Anh-Tu Nguyen
IMT Atlantique - DAPI
A novel deep learning-based approach for sleep apnea detection using single-lead ECG signals
Aug 05, 2022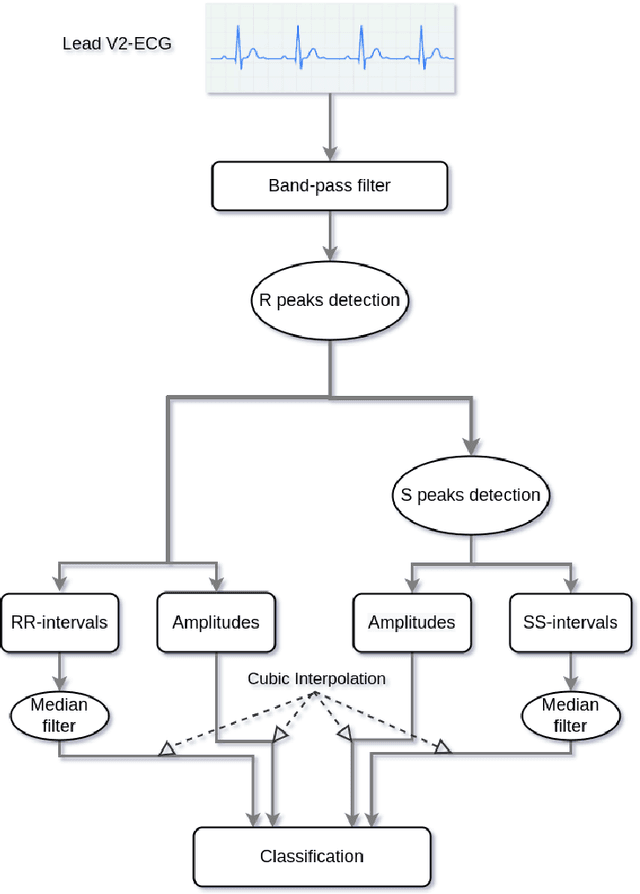
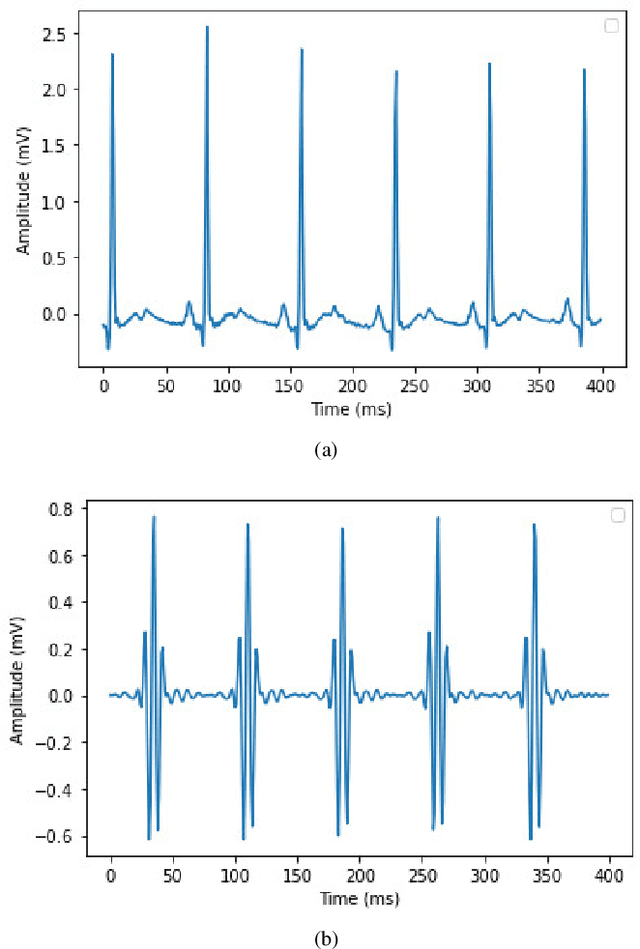
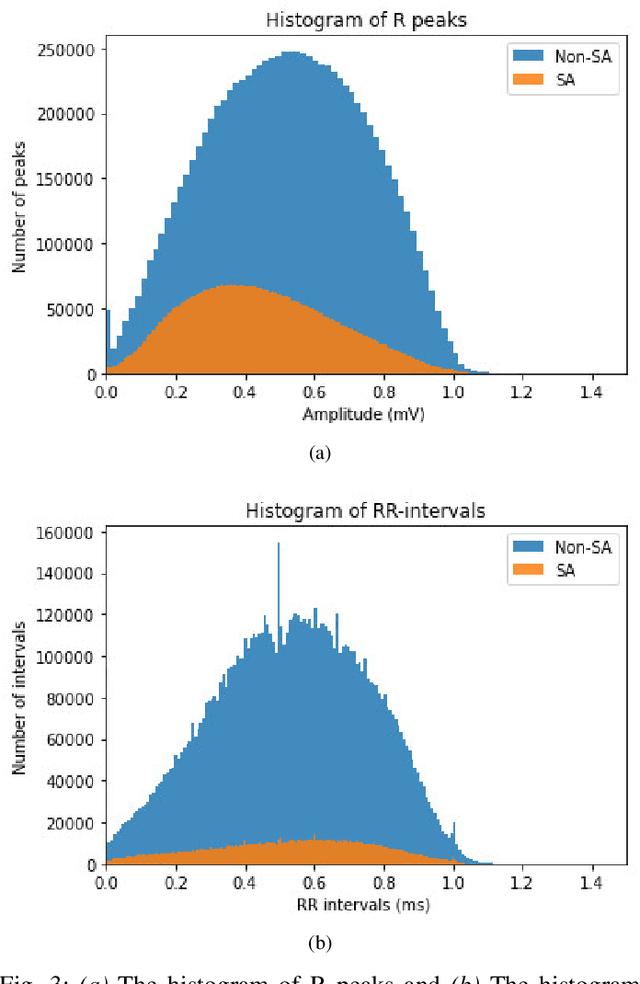
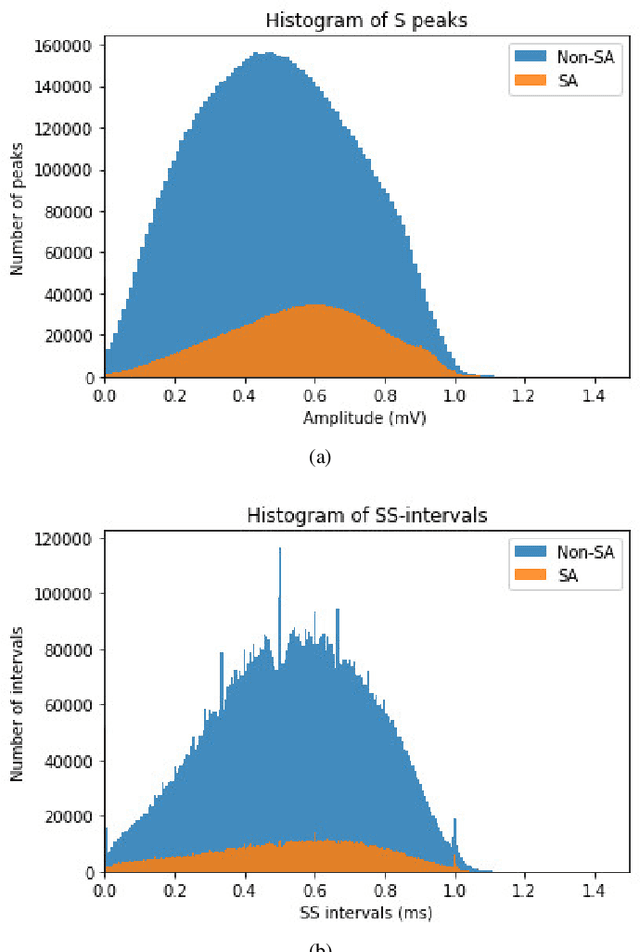
Abstract:Sleep apnea (SA) is a type of sleep disorder characterized by snoring and chronic sleeplessness, which can lead to serious conditions such as high blood pressure, heart failure, and cardiomyopathy (enlargement of the muscle tissue of the heart). The electrocardiogram (ECG) plays a critical role in identifying SA since it might reveal abnormal cardiac activity. Recent research on ECG-based SA detection has focused on feature engineering techniques that extract specific characteristics from multiple-lead ECG signals and use them as classification model inputs. In this study, a novel method of feature extraction based on the detection of S peaks is proposed to enhance the detection of adjacent SA segments using a single-lead ECG. In particular, ECG features collected from a single lead (V2) are used to identify SA episodes. On the extracted features, a CNN model is trained to detect SA. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method detects SA from single-lead ECG data is more accurate than existing state-of-the-art methods, with 91.13% classification accuracy, 92.58% sensitivity, and 88.75% specificity. Moreover, the further usage of features associated with the S peaks enhances the classification accuracy by 0.85%. Our findings indicate that the proposed machine learning system has the potential to be an effective method for detecting SA episodes.
Obstacle Avoidance for Autonomous Mobile Robots Based on Mapping Method
Sep 14, 2021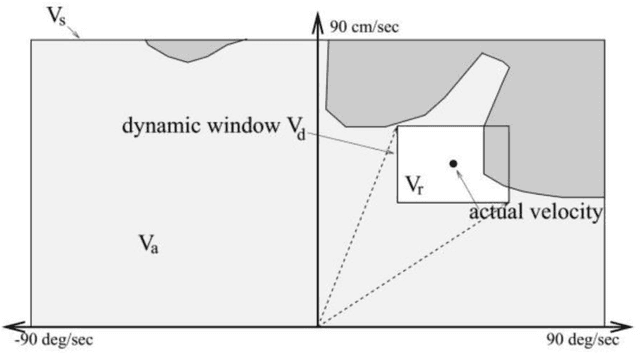
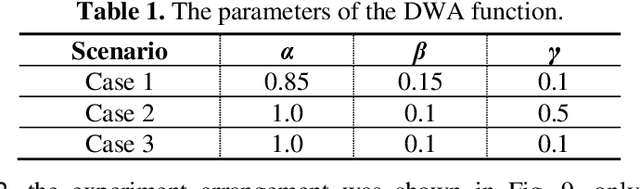
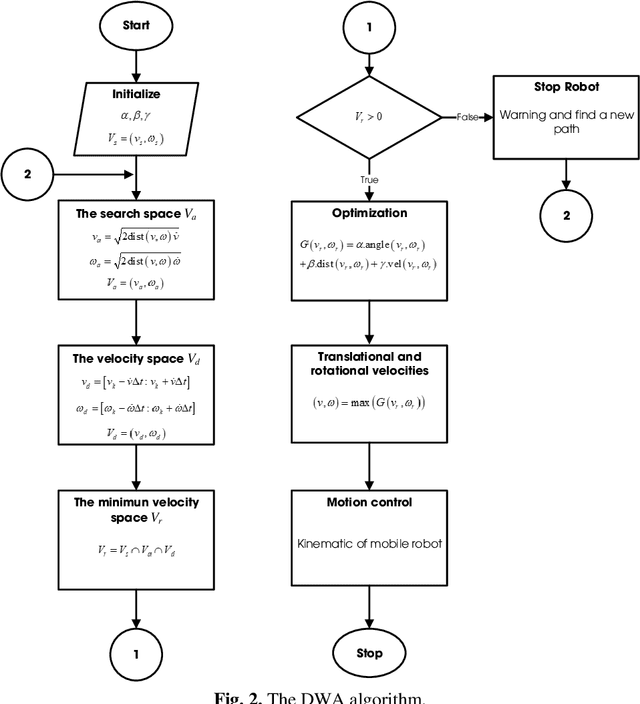
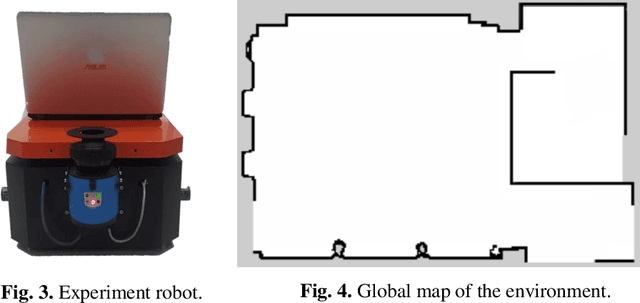
Abstract:In recent years, the mobile robot has been considerable attention to researchers for its application in various environments. For a mobile robot navigating its way from starting point to a goal point while traversing through deterrents, needs to recognize the obstacles and generate new trajectories to reach the destination. This paper presents an obstacle avoidance method for mobile robots using an open-source in robot operation system (ROS) combining with the dynamic window approach (DWA) algorithm. The experiment is carried out using a mobile robot in which the navigation data is based on data collecting by a laser scanner. The experimental results show that the robot could work well in environments containing static and dynamic obstacles.
A study and design of localization system for mobile robot based on ROS
Sep 12, 2021Abstract:In recent years, the mobile robot has been the concern of numerous researcher since they are widely applied in various fields of daily life. This paper applies a virtual robot operating system (ROS) platform to develop a localization system for robot motion. The proposed system is based on the combination of relative and absolute measurement methods, in which the data from the encoder, digital compass, and laser scanner sensor are fused using the extended Kalman filter (EKF). The system also successfully eliminates the errors caused by the environment as well as the error accumulation. The experimental results show good accuracy and stability of position and orientation which can be further applied for the robot working in the indoor environment.
Shared lateral control with on-line adaptation of the automation degree for driver steering assist system: A weighting design approach
Mar 04, 2020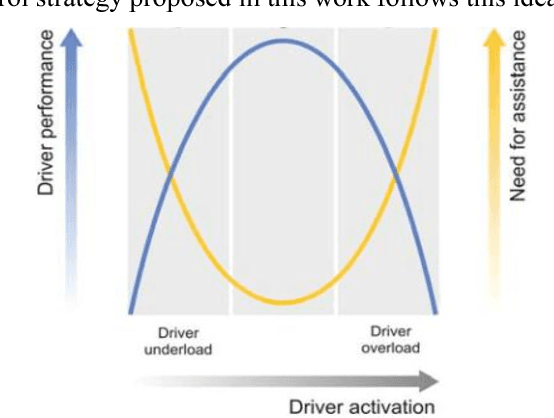
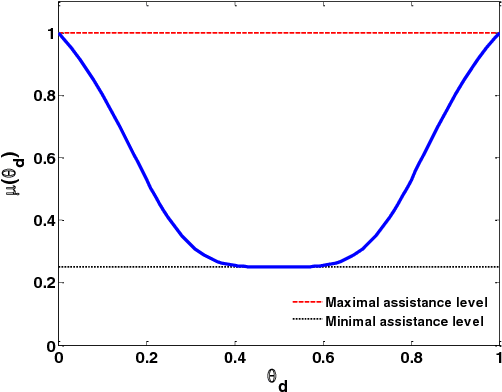
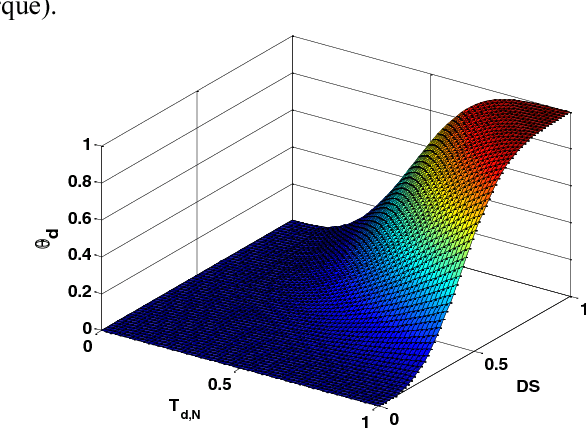
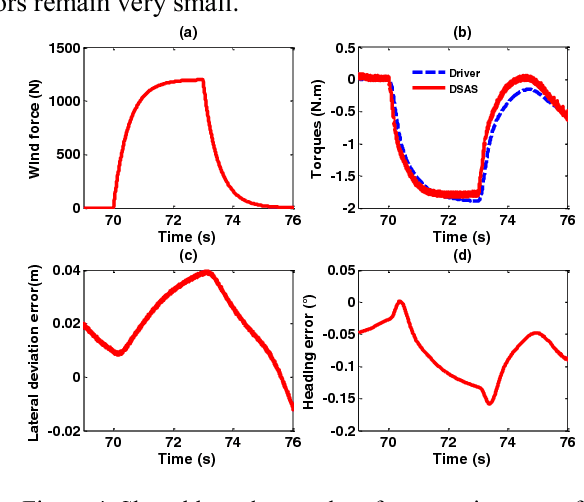
Abstract:This paper addresses the shared lateral control for both lane-keeping and obstacle avoidance tasks of a driver steering assist system (DSAS). In this work, we propose a novel approach to deal with the interactions between the human (driver) and the machine (DSAS) by introducing into the vehicle system a fictive nonlinear term representing the driver activity. In this way, the actions of the DSAS are computed according to the driver behaviors (actions and intentions). Based on Takagi-Sugeno control technique together with Lyapunov stability tools, the designed controller is able to handle a large range of variation of vehicle longitudinal speed. In particular, this controller can deal with the system state constraints and also the control input saturation. As will be discussed later, the consideration of these constraints into the control design improves significantly the closed-loop performance under various driving situations. The interests of the proposed method are validated by simulations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge