into task-oriented dialogues.
Question Answering in Natural Language: the Special Case of Temporal Expressions
Nov 23, 2023Abstract:Although general question answering has been well explored in recent years, temporal question answering is a task which has not received as much focus. Our work aims to leverage a popular approach used for general question answering, answer extraction, in order to find answers to temporal questions within a paragraph. To train our model, we propose a new dataset, inspired by SQuAD, specifically tailored to provide rich temporal information. We chose to adapt the corpus WikiWars, which contains several documents on history's greatest conflicts. Our evaluation shows that a deep learning model trained to perform pattern matching, often used in general question answering, can be adapted to temporal question answering, if we accept to ask questions whose answers must be directly present within a text.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge