Anthony Schmiedler
Automated Human Claustrum Segmentation using Deep Learning Technologies
Nov 18, 2019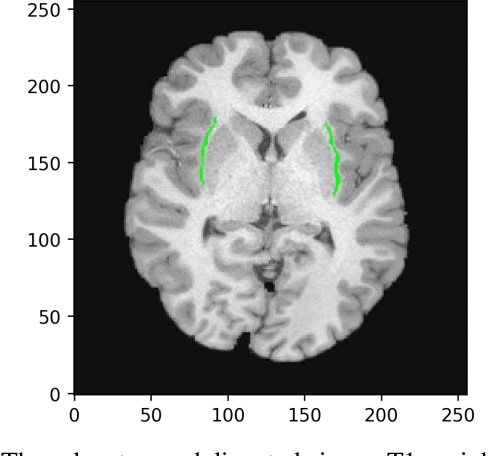
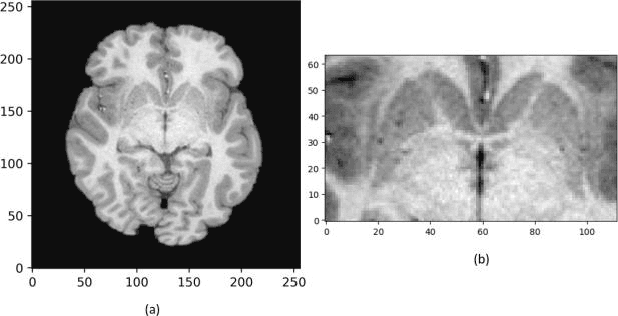
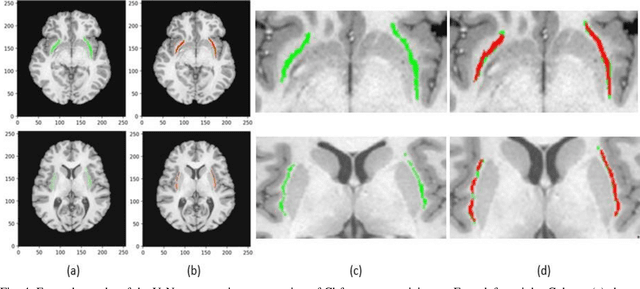
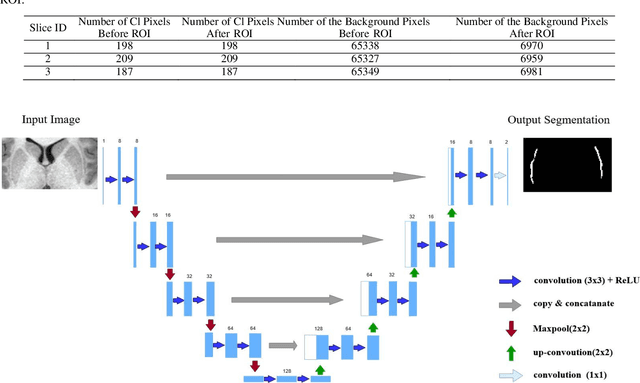
Abstract:In recent years, Deep Learning (DL) has shown promising results in conducting AI tasks such as computer vision and image segmentation. Specifically, Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) models in DL have been applied to prevention,detection, and diagnosis in predictive medicine. Image segmentation plays a significant role in disease detection and prevention.However, there are enormous challenges in performing DL-based automatic segmentation due to the nature of medical images such as heterogeneous modalities and formats, insufficient labeled training data, and the high-class imbalance in the labeled data. Furthermore, automating segmentation of medical images,like magnetic resonance images (MRI), becomes a challenging task. The need for automated segmentation or annotation is what motivates our work. In this paper, we propose a fully automated approach that aims to segment the human claustrum for analytical purposes. We applied a U-Net CNN model to segment the claustrum (Cl) from a MRI dataset. With this approach, we have achieved an average Dice per case score of 0.72 for Cl segmentation, with K=5 for cross-validation. The expert in the medical domain also evaluates these results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge