Amir D. Gat
Inertial Inchworm Crawling
Jun 03, 2020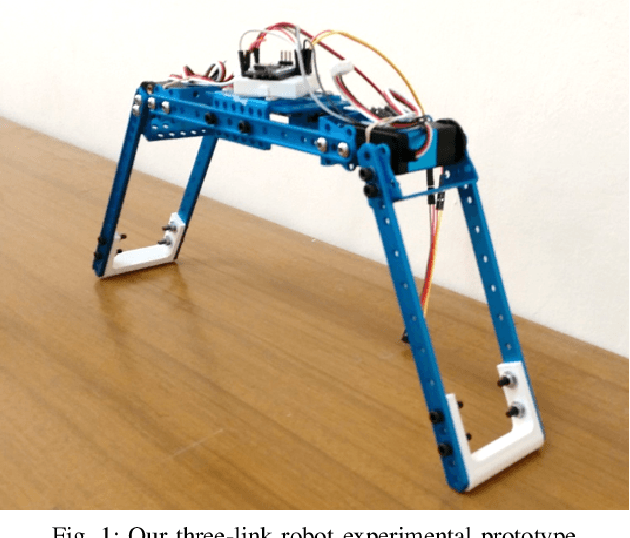
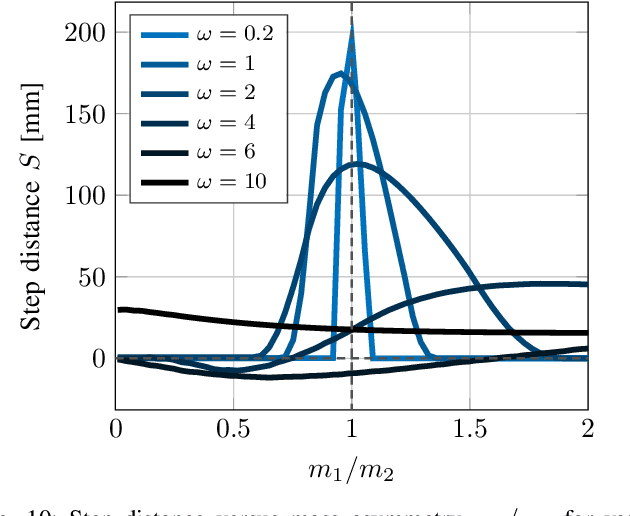
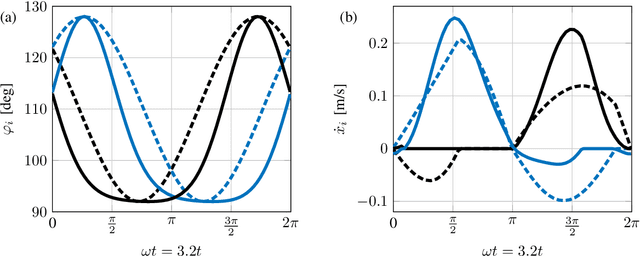
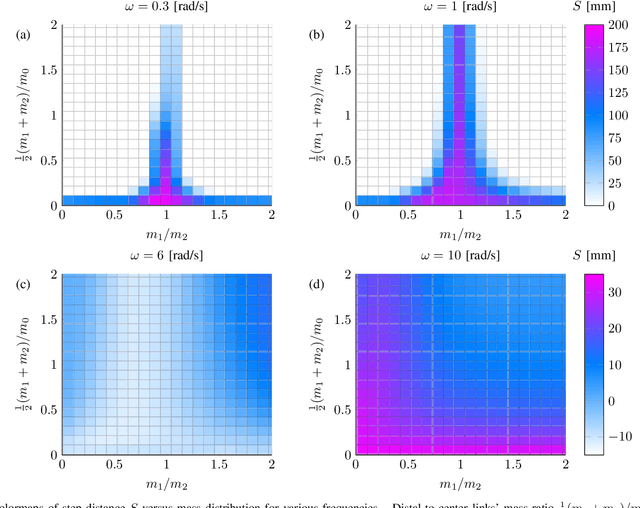
Abstract:Inchworm crawling allows for both quasistatic and dynamic gaits at a wide range of actuation frequencies. This locomotion mechanism is common in nonskeletal animals and exploited extensively in the bio-inspired field of soft robotics. In this work we develop and simulate the hybrid dynamic crawling of a three-link robot, with passive frictional contacts. We fabricate and experimentally test such robot under periodic inputs of joints' angles, with good agreement to the theoretical predictions. This allows to comprehend and exploit the effects of inertia in order to find optimal performance in inputs' parameters. A simple criterion of robustness to uncertainties in friction is proposed. Tuning the inputs according to this criterion improves the robustness of low-frequency actuation, while increasing the frequency allows for gaits with both high advancement velocity and robustness. Finally, the advantages of uneven mass distribution are studied. Time-scaling technique is introduced to shape inputs that achieve similar effect without reassembling the robot. A machine-learning based optimization is applied to these inputs to further improve the robot's performance.
Understanding Legged Crawling for Soft-Robotics
Nov 17, 2019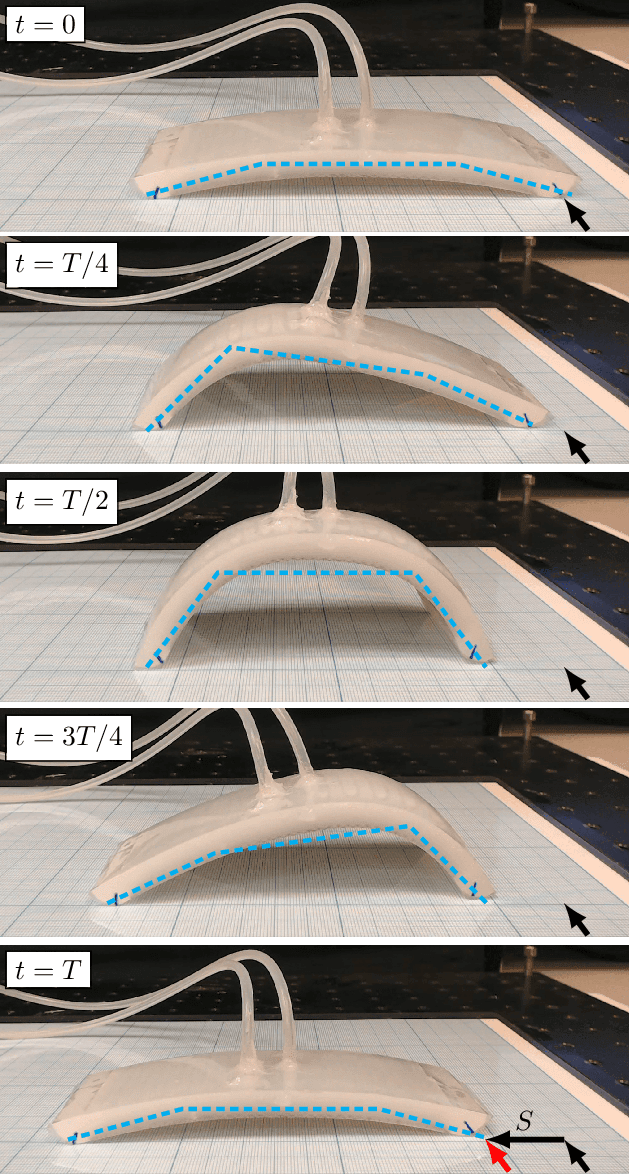
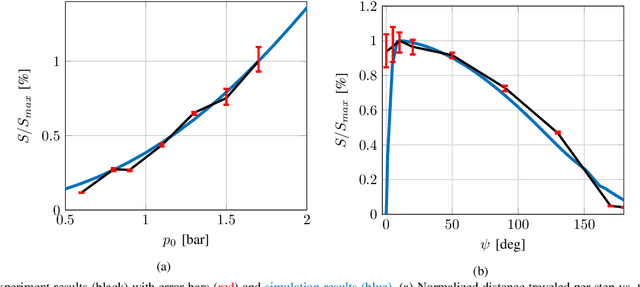
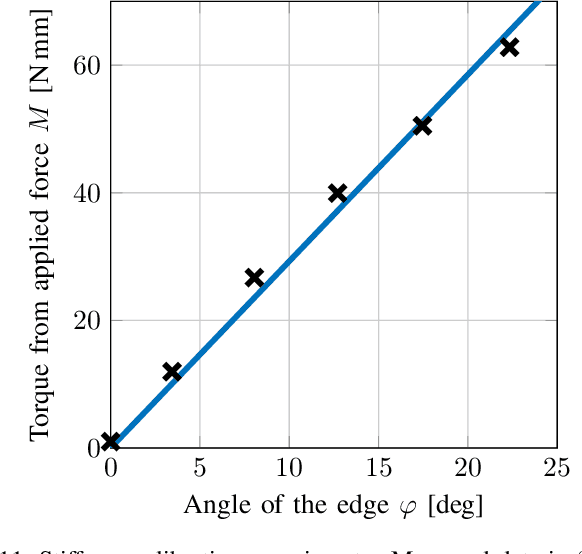
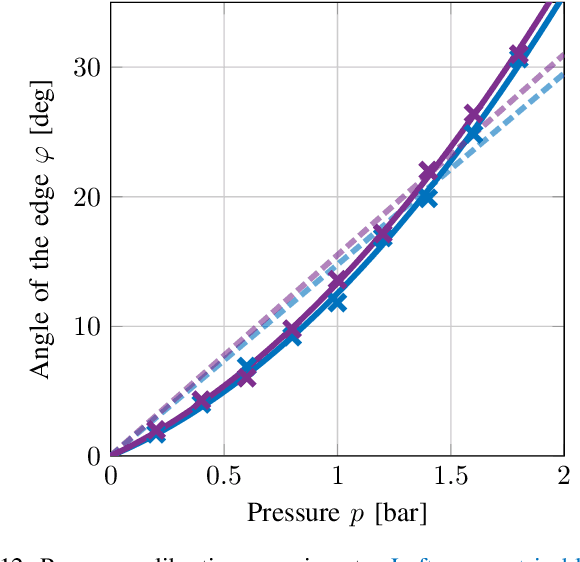
Abstract:Crawling is a common locomotion mechanism in soft robots and nonskeletal animals. In this work we propose modeling soft-robotic legged locomotion by approximating it with an equivalent articulated robot with elastic joints. For concreteness we study our soft robot with two bending actuators via an articulated three-link model. The solution of statically indeterminate systems with stick-slip contact transitions requires for a novel hybrid-quasitatic analysis. Then, we utilize our analysis to investigate the influence of phase-shifted harmonic inputs on performance of crawling gaits, including sensitivity analysis to friction uncertainties and energetic cost of transport. We achieve optimal values of gait parameters. Finally, we fabricate and test a fluid-driven soft robot. The experiments display remarkable agreement with the theoretical analysis, proving that our simple model correctly captures and explains the fundamental principles of inchworm crawling and can be applied to other soft-robotic legged robots.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge