Alexander Quevedo
Agave crop segmentation and maturity classification with deep learning data-centric strategies using very high-resolution satellite imagery
Mar 21, 2023Abstract:The responsible and sustainable agave-tequila production chain is fundamental for the social, environment and economic development of Mexico's agave regions. It is therefore relevant to develop new tools for large scale automatic agave region monitoring. In this work, we present an Agave tequilana Weber azul crop segmentation and maturity classification using very high resolution satellite imagery, which could be useful for this task. To achieve this, we solve real-world deep learning problems in the very specific context of agave crop segmentation such as lack of data, low quality labels, highly imbalanced data, and low model performance. The proposed strategies go beyond data augmentation and data transfer combining active learning and the creation of synthetic images with human supervision. As a result, the segmentation performance evaluated with Intersection over Union (IoU) value increased from 0.72 to 0.90 in the test set. We also propose a method for classifying agave crop maturity with 95\% accuracy. With the resulting accurate models, agave production forecasting can be made available for large regions. In addition, some supply-demand problems such excessive supplies of agave or, deforestation, could be detected early.
Jalisco's multiclass land cover analysis and classification using a novel lightweight convnet with real-world multispectral and relief data
Jan 26, 2022
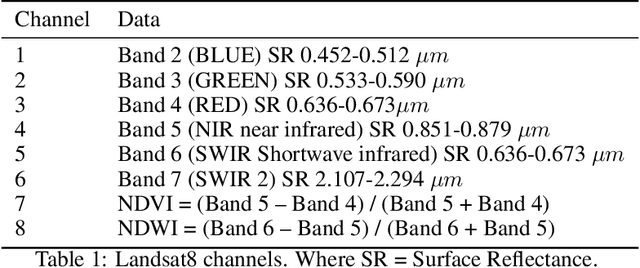
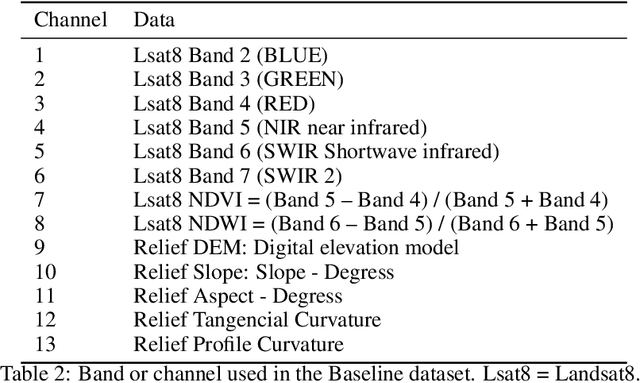
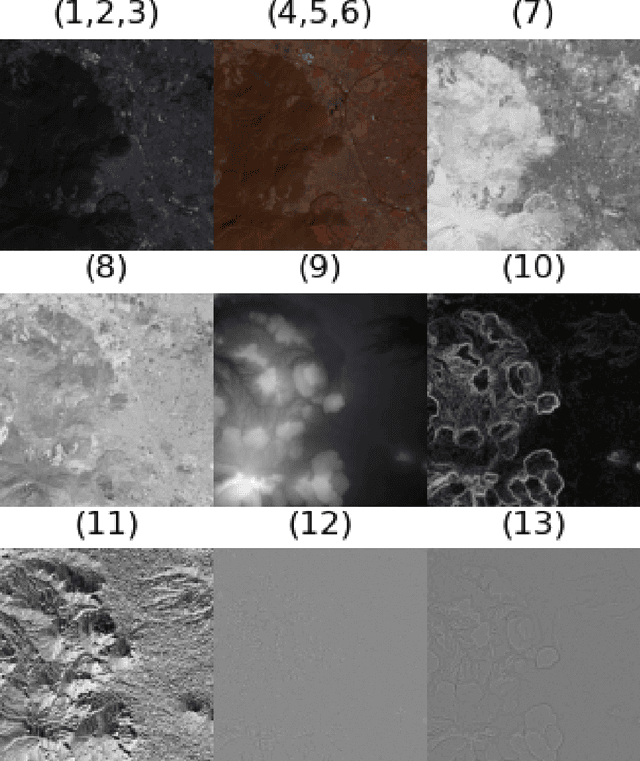
Abstract:The understanding of global climate change, agriculture resilience, and deforestation control rely on the timely observations of the Land Use and Land Cover Change (LULCC). Recently, some deep learning (DL) methods have been adapted to make an automatic classification of Land Cover (LC) for global and homogeneous data. However, most of these DL models can not apply effectively to real-world data. i.e. a large number of classes, multi-seasonal data, diverse climate regions, high imbalance label dataset, and low-spatial resolution. In this work, we present our novel lightweight (only 89k parameters) Convolution Neural Network (ConvNet) to make LC classification and analysis to handle these problems for the Jalisco region. In contrast to the global approaches, the regional data provide the context-specificity that is required for policymakers to plan the land use and management, conservation areas, or ecosystem services. In this work, we combine three real-world open data sources to obtain 13 channels. Our embedded analysis anticipates the limited performance in some classes and gives us the opportunity to group the most similar, as a result, the test accuracy performance increase from 73 % to 83 %. We hope that this research helps other regional groups with limited data sources or computational resources to attain the United Nations Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) concerning Life on Land.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge