Ali Al-Shaikhi
King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals, Electrical Engineering Department
Recursions Are All You Need: Towards Efficient Deep Unfolding Networks
May 09, 2023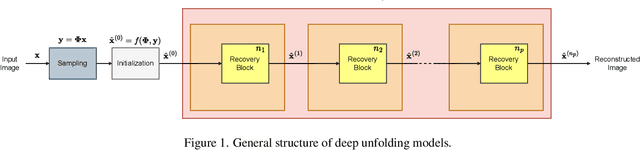
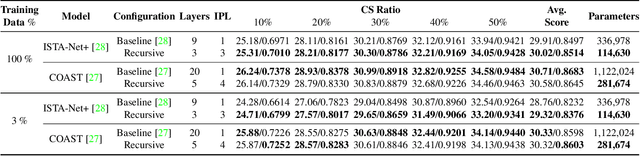

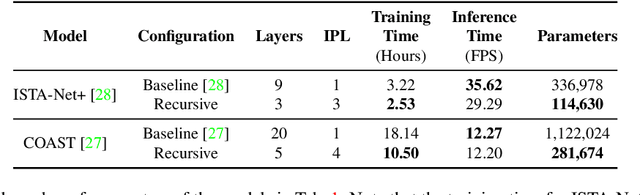
Abstract:The use of deep unfolding networks in compressive sensing (CS) has seen wide success as they provide both simplicity and interpretability. However, since most deep unfolding networks are iterative, this incurs significant redundancies in the network. In this work, we propose a novel recursion-based framework to enhance the efficiency of deep unfolding models. First, recursions are used to effectively eliminate the redundancies in deep unfolding networks. Secondly, we randomize the number of recursions during training to decrease the overall training time. Finally, to effectively utilize the power of recursions, we introduce a learnable unit to modulate the features of the model based on both the total number of iterations and the current iteration index. To evaluate the proposed framework, we apply it to both ISTA-Net+ and COAST. Extensive testing shows that our proposed framework allows the network to cut down as much as 75% of its learnable parameters while mostly maintaining its performance, and at the same time, it cuts around 21% and 42% from the training time for ISTA-Net+ and COAST respectively. Moreover, when presented with a limited training dataset, the recursive models match or even outperform their respective non-recursive baseline. Codes and pretrained models are available at https://github.com/Rawwad-Alhejaili/Recursions-Are-All-You-Need .
Sensor-based, time-critical mobility of autonomous robots in cluttered spaces: a harmonic potential approach
Aug 26, 2018Abstract:This paper suggests an integrated navigation system for an unmanned ground vehicle operating in an unknown cluttered environment. The navigator supports time-critical mobility making it possible for a mobile robot to reach a target from the first attempt without the need for a dedicated exploration and mapping stage. The robot only uses necessary and sufficient egocentric local sensory data collected on its way to the target. The construction of the navigation structure revolves around key properties of the harmonic potential field approach to motion planning. The robots trajectory is well-behaved and direct-to-the-goal. It contains only the minimum number of detours necessary to accommodate the sensory data and maintain the robot in a safe, goal-oriented state. The navigation structure is developed and its theoretical basis is explained. Extensive experimental validation of its properties and performance is carried-out using the X80 robotic platform
* 32 pages, 56 figures, Journal paper
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge