Anne Boyer
KIWI
Multi-source Data Mining for e-Learning
Sep 17, 2020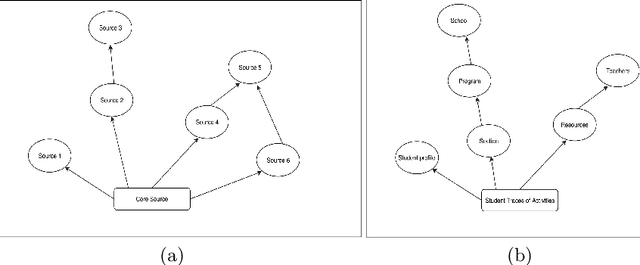
Abstract:Data mining is the task of discovering interesting, unexpected or valuable structures in large datasets and transforming them into an understandable structure for further use . Different approaches in the domain of data mining have been proposed, among which pattern mining is the most important one. Pattern mining mining involves extracting interesting frequent patterns from data. Pattern mining has grown to be a topic of high interest where it is used for different purposes, for example, recommendations. Some of the most common challenges in this domain include reducing the complexity of the process and avoiding the redundancy within the patterns. So far, pattern mining has mainly focused on the mining of a single data source. However, with the increase in the amount of data, in terms of volume, diversity of sources and nature of data, mining multi-source and heterogeneous data has become an emerging challenge in this domain. This challenge is the main focus of our work where we propose to mine multi-source data in order to extract interesting frequent patterns.
Toward a Robust Diversity-Based Model to Detect Changes of Context
Jan 08, 2016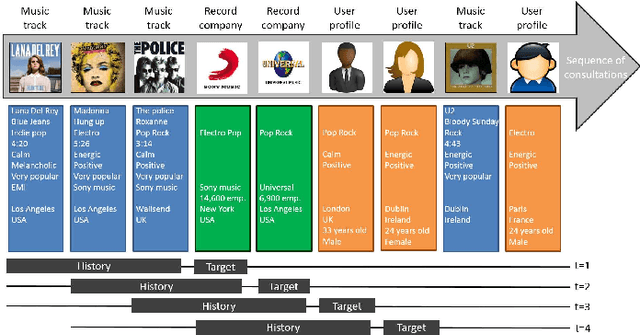
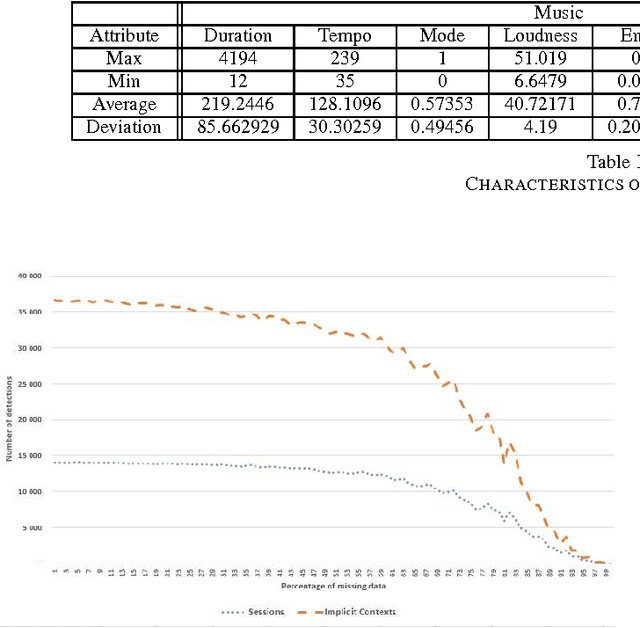
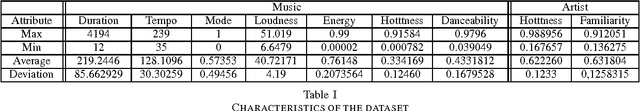
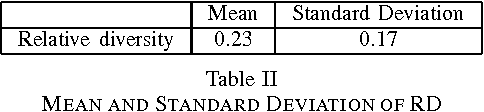
Abstract:Being able to automatically and quickly understand the user context during a session is a main issue for recommender systems. As a first step toward achieving that goal, we propose a model that observes in real time the diversity brought by each item relatively to a short sequence of consultations, corresponding to the recent user history. Our model has a complexity in constant time, and is generic since it can apply to any type of items within an online service (e.g. profiles, products, music tracks) and any application domain (e-commerce, social network, music streaming), as long as we have partial item descriptions. The observation of the diversity level over time allows us to detect implicit changes. In the long term, we plan to characterize the context, i.e. to find common features among a contiguous sub-sequence of items between two changes of context determined by our model. This will allow us to make context-aware and privacy-preserving recommendations, to explain them to users. As this is an ongoing research, the first step consists here in studying the robustness of our model while detecting changes of context. In order to do so, we use a music corpus of 100 users and more than 210,000 consultations (number of songs played in the global history). We validate the relevancy of our detections by finding connections between changes of context and events, such as ends of session. Of course, these events are a subset of the possible changes of context, since there might be several contexts within a session. We altered the quality of our corpus in several manners, so as to test the performances of our model when confronted with sparsity and different types of items. The results show that our model is robust and constitutes a promising approach.
A new Recommender system based on target tracking: a Kalman Filter approach
Dec 15, 2010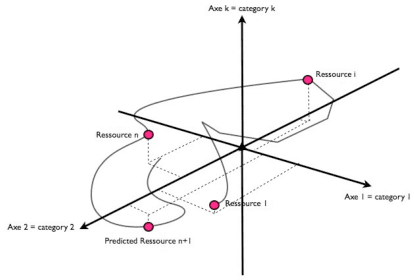
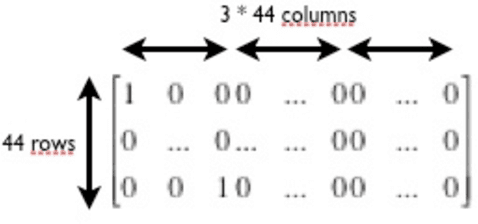
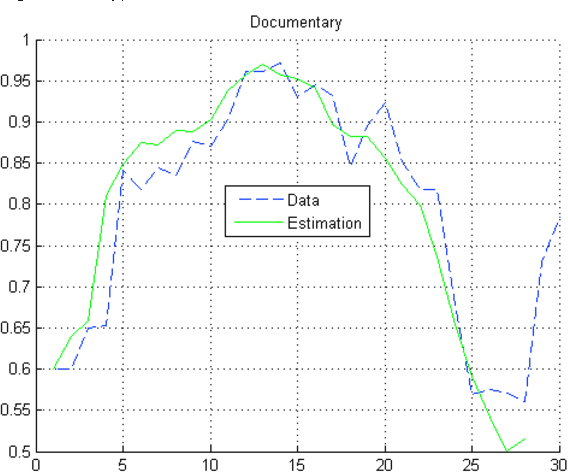
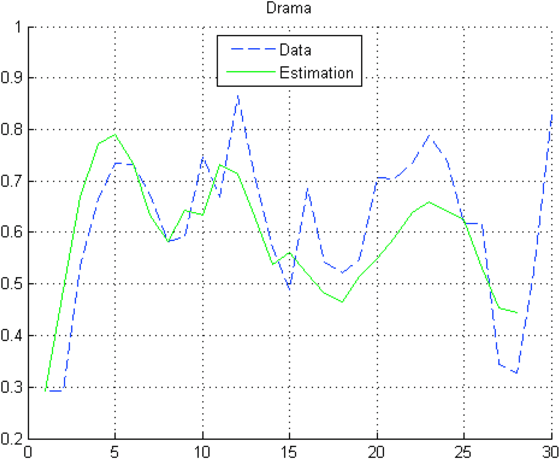
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a new approach for recommender systems based on target tracking by Kalman filtering. We assume that users and their seen resources are vectors in the multidimensional space of the categories of the resources. Knowing this space, we propose an algorithm based on a Kalman filter to track users and to predict the best prediction of their future position in the recommendation space.
Target tracking in the recommender space: Toward a new recommender system based on Kalman filtering
Nov 10, 2010



Abstract:In this paper, we propose a new approach for recommender systems based on target tracking by Kalman filtering. We assume that users and their seen resources are vectors in the multidimensional space of the categories of the resources. Knowing this space, we propose an algorithm based on a Kalman filter to track users and to predict the best prediction of their future position in the recommendation space.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge