Get our free extension to see links to code for papers anywhere online!Free add-on: code for papers everywhere!Free add-on: See code for papers anywhere!
Anton Bryl
Adversarial Neural Networks for Cross-lingual Sequence Tagging
Aug 14, 2018Figures and Tables: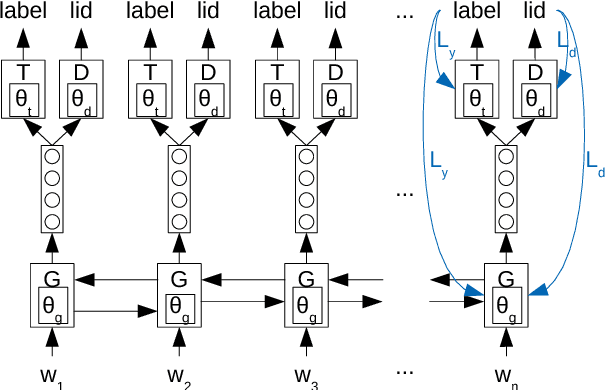
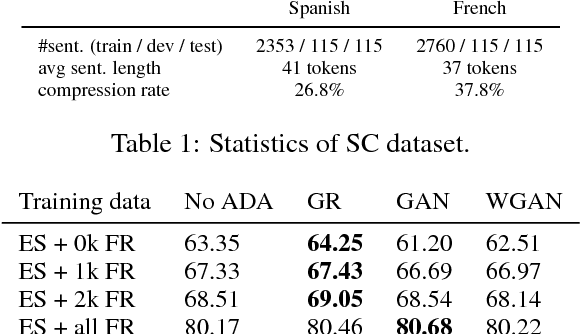

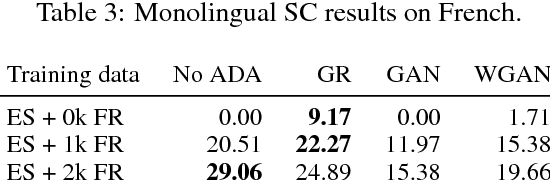




Abstract:We study cross-lingual sequence tagging with little or no labeled data in the target language. Adversarial training has previously been shown to be effective for training cross-lingual sentence classifiers. However, it is not clear if language-agnostic representations enforced by an adversarial language discriminator will also enable effective transfer for token-level prediction tasks. Therefore, we experiment with different types of adversarial training on two tasks: dependency parsing and sentence compression. We show that adversarial training consistently leads to improved cross-lingual performance on each task compared to a conventionally trained baseline.
Via
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge