Anastasia Dimou
Shape Fragments
Dec 22, 2021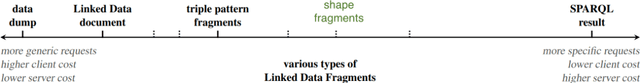
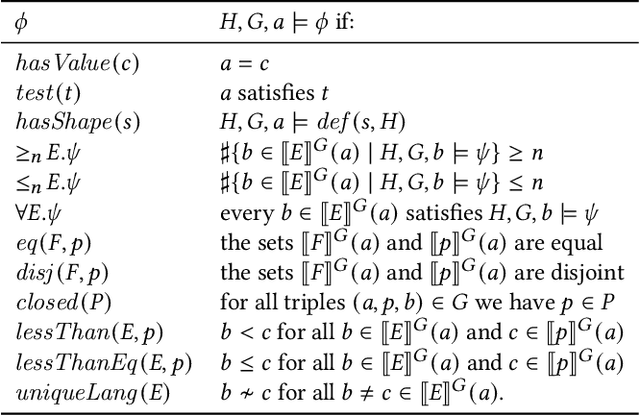

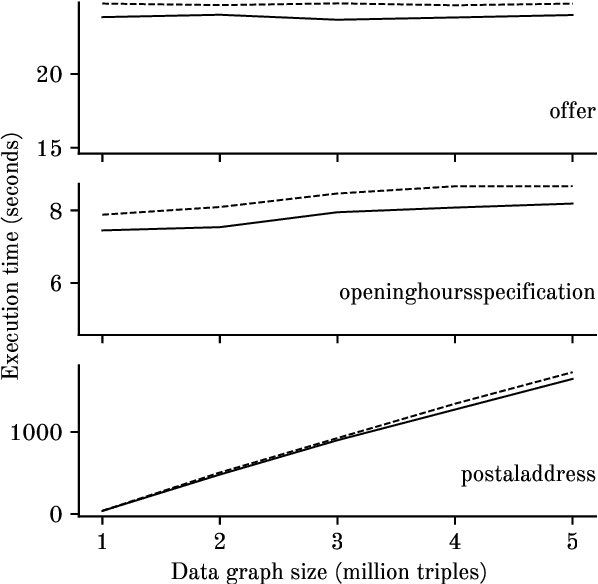
Abstract:In constraint languages for RDF graphs, such as ShEx and SHACL, constraints on nodes and their properties in RDF graphs are known as "shapes". Schemas in these languages list the various shapes that certain targeted nodes must satisfy for the graph to conform to the schema. Using SHACL, we propose in this paper a novel use of shapes, by which a set of shapes is used to extract a subgraph from an RDF graph, the so-called shape fragment. Our proposed mechanism fits in the framework of Linked Data Fragments. In this paper, (i) we define our extraction mechanism formally, building on recently proposed SHACL formalizations; (ii) we establish correctness properties, which relate shape fragments to notions of provenance for database queries; (iii) we compare shape fragments with SPARQL queries; (iv) we discuss implementation options; and (v) we present initial experiments demonstrating that shape fragments are a feasible new idea.
R2RML and RML Comparison for RDF Generation, their Rules Validation and Inconsistency Resolution
May 13, 2020


Abstract:In this paper, an overview of the state of the art on knowledge graph generation is provided, with focus on the two prevalent mapping languages: the W3C recommended R2RML and its generalisation RML. We look into details on their differences and explain how knowledge graphs, in the form of RDF graphs, can be generated with each one of the two mapping languages. Then we assess if the vocabulary terms were properly applied to the data and no violations occurred on their use, either using R2RML or RML to generate the desired knowledge graph.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge