Amina E. Hussein
Progress towards machine learning methodologies for laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy with an emphasis on soil analysis
Aug 15, 2022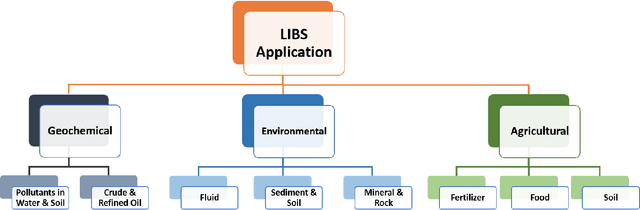
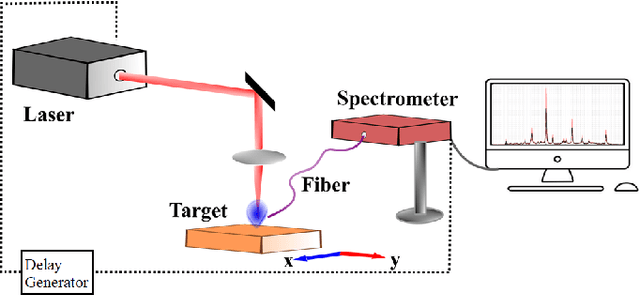
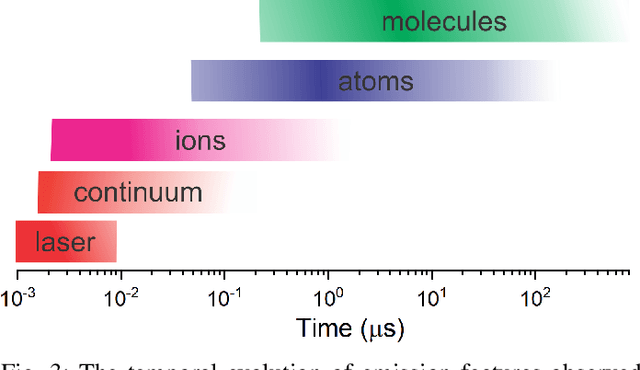
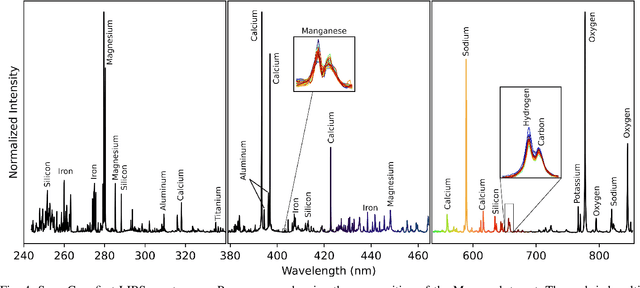
Abstract:Optical emission spectroscopy of laser-produced plasmas, commonly known as laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS), is an emerging analytical tool for rapid soil analysis. However, specific challenges with LIBS exist, such as matrix effects and quantification issues, that require further study in the application of LIBS, particularly for analysis of heterogeneous samples such as soils. Advancements in the applications of Machine Learning (ML) methods can address some of these issues, advancing the potential for LIBS in soil analysis. This article aims to review the progress of LIBS application combined with ML methods, focusing on methodological approaches used in reducing matrix effect, feature selection, quantification analysis, soil classification, and self-absorption. The performance of various adopted ML approaches is discussed, including their shortcomings and advantages, to provide researchers with a clear picture of the current status of ML applications in LIBS for improving its analytical capability. The challenges and prospects of LIBS development in soil analysis are proposed, offering a path toward future research. This review article emphasize ML tools for LIBS soil analysis that are broadly relevant for other LIBS applications.
What's in my closet?: Image classification using fuzzy logic
Dec 05, 2017



Abstract:A fuzzy system was created in MATLAB to identify an item of clothing as a dress, shirt, or pair of pants from a series of input images. The system was initialized using a high-contrast vector-image of each item of clothing as the state closest to a direct solution. Nine other user-input images (three of each item) were also used to determine the characteristic function of each item and recognize each pattern. Mamdani inference systems were used for edge location and identification of characteristic regions of interest for each item of clothing. Based on these non-dimensional trends, a second Mamdani fuzzy inference system was used to characterize each image as containing a shirt, a dress, or a pair of pants. An outline of the fuzzy inference system and image processing techniques used for creating an image pattern recognition system are discussed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge