Amit Meghanani
Position-invariant Fine-tuning of Speech Enhancement Models with Self-supervised Speech Representations
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Integrating front-end speech enhancement (SE) models with self-supervised learning (SSL)-based speech models is effective for downstream tasks in noisy conditions. SE models are commonly fine-tuned using SSL representations with mean squared error (MSE) loss between enhanced and clean speech. However, MSE is prone to exploiting positional embeddings in SSL models, allowing the objective to be minimised through positional correlations instead of content-related information. This work frames the problem as a general limitation of self-supervised representation fine-tuning and investigates it through representation-guided SE. Two strategies are considered: (1) zero-padding, previously explored in SSL pre-training but here examined in the fine-tuning setting, and (2) speed perturbations with a soft-DTW loss. Experiments show that the soft-DTW-based approach achieves faster convergence and improved downstream performance, underscoring the importance of position-invariant fine-tuning in SSL-based speech modelling.
Towards a Unified Benchmark for Arabic Pronunciation Assessment: Quranic Recitation as Case Study
Jun 09, 2025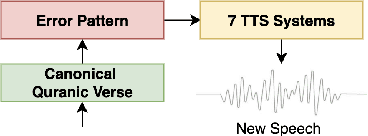
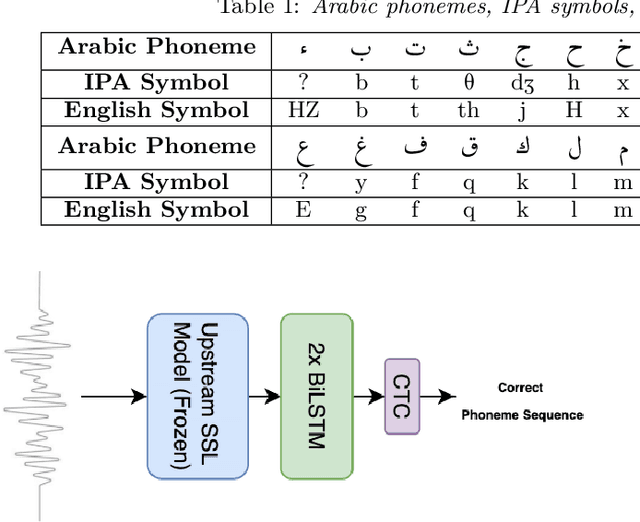
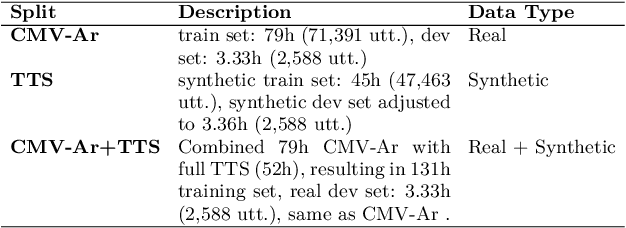
Abstract:We present a unified benchmark for mispronunciation detection in Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) using Qur'anic recitation as a case study. Our approach lays the groundwork for advancing Arabic pronunciation assessment by providing a comprehensive pipeline that spans data processing, the development of a specialized phoneme set tailored to the nuances of MSA pronunciation, and the creation of the first publicly available test set for this task, which we term as the Qur'anic Mispronunciation Benchmark (QuranMB.v1). Furthermore, we evaluate several baseline models to provide initial performance insights, thereby highlighting both the promise and the challenges inherent in assessing MSA pronunciation. By establishing this standardized framework, we aim to foster further research and development in pronunciation assessment in Arabic language technology and related applications.
LASER: Learning by Aligning Self-supervised Representations of Speech for Improving Content-related Tasks
Jun 13, 2024



Abstract:Self-supervised learning (SSL)-based speech models are extensively used for full-stack speech processing. However, it has been observed that improving SSL-based speech representations using unlabeled speech for content-related tasks is challenging and computationally expensive. Recent attempts have been made to address this issue with cost-effective self-supervised fine-tuning (SSFT) approaches. Continuing in this direction, a cost-effective SSFT method named "LASER: Learning by Aligning Self-supervised Representations" is presented. LASER is based on the soft-DTW alignment loss with temporal regularisation term. Experiments are conducted with HuBERT and WavLM models and evaluated on the SUPERB benchmark for two content-related tasks: automatic speech recognition (ASR) and phoneme recognition (PR). A relative improvement of 3.7% and 8.2% for HuBERT, and 4.1% and 11.7% for WavLM are observed, for the ASR and PR tasks respectively, with only < 3 hours of fine-tuning on a single GPU.
Improving Acoustic Word Embeddings through Correspondence Training of Self-supervised Speech Representations
Mar 13, 2024Abstract:Acoustic word embeddings (AWEs) are vector representations of spoken words. An effective method for obtaining AWEs is the Correspondence Auto-Encoder (CAE). In the past, the CAE method has been associated with traditional MFCC features. Representations obtained from self-supervised learning (SSL)-based speech models such as HuBERT, Wav2vec2, etc., are outperforming MFCC in many downstream tasks. However, they have not been well studied in the context of learning AWEs. This work explores the effectiveness of CAE with SSL-based speech representations to obtain improved AWEs. Additionally, the capabilities of SSL-based speech models are explored in cross-lingual scenarios for obtaining AWEs. Experiments are conducted on five languages: Polish, Portuguese, Spanish, French, and English. HuBERT-based CAE model achieves the best results for word discrimination in all languages, despite Hu-BERT being pre-trained on English only. Also, the HuBERT-based CAE model works well in cross-lingual settings. It outperforms MFCC-based CAE models trained on the target languages when trained on one source language and tested on target languages.
SCORE: Self-supervised Correspondence Fine-tuning for Improved Content Representations
Mar 10, 2024Abstract:There is a growing interest in cost-effective self-supervised fine-tuning (SSFT) of self-supervised learning (SSL)-based speech models to obtain task-specific representations. These task-specific representations are used for robust performance on various downstream tasks by fine-tuning on the labelled data. This work presents a cost-effective SSFT method named Self-supervised Correspondence (SCORE) fine-tuning to adapt the SSL speech representations for content-related tasks. The proposed method uses a correspondence training strategy, aiming to learn similar representations from perturbed speech and original speech. Commonly used data augmentation techniques for content-related tasks (ASR) are applied to obtain perturbed speech. SCORE fine-tuned HuBERT outperforms the vanilla HuBERT on SUPERB benchmark with only a few hours of fine-tuning (< 5 hrs) on a single GPU for automatic speech recognition, phoneme recognition, and query-by-example tasks, with relative improvements of 1.09%, 3.58%, and 12.65%, respectively. SCORE provides competitive results with the recently proposed SSFT method SPIN, using only 1/3 of the processed speech compared to SPIN.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge