Andreas Konstantinidis
Android Malware Detection with Unbiased Confidence Guarantees
Dec 17, 2023Abstract:The impressive growth of smartphone devices in combination with the rising ubiquity of using mobile platforms for sensitive applications such as Internet banking, have triggered a rapid increase in mobile malware. In recent literature, many studies examine Machine Learning techniques, as the most promising approach for mobile malware detection, without however quantifying the uncertainty involved in their detections. In this paper, we address this problem by proposing a machine learning dynamic analysis approach that provides provably valid confidence guarantees in each malware detection. Moreover the particular guarantees hold for both the malicious and benign classes independently and are unaffected by any bias in the data. The proposed approach is based on a novel machine learning framework, called Conformal Prediction, combined with a random forests classifier. We examine its performance on a large-scale dataset collected by installing 1866 malicious and 4816 benign applications on a real android device. We make this collection of dynamic analysis data available to the research community. The obtained experimental results demonstrate the empirical validity, usefulness and unbiased nature of the outputs produced by the proposed approach.
A GP-MOEA/D Approach for Modelling Total Electron Content over Cyprus
Nov 24, 2011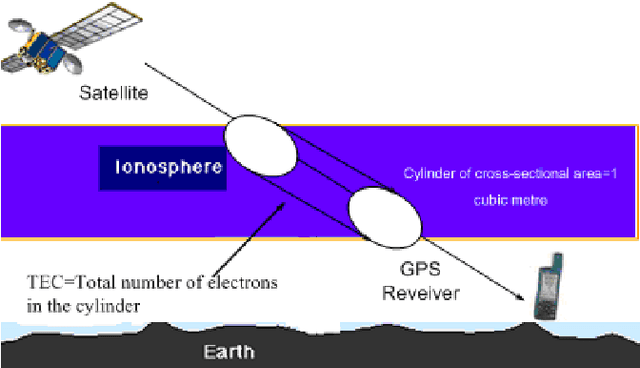
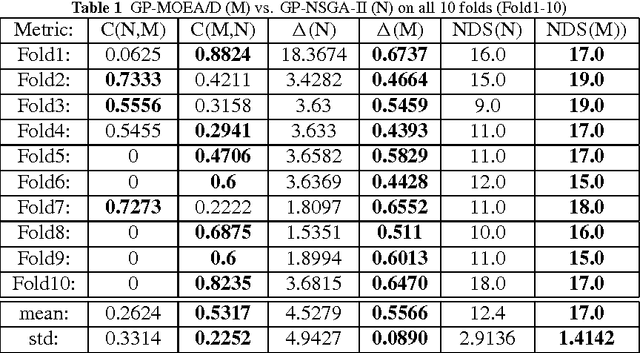
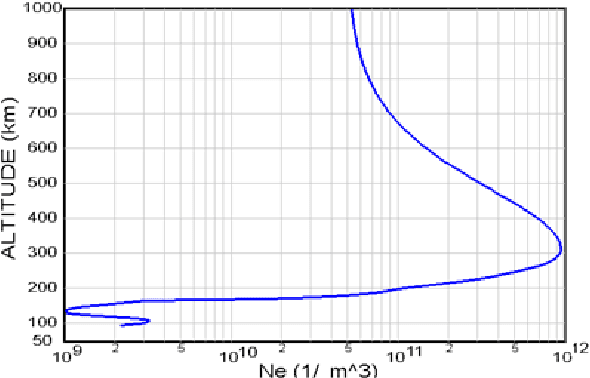
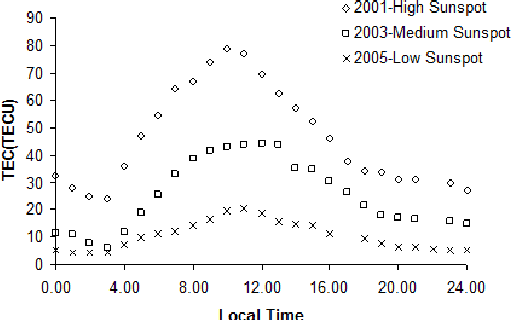
Abstract:Vertical Total Electron Content (vTEC) is an ionospheric characteristic used to derive the signal delay imposed by the ionosphere on near-vertical trans-ionospheric links. The major aim of this paper is to design a prediction model based on the main factors that influence the variability of this parameter on a diurnal, seasonal and long-term time-scale. The model should be accurate and general (comprehensive) enough for efficiently approximating the high variations of vTEC. However, good approximation and generalization are conflicting objectives. For this reason a Genetic Programming (GP) with Multi-objective Evolutionary Algorithm based on Decomposition characteristics (GP-MOEA/D) is designed and proposed for modeling vTEC over Cyprus. Experimental results show that the Multi-Objective GP-model, considering real vTEC measurements obtained over a period of 11 years, has produced a good approximation of the modeled parameter and can be implemented as a local model to account for the ionospheric imposed error in positioning. Particulary, the GP-MOEA/D approach performs better than a Single Objective Optimization GP, a GP with Non-dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm-II (NSGA-II) characteristics and the previously proposed Neural Network-based approach in most cases.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge