Andrei Ionut Damian
AiXpand AI OS -- Decentralized ubiquitous computing MLOps execution engine
Jun 14, 2023Abstract:Over the past few years, ubiquitous, or pervasive computing has gained popularity as the primary approach for a wide range of applications, including enterprise-grade systems, consumer applications, and gaming systems. Ubiquitous computing refers to the integration of computing technologies into everyday objects and environments, creating a network of interconnected devices that can communicate with each other and with humans. By using ubiquitous computing technologies, communities can become more connected and efficient, with members able to communicate and collaborate more easily. This enabled interconnectedness and collaboration can lead to a more successful and sustainable community. The spread of ubiquitous computing, however, has emphasized the importance of automated learning and smart applications in general. Even though there have been significant strides in Artificial Intelligence and Deep Learning, large scale adoption has been hesitant due to mounting pressure on expensive and highly complex cloud numerical-compute infrastructures. Adopting, and even developing, practical machine learning systems can come with prohibitive costs, not only in terms of complex infrastructures but also of solid expertise in Data Science and Machine Learning. In this paper we present an innovative approach for low-code development and deployment of end-to-end AI cooperative application pipelines. We address infrastructure allocation, costs, and secure job distribution in a fully decentralized global cooperative community based on tokenized economics.
ProVe -- Self-supervised pipeline for automated product replacement and cold-starting based on neural language models
Jun 26, 2020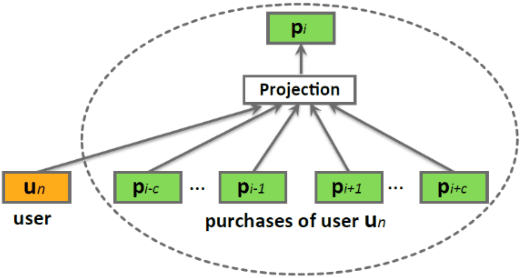
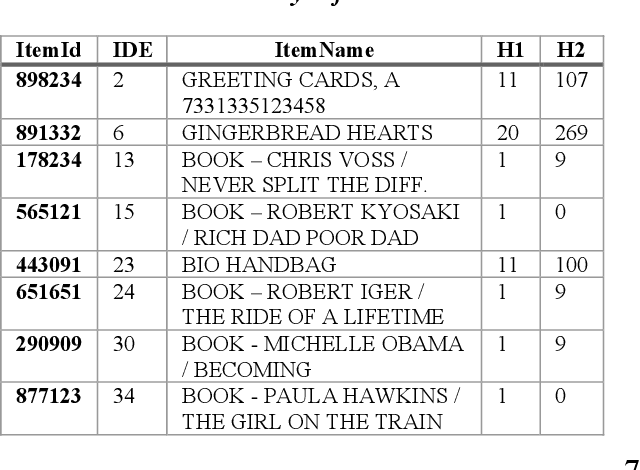
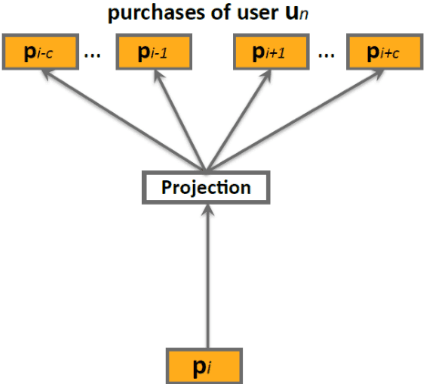
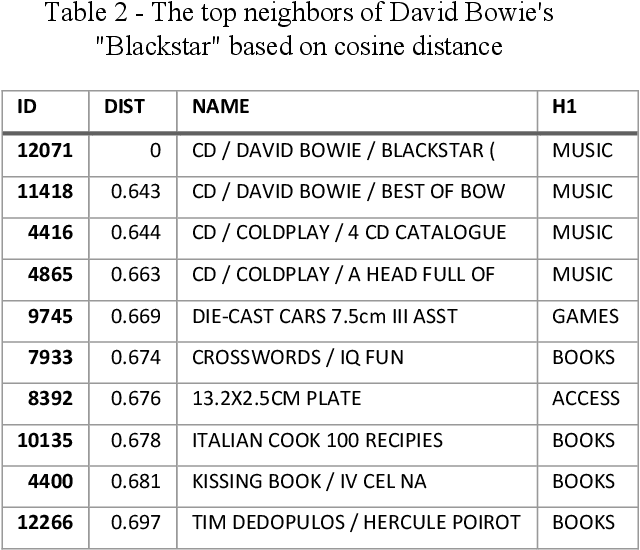
Abstract:In retail vertical industries, businesses are dealing with human limitation of quickly understanding and adapting to new purchasing behaviors. Moreover, retail businesses need to overcome the human limitation of properly managing a massive selection of products/brands/categories. These limitations lead to deficiencies from both commercial (e.g. loss of sales, decrease in customer satisfaction) and operational perspective (e.g. out-of-stock, over-stock). In this paper, we propose a pipeline approach based on Natural Language Understanding, for recommending the most suitable replacements for products that are out-of-stock. Moreover, we will propose a solution for managing products that were newly introduced in a retailer's portfolio with almost no transactional history. This solution will help businesses: automatically assign the new products to the right category; recommend complementary products for cross-sell from day 1; perform sales predictions even with almost no transactional history. Finally, the vector space model resulted by applying the pipeline presented in this paper is directly used as semantic information in deep learning-based demand forecasting solutions, leading to more accurate predictions. The whole research and experimentation process have been done using real-life private transactional data, however the source code is available on https://github.com/Lummetry/ProVe
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge