Ali Moeini
Enhancing Aspect-based Sentiment Analysis with ParsBERT in Persian Language
Feb 03, 2025



Abstract:In the era of pervasive internet use and the dominance of social networks, researchers face significant challenges in Persian text mining including the scarcity of adequate datasets in Persian and the inefficiency of existing language models. This paper specifically tackles these challenges, aiming to amplify the efficiency of language models tailored to the Persian language. Focusing on enhancing the effectiveness of sentiment analysis, our approach employs an aspect-based methodology utilizing the ParsBERT model, augmented with a relevant lexicon. The study centers on sentiment analysis of user opinions extracted from the Persian website 'Digikala.' The experimental results not only highlight the proposed method's superior semantic capabilities but also showcase its efficiency gains with an accuracy of 88.2% and an F1 score of 61.7. The importance of enhancing language models in this context lies in their pivotal role in extracting nuanced sentiments from user-generated content, ultimately advancing the field of sentiment analysis in Persian text mining by increasing efficiency and accuracy.
D2RLIR : an improved and diversified ranking function in interactive recommendation systems based on deep reinforcement learning
Oct 29, 2021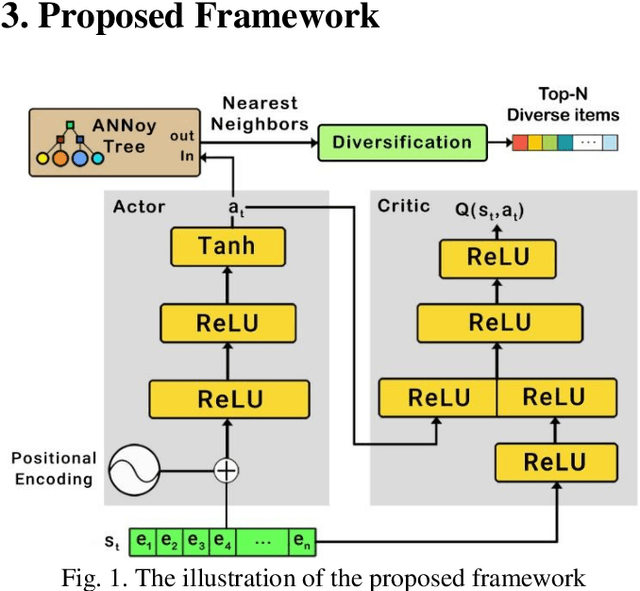

Abstract:Recently, interactive recommendation systems based on reinforcement learning have been attended by researchers due to the consider recommendation procedure as a dynamic process and update the recommendation model based on immediate user feedback, which is neglected in traditional methods. The existing works have two significant drawbacks. Firstly, inefficient ranking function to produce the Top-N recommendation list. Secondly, focusing on recommendation accuracy and inattention to other evaluation metrics such as diversity. This paper proposes a deep reinforcement learning based recommendation system by utilizing Actor-Critic architecture to model dynamic users' interaction with the recommender agent and maximize the expected long-term reward. Furthermore, we propose utilizing Spotify's ANNoy algorithm to find the most similar items to generated action by actor-network. After that, the Total Diversity Effect Ranking algorithm is used to generate the recommendations concerning relevancy and diversity. Moreover, we apply positional encoding to compute representations of the user's interaction sequence without using sequence-aligned recurrent neural networks. Extensive experiments on the MovieLens dataset demonstrate that our proposed model is able to generate a diverse while relevance recommendation list based on the user's preferences.
A Hybrid Approach to Enhance Pure Collaborative Filtering based on Content Feature Relationship
May 17, 2020


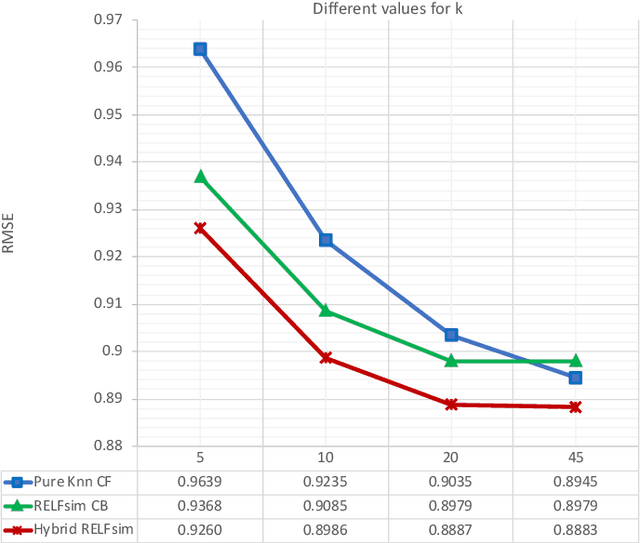
Abstract:Recommendation systems get expanding significance because of their applications in both the scholarly community and industry. With the development of additional data sources and methods of extracting new information other than the rating history of clients on items, hybrid recommendation algorithms, in which some methods have usually been combined to improve performance, have become pervasive. In this work, we first introduce a novel method to extract the implicit relationship between content features using a sort of well-known methods from the natural language processing domain, namely Word2Vec. In contrast to the typical use of Word2Vec, we utilize some features of items as words of sentences to produce neural feature embeddings, through which we can calculate the similarity between features. Next, we propose a novel content-based recommendation system that employs the relationship to determine vector representations for items by which the similarity between items can be computed (RELFsim). Our evaluation results demonstrate that it can predict the preference a user would have for a set of items as good as pure collaborative filtering. This content-based algorithm is also embedded in a pure item-based collaborative filtering algorithm to deal with the cold-start problem and enhance its accuracy. Our experiments on a benchmark movie dataset corroborate that the proposed approach improves the accuracy of the system.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge