Ana Mafalda Ribeiro
PUFFIN: A Path-Unifying Feed-Forward Interfaced Network for Vapor Pressure Prediction
Jul 08, 2023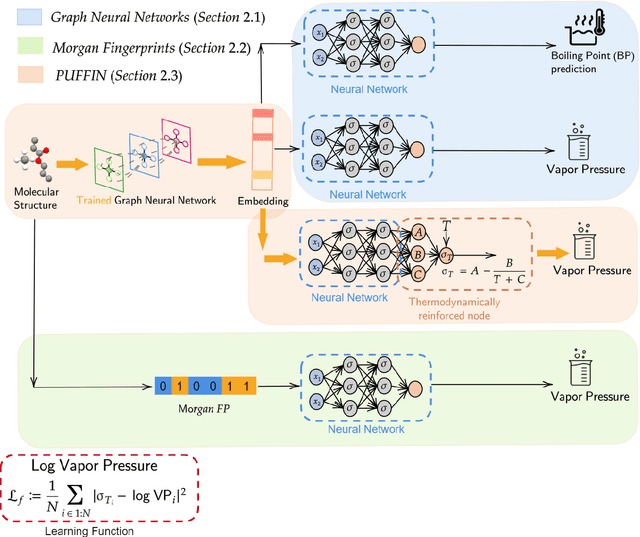
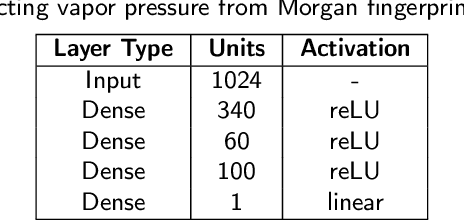
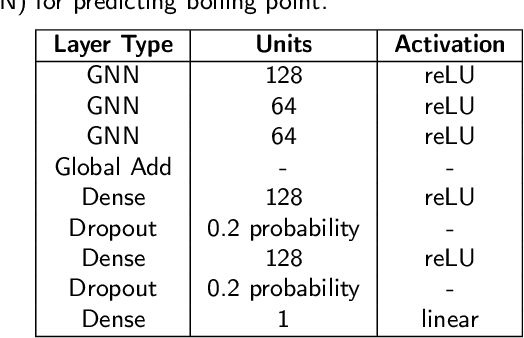
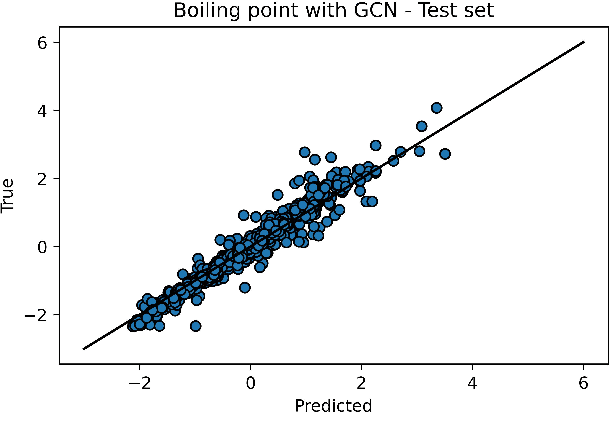
Abstract:Accurately predicting vapor pressure is vital for various industrial and environmental applications. However, obtaining accurate measurements for all compounds of interest is not possible due to the resource and labor intensity of experiments. The demand for resources and labor further multiplies when a temperature-dependent relationship for predicting vapor pressure is desired. In this paper, we propose PUFFIN (Path-Unifying Feed-Forward Interfaced Network), a machine learning framework that combines transfer learning with a new inductive bias node inspired by domain knowledge (the Antoine equation) to improve vapor pressure prediction. By leveraging inductive bias and transfer learning using graph embeddings, PUFFIN outperforms alternative strategies that do not use inductive bias or that use generic descriptors of compounds. The framework's incorporation of domain-specific knowledge to overcome the limitation of poor data availability shows its potential for broader applications in chemical compound analysis, including the prediction of other physicochemical properties. Importantly, our proposed machine learning framework is partially interpretable, because the inductive Antoine node yields network-derived Antoine equation coefficients. It would then be possible to directly incorporate the obtained analytical expression in process design software for better prediction and control of processes occurring in industry and the environment.
Efficient hybrid modeling and sorption model discovery for non-linear advection-diffusion-sorption systems: A systematic scientific machine learning approach
Mar 30, 2023Abstract:This study presents a systematic machine learning approach for creating efficient hybrid models and discovering sorption uptake models in non-linear advection-diffusion-sorption systems. It demonstrates an effective method to train these complex systems using gradient based optimizers, adjoint sensitivity analysis, and JIT-compiled vector Jacobian products, combined with spatial discretization and adaptive integrators. Sparse and symbolic regression were employed to identify missing functions in the artificial neural network. The robustness of the proposed method was tested on an in-silico data set of noisy breakthrough curve observations of fixed-bed adsorption, resulting in a well-fitted hybrid model. The study successfully reconstructed sorption uptake kinetics using sparse and symbolic regression, and accurately predicted breakthrough curves using identified polynomials, highlighting the potential of the proposed framework for discovering sorption kinetic law structures.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge