Alfonso Valderrama
Measuring the Predictability of Recommender Systems using Structural Complexity Metrics
Apr 12, 2024

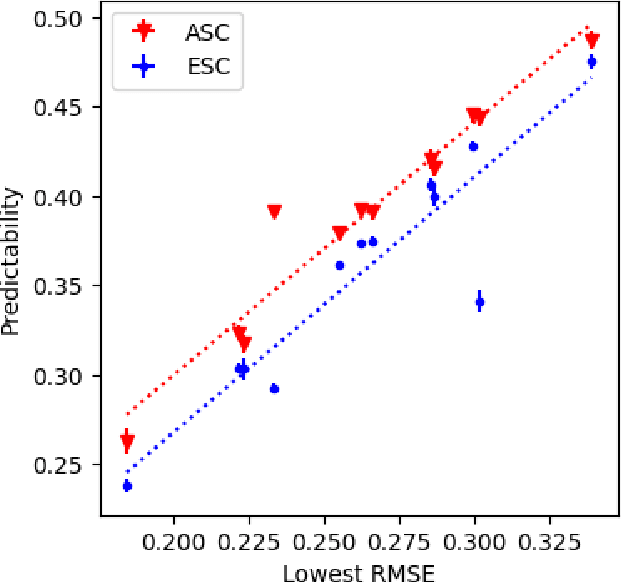
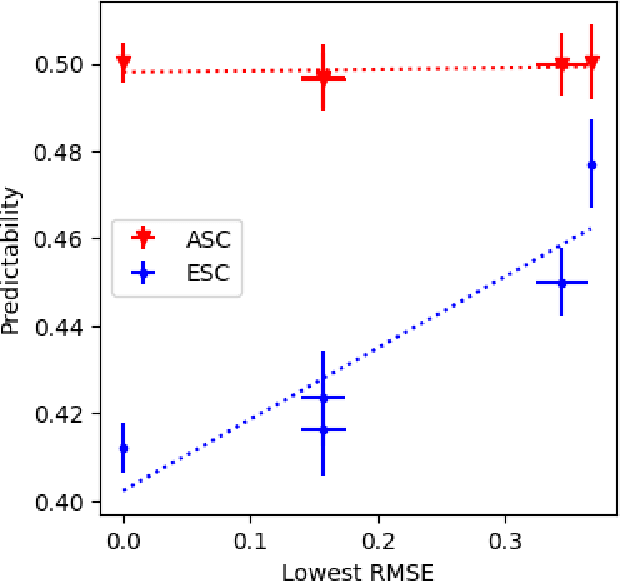
Abstract:Recommender systems (RS) are central to the filtering and curation of online content. These algorithms predict user ratings for unseen items based on past preferences. Despite their importance, the innate predictability of RS has received limited attention. This study introduces data-driven metrics to measure the predictability of RS based on the structural complexity of the user-item rating matrix. A low predictability score indicates complex and unpredictable user-item interactions, while a high predictability score reveals less complex patterns with predictive potential. We propose two strategies that use singular value decomposition (SVD) and matrix factorization (MF) to measure structural complexity. By perturbing the data and evaluating the prediction of the perturbed version, we explore the structural consistency indicated by the SVD singular vectors. The assumption is that a random perturbation of highly structured data does not change its structure. Empirical results show a high correlation between our metrics and the accuracy of the best-performing prediction algorithms on real data sets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge