Apoorva Gokhale
Reducing Racial Bias in Facial Age Prediction using Unsupervised Domain Adaptation in Regression
Apr 05, 2021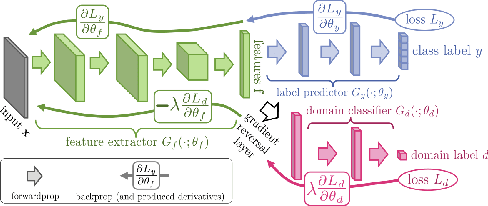


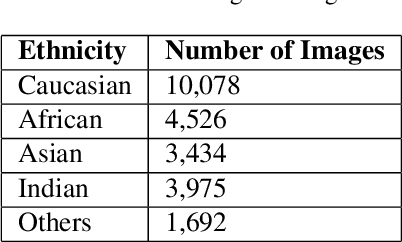
Abstract:We propose an approach for unsupervised domain adaptation for the task of estimating someone's age from a given face image. In order to avoid the propagation of racial bias in most publicly available face image datasets into the inefficacy of models trained on them, we perform domain adaptation to motivate the predictor to learn features that are invariant to ethnicity, enhancing the generalization performance across faces of people from different ethnic backgrounds. Exploiting the ordinality of age, we also impose ranking constraints on the prediction of the model and design our model such that it takes as input a pair of images, and outputs both the relative age difference and the rank of the first identity with respect to the other in terms of their ages. Furthermore, we implement Multi-Dimensional Scaling to retrieve absolute ages from the predicted age differences from as few as two labeled images from the domain to be adapted to. We experiment with a publicly available dataset with age labels, dividing it into subsets based on the ethnicity labels, and evaluating the performance of our approach on the data from an ethnicity different from the one that the model is trained on. Additionally, we impose a constraint to preserve the sanity of the predictions with respect to relative and absolute ages, and another to ensure the smoothness of the predictions with respect to the input. We experiment extensively and compare various domain adaptation approaches for the task of regression.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge