Amiya Nayak
Hybrid LLM-Enhanced Intrusion Detection for Zero-Day Threats in IoT Networks
Jul 10, 2025



Abstract:This paper presents a novel approach to intrusion detection by integrating traditional signature-based methods with the contextual understanding capabilities of the GPT-2 Large Language Model (LLM). As cyber threats become increasingly sophisticated, particularly in distributed, heterogeneous, and resource-constrained environments such as those enabled by the Internet of Things (IoT), the need for dynamic and adaptive Intrusion Detection Systems (IDSs) becomes increasingly urgent. While traditional methods remain effective for detecting known threats, they often fail to recognize new and evolving attack patterns. In contrast, GPT-2 excels at processing unstructured data and identifying complex semantic relationships, making it well-suited to uncovering subtle, zero-day attack vectors. We propose a hybrid IDS framework that merges the robustness of signature-based techniques with the adaptability of GPT-2-driven semantic analysis. Experimental evaluations on a representative intrusion dataset demonstrate that our model enhances detection accuracy by 6.3%, reduces false positives by 9.0%, and maintains near real-time responsiveness. These results affirm the potential of language model integration to build intelligent, scalable, and resilient cybersecurity defences suited for modern connected environments.
LLM-Based Threat Detection and Prevention Framework for IoT Ecosystems
May 01, 2025Abstract:The increasing complexity and scale of the Internet of Things (IoT) have made security a critical concern. This paper presents a novel Large Language Model (LLM)-based framework for comprehensive threat detection and prevention in IoT environments. The system integrates lightweight LLMs fine-tuned on IoT-specific datasets (IoT-23, TON_IoT) for real-time anomaly detection and automated, context-aware mitigation strategies optimized for resource-constrained devices. A modular Docker-based deployment enables scalable and reproducible evaluation across diverse network conditions. Experimental results in simulated IoT environments demonstrate significant improvements in detection accuracy, response latency, and resource efficiency over traditional security methods. The proposed framework highlights the potential of LLM-driven, autonomous security solutions for future IoT ecosystems.
Differential Privacy-Driven Framework for Enhancing Heart Disease Prediction
Apr 25, 2025Abstract:With the rapid digitalization of healthcare systems, there has been a substantial increase in the generation and sharing of private health data. Safeguarding patient information is essential for maintaining consumer trust and ensuring compliance with legal data protection regulations. Machine learning is critical in healthcare, supporting personalized treatment, early disease detection, predictive analytics, image interpretation, drug discovery, efficient operations, and patient monitoring. It enhances decision-making, accelerates research, reduces errors, and improves patient outcomes. In this paper, we utilize machine learning methodologies, including differential privacy and federated learning, to develop privacy-preserving models that enable healthcare stakeholders to extract insights without compromising individual privacy. Differential privacy introduces noise to data to guarantee statistical privacy, while federated learning enables collaborative model training across decentralized datasets. We explore applying these technologies to Heart Disease Data, demonstrating how they preserve privacy while delivering valuable insights and comprehensive analysis. Our results show that using a federated learning model with differential privacy achieved a test accuracy of 85%, ensuring patient data remained secure and private throughout the process.
LLMs meet Federated Learning for Scalable and Secure IoT Management
Apr 22, 2025Abstract:The rapid expansion of IoT ecosystems introduces severe challenges in scalability, security, and real-time decision-making. Traditional centralized architectures struggle with latency, privacy concerns, and excessive resource consumption, making them unsuitable for modern large-scale IoT deployments. This paper presents a novel Federated Learning-driven Large Language Model (FL-LLM) framework, designed to enhance IoT system intelligence while ensuring data privacy and computational efficiency. The framework integrates Generative IoT (GIoT) models with a Gradient Sensing Federated Strategy (GSFS), dynamically optimizing model updates based on real-time network conditions. By leveraging a hybrid edge-cloud processing architecture, our approach balances intelligence, scalability, and security in distributed IoT environments. Evaluations on the IoT-23 dataset demonstrate that our framework improves model accuracy, reduces response latency, and enhances energy efficiency, outperforming traditional FL techniques (i.e., FedAvg, FedOpt). These findings highlight the potential of integrating LLM-powered federated learning into large-scale IoT ecosystems, paving the way for more secure, scalable, and adaptive IoT management solutions.
Blockchain Meets Adaptive Honeypots: A Trust-Aware Approach to Next-Gen IoT Security
Apr 22, 2025Abstract:Edge computing-based Next-Generation Wireless Networks (NGWN)-IoT offer enhanced bandwidth capacity for large-scale service provisioning but remain vulnerable to evolving cyber threats. Existing intrusion detection and prevention methods provide limited security as adversaries continually adapt their attack strategies. We propose a dynamic attack detection and prevention approach to address this challenge. First, blockchain-based authentication uses the Deoxys Authentication Algorithm (DAA) to verify IoT device legitimacy before data transmission. Next, a bi-stage intrusion detection system is introduced: the first stage uses signature-based detection via an Improved Random Forest (IRF) algorithm. In contrast, the second stage applies feature-based anomaly detection using a Diffusion Convolution Recurrent Neural Network (DCRNN). To ensure Quality of Service (QoS) and maintain Service Level Agreements (SLA), trust-aware service migration is performed using Heap-Based Optimization (HBO). Additionally, on-demand virtual High-Interaction honeypots deceive attackers and extract attack patterns, which are securely stored using the Bimodal Lattice Signature Scheme (BLISS) to enhance signature-based Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS). The proposed framework is implemented in the NS3 simulation environment and evaluated against existing methods across multiple performance metrics, including accuracy, attack detection rate, false negative rate, precision, recall, ROC curve, memory usage, CPU usage, and execution time. Experimental results demonstrate that the framework significantly outperforms existing approaches, reinforcing the security of NGWN-enabled IoT ecosystems
On the Dynamics of Training Attention Models
Nov 19, 2020

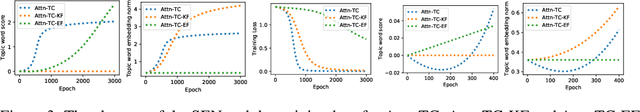

Abstract:The attention mechanism has been widely used in deep neural networks as a model component. By now, it has become a critical building block in many state-of-the-art natural language models. Despite its great success established empirically, the working mechanism of attention has not been investigated at a sufficient theoretical depth to date. In this paper, we set up a simple text classification task and study the dynamics of training a simple attention-based classification model using gradient descent. In this setting, we show that, for the discriminative words that the model should attend to, a persisting identity exists relating its embedding and the inner product of its key and the query. This allows us to prove that training must converge to attending to the discriminative words when the attention output is classified by a linear classifier. Experiments are performed, which validates our theoretical analysis and provides further insights.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge