Alexandra Iacob
Contextual Bandits for Advertising Campaigns: A Diffusion-Model Independent Approach (Extended Version)
Jan 13, 2022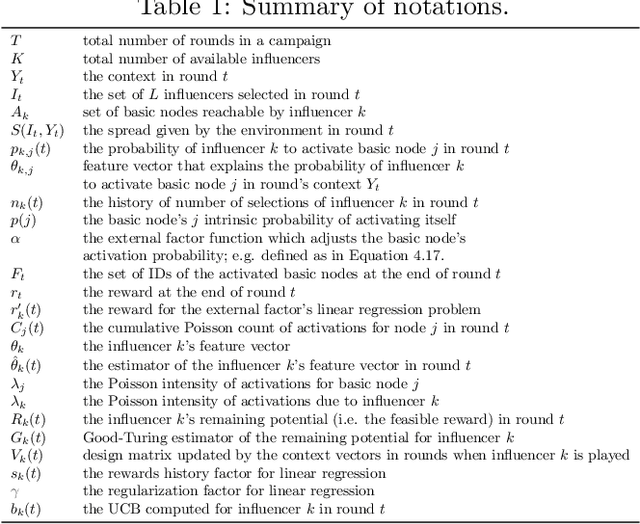
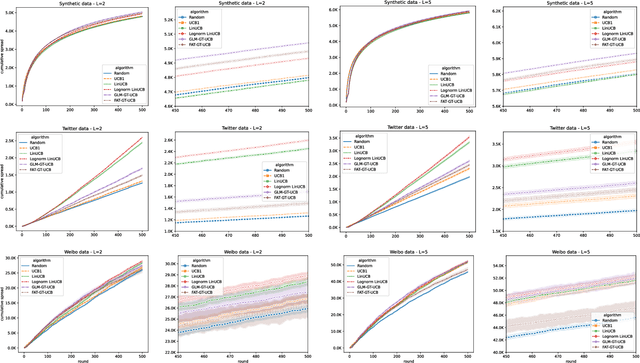
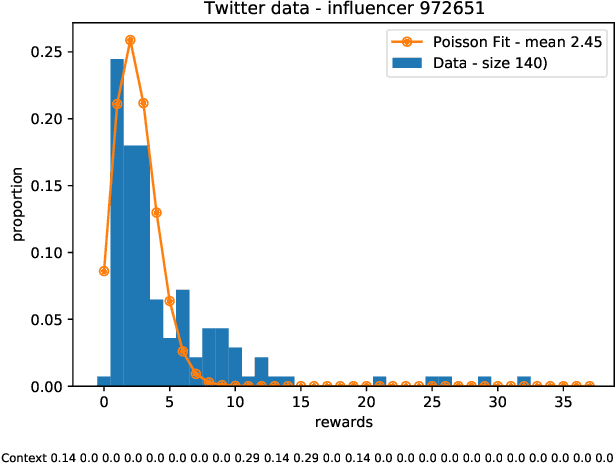
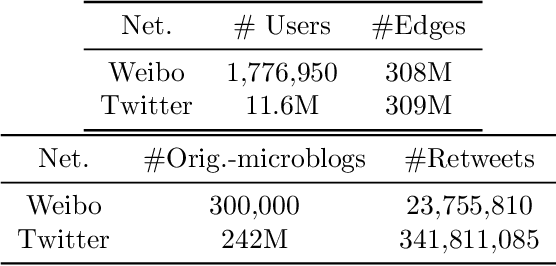
Abstract:Motivated by scenarios of information diffusion and advertising in social media, we study an influence maximization problem in which little is assumed to be known about the diffusion network or about the model that determines how information may propagate. In such a highly uncertain environment, one can focus on multi-round diffusion campaigns, with the objective to maximize the number of distinct users that are influenced or activated, starting from a known base of few influential nodes. During a campaign, spread seeds are selected sequentially at consecutive rounds, and feedback is collected in the form of the activated nodes at each round. A round's impact (reward) is then quantified as the number of newly activated nodes. Overall, one must maximize the campaign's total spread, as the sum of rounds' rewards. In this setting, an explore-exploit approach could be used to learn the key underlying diffusion parameters, while running the campaign. We describe and compare two methods of contextual multi-armed bandits, with upper-confidence bounds on the remaining potential of influencers, one using a generalized linear model and the Good-Turing estimator for remaining potential (GLM-GT-UCB), and another one that directly adapts the LinUCB algorithm to our setting (LogNorm-LinUCB). We show that they outperform baseline methods using state-of-the-art ideas, on synthetic and real-world data, while at the same time exhibiting different and complementary behavior, depending on the scenarios in which they are deployed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge