Alexandre C. B. Delbem
The Effects of Relative Importance of User Constraints in Cloud of Things Resource Discovery: A Case Study
Nov 16, 2016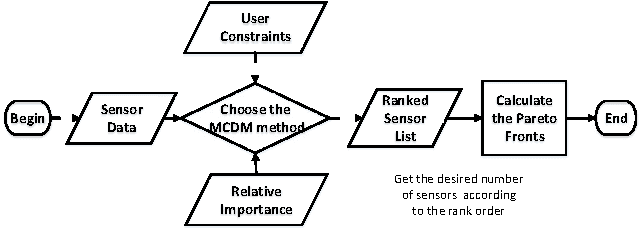
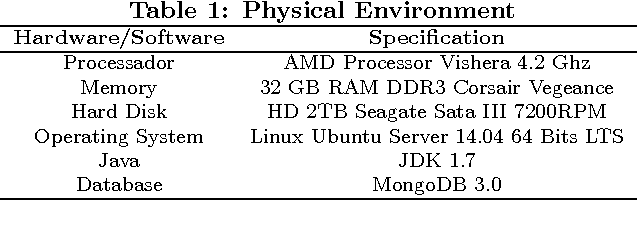

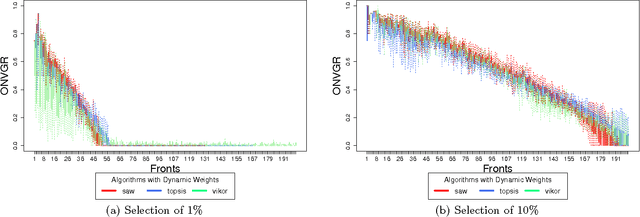
Abstract:Over the last few years, the number of smart objects connected to the Internet has grown exponentially in comparison to the number of services and applications. The integration between Cloud Computing and Internet of Things, named as Cloud of Things, plays a key role in managing the connected things, their data and services. One of the main challenges in Cloud of Things is the resource discovery of the smart objects and their reuse in different contexts. Most of the existent work uses some kind of multi-criteria decision analysis algorithm to perform the resource discovery, but do not evaluate the impact that the user constraints has in the final solution. In this paper, we analyse the behaviour of the SAW, TOPSIS and VIKOR multi-objective decision analyses algorithms and the impact of user constraints on them. We evaluated the quality of the proposed solutions using the Pareto-optimality concept.
* Proceedings of the 9th IEEE/ACM International Conference on Utility and Cloud Computing (UCC 2016) Shaghai, China, December, 2016
Representation of Evolutionary Algorithms in FPGA Cluster for Project of Large-Scale Networks
Dec 17, 2014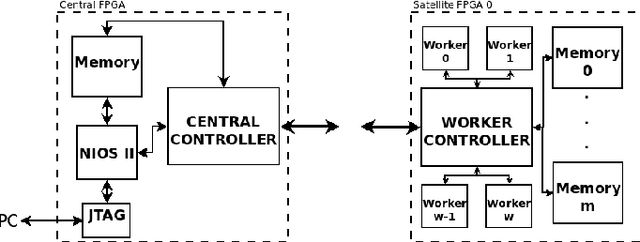
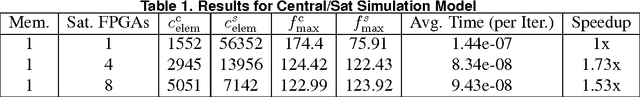
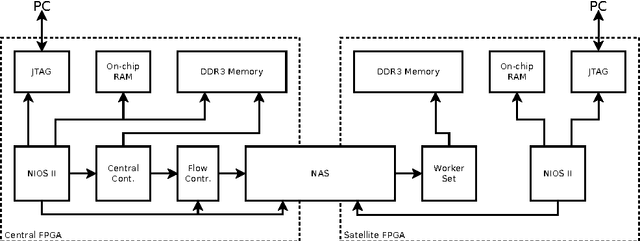
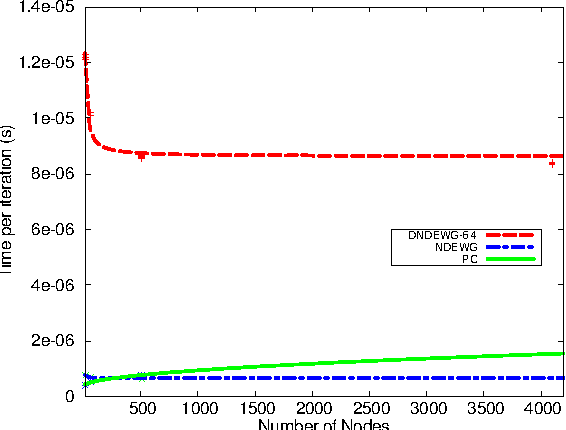
Abstract:Many problems are related to network projects, such as electric distribution, telecommunication and others. Most of them can be represented by graphs, which manipulate thousands or millions of nodes, becoming almost an impossible task to obtain real-time solutions. Many efficient solutions use Evolutionary Algorithms (EA), where researches show that performance of EAs can be substantially raised by using an appropriate representation, such as the Node-Depth Encoding (NDE). The objective of this work was to partition an implementation on single-FPGA (Field-Programmable Gate Array) based on NDE from 512 nodes to a multi-FPGAs approach, expanding the system to 4096 nodes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge