Alexander Te-Wei Shieh
Towards Generating Citation Sentences for Multiple References with Intent Control
Dec 09, 2021


Abstract:Machine-generated citation sentences can aid automated scientific literature review and assist article writing. Current methods in generating citation text were limited to single citation generation using the citing document and a cited document as input. However, in real-world situations, writers often summarize several studies in one sentence or discuss relevant information across the entire paragraph. In addition, multiple citation intents have been previously identified, implying that writers may need control over the intents of generated sentences to cover different scenarios. Therefore, this work focuses on generating multiple citations and releasing a newly collected dataset named CiteMI to drive the future research. We first build a novel generation model with the Fusion-in-Decoder approach to cope with multiple long inputs. Second, we incorporate the predicted citation intents into training for intent control. The experiments demonstrate that the proposed approaches provide much more comprehensive features for generating citation sentences.
Towards Understanding of Medical Randomized Controlled Trials by Conclusion Generation
Oct 03, 2019
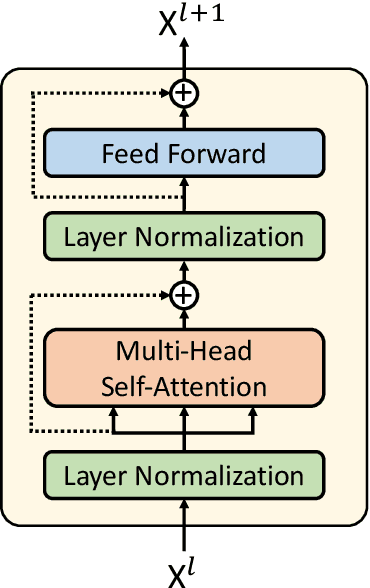


Abstract:Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) represent the paramount evidence of clinical medicine. Using machines to interpret the massive amount of RCTs has the potential of aiding clinical decision-making. We propose a RCT conclusion generation task from the PubMed 200k RCT sentence classification dataset to examine the effectiveness of sequence-to-sequence models on understanding RCTs. We first build a pointer-generator baseline model for conclusion generation. Then we fine-tune the state-of-the-art GPT-2 language model, which is pre-trained with general domain data, for this new medical domain task. Both automatic and human evaluation show that our GPT-2 fine-tuned models achieve improved quality and correctness in the generated conclusions compared to the baseline pointer-generator model. Further inspection points out the limitations of this current approach and future directions to explore.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge