Arijit Laha
Enhancing Support for Knowledge Works: A relatively unexplored vista of computing research
Dec 22, 2011
Abstract:Let us envision a new class of IT systems, the "Support Systems for Knowledge Works" or SSKW. An SSKW can be defined as a system built for providing comprehensive support to human knowledge-workers while performing instances of complex knowledge-works of a particular type within a particular domain of professional activities To get an idea what an SSKW-enabled work environment can be like, let us look into a hypothetical scenario that depicts the interaction between a physician and a patient-care SSKW during the activity of diagnosing a patient.
Fuzzy Rules and Evidence Theory for Satellite Image Analysis
Apr 08, 2011

Abstract:Design of a fuzzy rule based classifier is proposed. The performance of the classifier for multispectral satellite image classification is improved using Dempster- Shafer theory of evidence that exploits information of the neighboring pixels. The classifiers are tested rigorously with two known images and their performance are found to be better than the results available in the literature. We also demonstrate the improvement of performance while using D-S theory along with fuzzy rule based classifiers over the basic fuzzy rule based classifiers for all the test cases.
An Agent-based Architecture for a Knowledge-work Support System
Apr 08, 2011



Abstract:Enhancement of technology-based system support for knowledge workers is an issue of great importance. The "Knowledge work Support System (KwSS)" framework analyzes this issue from a holistic perspective. KwSS proposes a set of design principles for building a comprehensive IT-based support system, which enhances the capability of a human agent for performing a set of complex and interrelated knowledge-works relevant to one or more target task-types within a domain of professional activities. In this paper, we propose a high-level, software-agent based architecture for realizing a KwSS system that incorporates these design principles. Here we focus on developing a number of crucial enabling components of the architecture, including (1) an Activity Theory-based novel modeling technique for knowledgeintensive activities; (2) a graph theoretic formalism for representing these models in a knowledge base in conjunction with relevant entity taxonomies/ontologies; and (3) an algorithm for reasoning, using the knowledge base, about various aspects of possible supports for activities at performance-time.
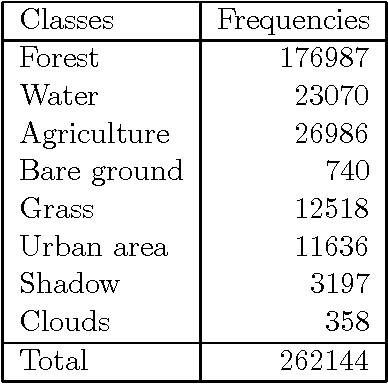
Land cover classification using fuzzy rules and aggregation of contextual information through evidence theory
Nov 23, 2009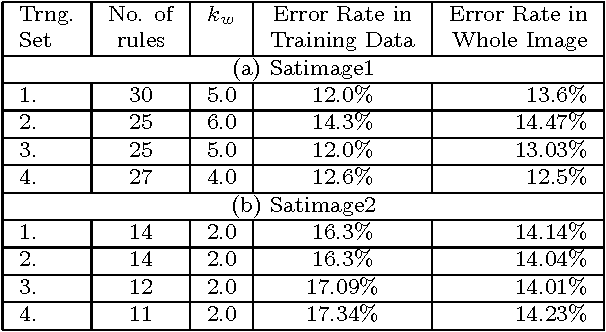
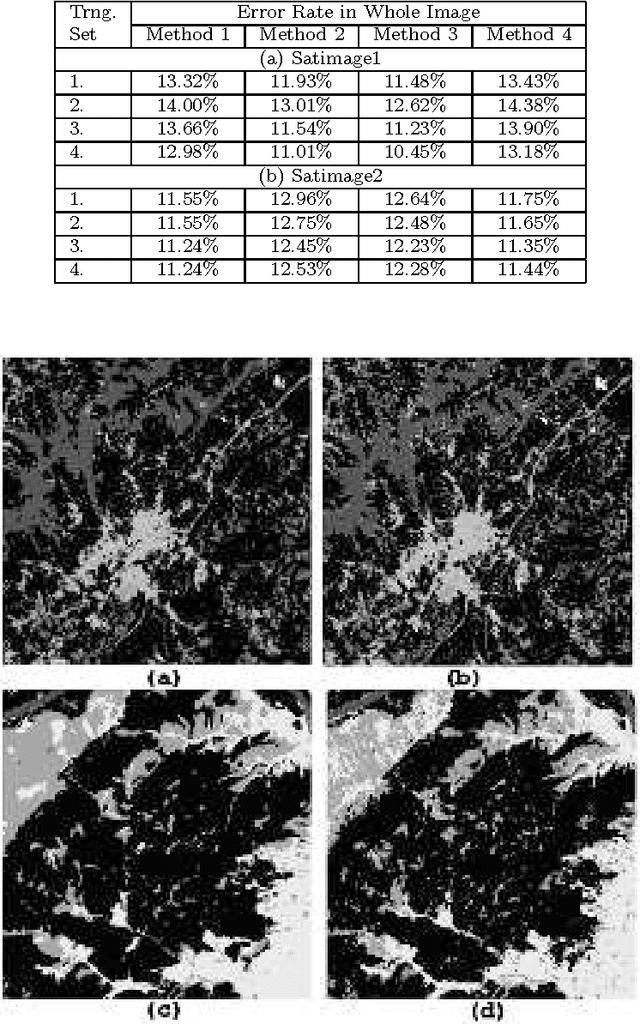
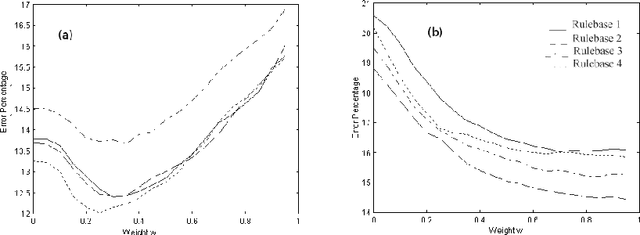
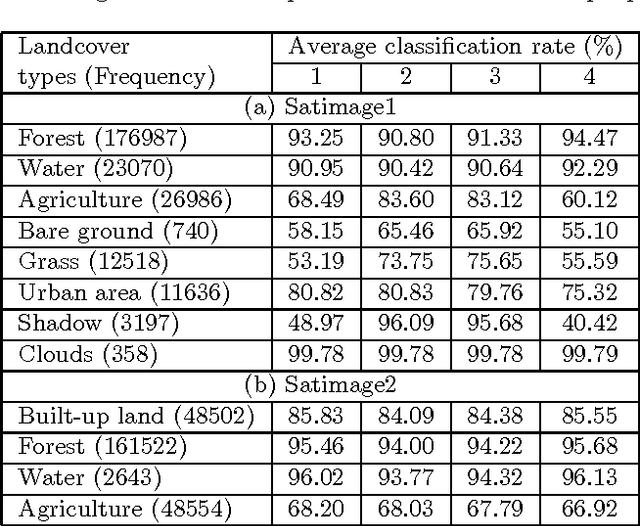
Abstract:Land cover classification using multispectral satellite image is a very challenging task with numerous practical applications. We propose a multi-stage classifier that involves fuzzy rule extraction from the training data and then generation of a possibilistic label vector for each pixel using the fuzzy rule base. To exploit the spatial correlation of land cover types we propose four different information aggregation methods which use the possibilistic class label of a pixel and those of its eight spatial neighbors for making the final classification decision. Three of the aggregation methods use Dempster-Shafer theory of evidence while the remaining one is modeled after the fuzzy k-NN rule. The proposed methods are tested with two benchmark seven channel satellite images and the results are found to be quite satisfactory. They are also compared with a Markov random field (MRF) model-based contextual classification method and found to perform consistently better.
* 14 pages, 2 figures
Designing fuzzy rule based classifier using self-organizing feature map for analysis of multispectral satellite images
Nov 23, 2009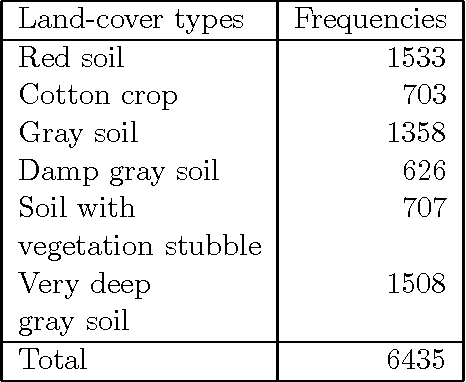
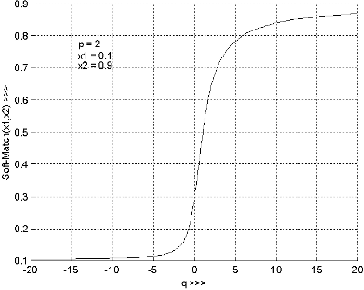

Abstract:We propose a novel scheme for designing fuzzy rule based classifier. An SOFM based method is used for generating a set of prototypes which is used to generate a set of fuzzy rules. Each rule represents a region in the feature space that we call the context of the rule. The rules are tuned with respect to their context. We justified that the reasoning scheme may be different in different context leading to context sensitive inferencing. To realize context sensitive inferencing we used a softmin operator with a tunable parameter. The proposed scheme is tested on several multispectral satellite image data sets and the performance is found to be much better than the results reported in the literature.
* 23 pages, 7 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge