Alexander Baturo
What Drives the International Development Agenda? An NLP Analysis of the United Nations General Debate 1970-2016
Aug 19, 2017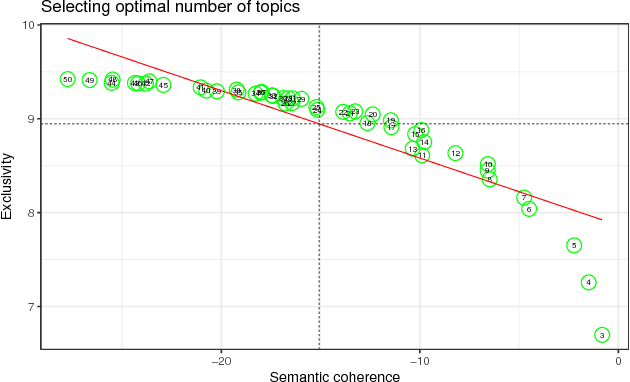
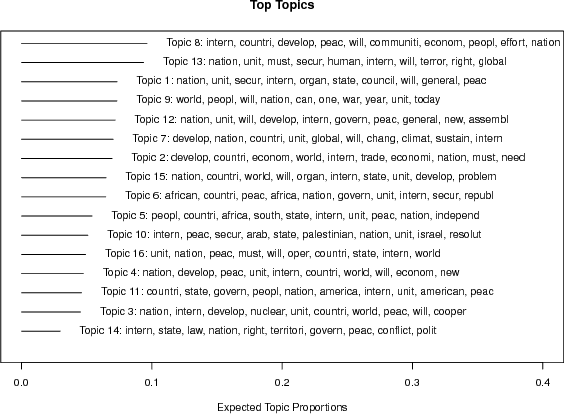

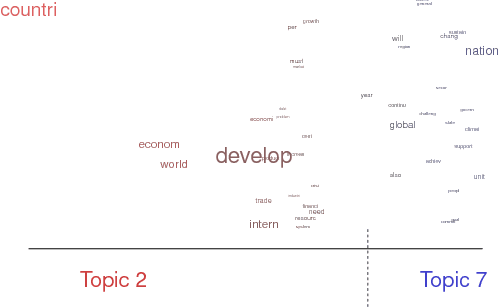
Abstract:There is surprisingly little known about agenda setting for international development in the United Nations (UN) despite it having a significant influence on the process and outcomes of development efforts. This paper addresses this shortcoming using a novel approach that applies natural language processing techniques to countries' annual statements in the UN General Debate. Every year UN member states deliver statements during the General Debate on their governments' perspective on major issues in world politics. These speeches provide invaluable information on state preferences on a wide range of issues, including international development, but have largely been overlooked in the study of global politics. This paper identifies the main international development topics that states raise in these speeches between 1970 and 2016, and examine the country-specific drivers of international development rhetoric.
Understanding State Preferences With Text As Data: Introducing the UN General Debate Corpus
Jul 10, 2017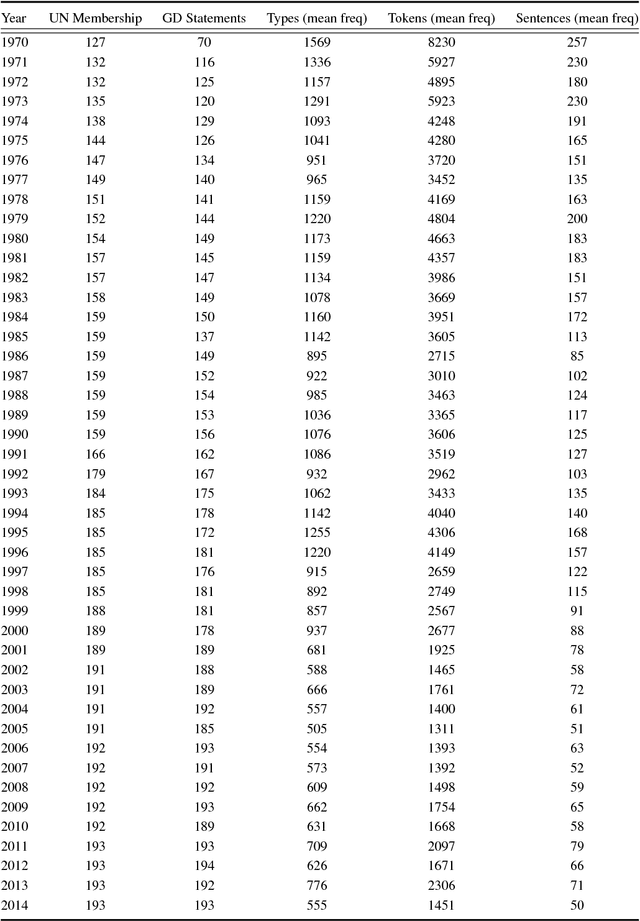
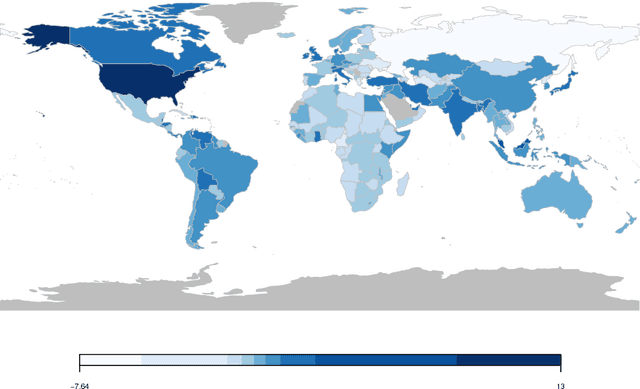

Abstract:Every year at the United Nations, member states deliver statements during the General Debate discussing major issues in world politics. These speeches provide invaluable information on governments' perspectives and preferences on a wide range of issues, but have largely been overlooked in the study of international politics. This paper introduces a new dataset consisting of over 7,701 English-language country statements from 1970-2016. We demonstrate how the UN General Debate Corpus (UNGDC) can be used to derive country positions on different policy dimensions using text analytic methods. The paper provides applications of these estimates, demonstrating the contribution the UNGDC can make to the study of international politics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge