Ambre Davat
GIPSA-lab, LIG
A study on the Lombard Effect in telepresence robotics
May 30, 2023Abstract:In this study, we present a new experiment in order to study the Lombard effect in telepresence robotics. In this experiment, one person talks with a robot controled remotely by someone in a different room. The remote pilot (R) is immersed in both environments, while the local interlocutor (L) interacts directly with the robot. In this context, the position of the noise source, in the remote or in the local room, may modify the subjects' voice adaptations. In order to study in details this phenomenon, we propose four particular conditions: no added noise, noise in room R heard only by R, virtual noise in room L heard only by R, and noise in room L heard by both R and L. We measured the variations of maximum intensity in order to quantify the Lombard effect. Our results show that there is indeed a modification of voice intensity in all noisy conditions. However, the amplitude of this modification varies depending on the condition.
Towards a model of "social touch'' for ubiquitous communication
May 30, 2023Abstract:One of the challenges of telepresence robotics is to provide ubiquitous social-interpersonalimmersion. In order to achieve this, there is a need to understand and model the factors that wouldallow the users to control the transmission of their vocal productions, and to give them perception,proprioception and inter-proprioception of this control. This model for transferring sociallyembodied vocal distance should take into account all parameters involved in the social-interpersonaleffect of vocal productions, especially intensity. It should also integrate the background informationwhich is relevant for the speakers to express their intentions. In this paper, we present a firstexperiment for measuring, analyzing and modeling how human beings perceive the distance to aninterlocutor, depending on socio-affective variations in the vocal productions of this interlocutor.These results will be the reference for the models which will be implanted in our telepresence robot:Robair Social Touch.
* in French language
Can we hear physical and social space together through prosody?
May 22, 2023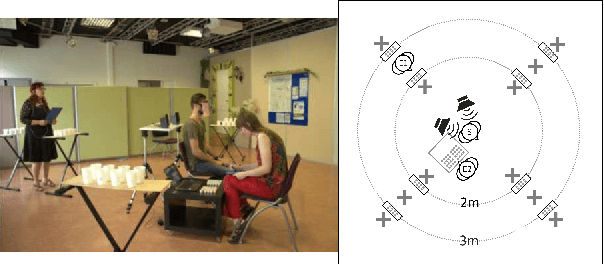
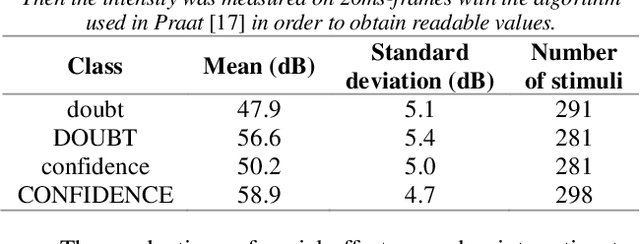

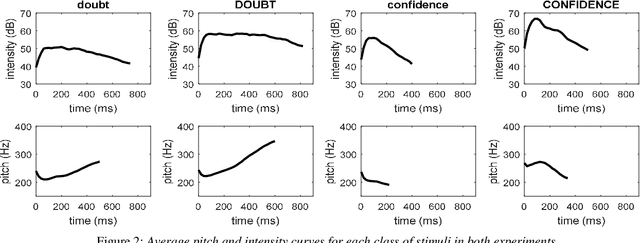
Abstract:When human listeners try to guess the spatial position of a speech source, they are influenced by the speaker's production level, regardless of the intensity level reaching their ears. Because the perception of distance is a very difficult task, they rely on their own experience, which tells them that a whispering talker is close to them, and that a shouting talker is far away. This study aims to test if similar results could be obtained for prosodic variations produced by a human speaker in an everyday life environment. It consists in a localization task, during which blindfolded subjects had to estimate the incoming voice direction, speaker orientation and distance of a trained female speaker, who uttered single words, following instructions concerning intensity and social-affect to be performed. This protocol was implemented in two experiments. First, a complex pretext task was used in order to distract the subjects from the strange behavior of the speaker. On the contrary, during the second experiment, the subjects were fully aware of the prosodic variations, which allowed them to adapt their perception. Results show the importance of the pretext task, and suggest that the perception of the speaker's orientation can be influenced by voice intensity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge