Alessia Amelio
Time Series Vector Autoregression Prediction of the Ecological Footprint based on Energy Parameters
Oct 25, 2019

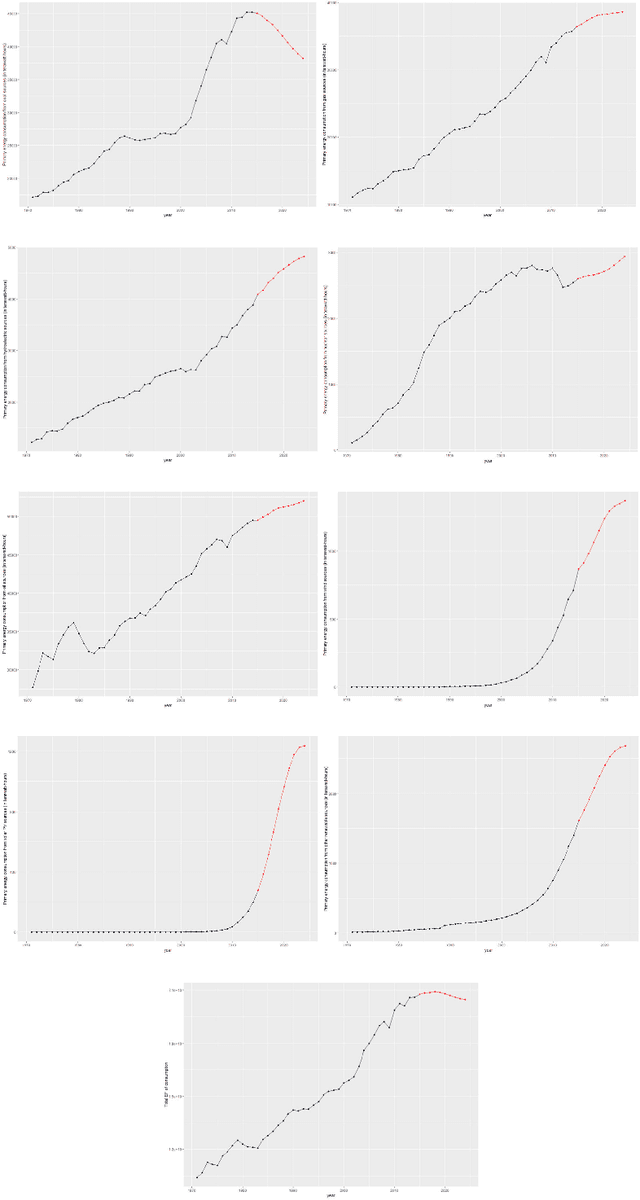
Abstract:Sustainability became the most important component of world development, as countries worldwide fight the battle against the climate change. To understand the effects of climate change, the ecological footprint, along with the biocapacity should be observed. The big part of the ecological footprint, the carbon footprint, is most directly associated with the energy, and specifically fuel sources. This paper develops a time series vector autoregression prediction model of the ecological footprint based on energy parameters. The objective of the paper is to forecast the EF based solely on energy parameters and determine the relationship between the energy and the EF. The dataset included global yearly observations of the variables for the period 1971-2014. Predictions were generated for every variable that was used in the model for the period 2015-2024. The results indicate that the ecological footprint of consumption will continue increasing, as well as the primary energy consumption from different sources. However, the energy consumption from coal sources is predicted to have a declining trend.
Comparing Multilayer Perceptron and Multiple Regression Models for Predicting Energy Use in the Balkans
Oct 26, 2018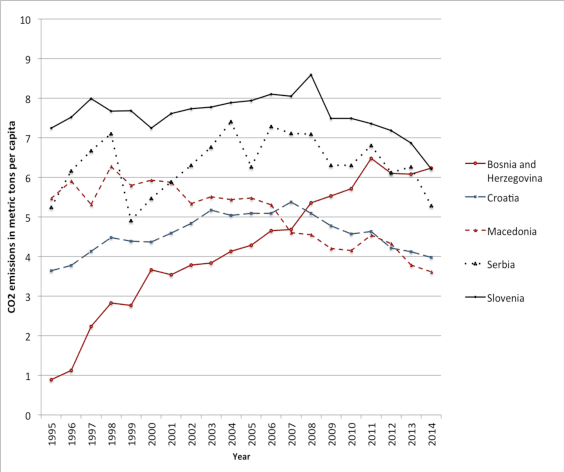


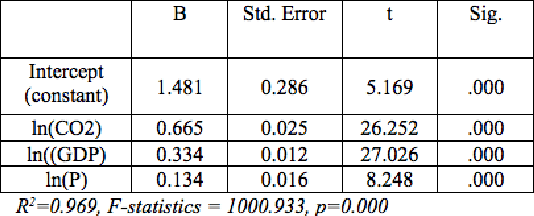
Abstract:Global demographic and economic changes have a critical impact on the total energy consumption, which is why demographic and economic parameters have to be taken into account when making predictions about the energy consumption. This research is based on the application of a multiple linear regression model and a neural network model, in particular multilayer perceptron, for predicting the energy consumption. Data from five Balkan countries has been considered in the analysis for the period 1995-2014. Gross domestic product, total number of population, and CO2 emission were taken as predictor variables, while the energy consumption was used as the dependent variable. The analyses showed that CO2 emissions have the highest impact on the energy consumption, followed by the gross domestic product, while the population number has the lowest impact. The results from both analyses are then used for making predictions on the same data, after which the obtained values were compared with the real values. It was observed that the multilayer perceptron model predicts better the energy consumption than the regression model.
CT Image Registration in Acute Stroke Monitoring
Jun 28, 2018



Abstract:We present a new system based on tracking the temporal evolution of stroke lesions using an image registration technique on CT exams of the patient's brain. The system is able to compare past CT exams with the most recent one related to stroke event in order to evaluate past lesions which are not related to stroke. Then, it can compare recent CT exams related to the current stroke for assessing the evolution of the lesion over time. A new similarity measure is also introduced for the comparison of the source and target images during image registration. It will result in a cheaper, faster and more accessible evaluation of the acute phase of the stroke overcoming the current limitations of the proposed systems in the state-of-the-art.
Statistical Analysis of Dice CAPTCHA Usability
Jun 30, 2017



Abstract:In this paper the elements of the CAPTCHA usability are analyzed. CAPTCHA, as a time progressive element in computer science, has been under constant interest of ordinary, professional as well as the scientific users of the Internet. The analysis is given based on the usability elements of CAPTCHA which are abbreviated as user-centric approach to the CAPTCHA. To demonstrate it, the specific type of Dice CAPTCHA is used in the experiment. The experiment is conducted on 190 Internet users with different demographic characteristics on laptop and tablet computers. The obtained results are statistically processed. At the end, the results are compared and conclusion of their use is drawn.
The $\mathcal{E}$-Average Common Submatrix: Approximate Searching in a Restricted Neighborhood
Jun 19, 2017Abstract:This paper introduces a new (dis)similarity measure for 2D arrays, extending the Average Common Submatrix measure. This is accomplished by: (i) considering the frequency of matching patterns, (ii) restricting the pattern matching to a fixed-size neighborhood, and (iii) computing a distance-based approximate matching. This will achieve better performances with low execution time and larger information retrieval.
Analysis of the Human-Computer Interaction on the Example of Image-based CAPTCHA by Association Rule Mining
Dec 06, 2016
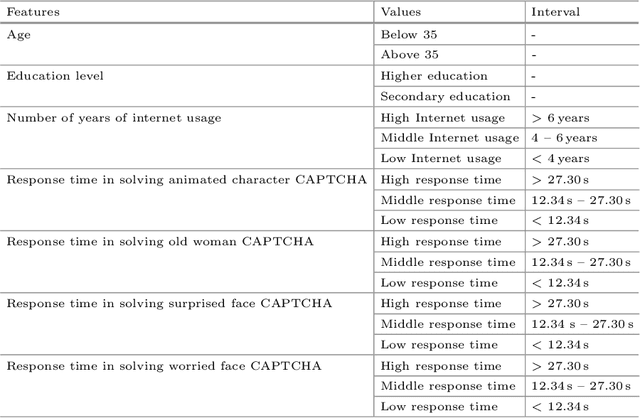
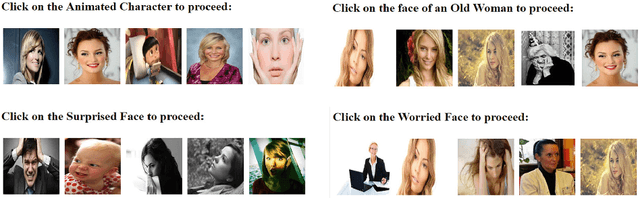

Abstract:The paper analyzes the interaction between humans and computers in terms of response time in solving the image-based CAPTCHA. In particular, the analysis focuses on the attitude of the different Internet users in easily solving four different types of image-based CAPTCHAs which include facial expressions like: animated character, old woman, surprised face, worried face. To pursue this goal, an experiment is realized involving 100 Internet users in solving the four types of CAPTCHAs, differentiated by age, Internet experience, and education level. The response times are collected for each user. Then, association rules are extracted from user data, for evaluating the dependence of the response time in solving the CAPTCHA from age, education level and experience in internet usage by statistical analysis. The results implicitly capture the users' psychological states showing in what states the users are more sensible. It reveals to be a novelty and a meaningful analysis in the state-of-the-art.
Document Image Coding and Clustering for Script Discrimination
Sep 21, 2016
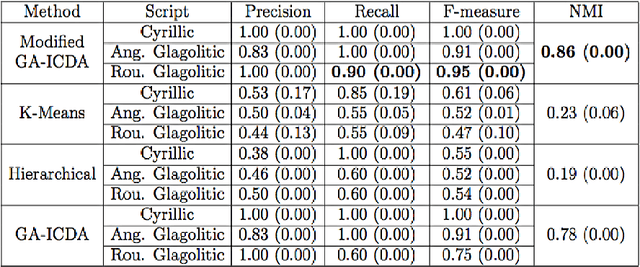
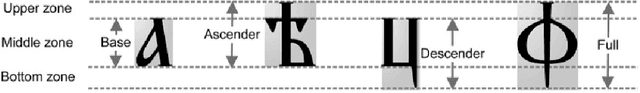
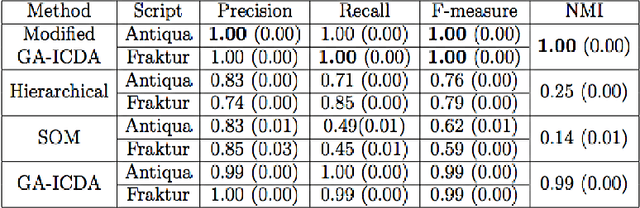
Abstract:The paper introduces a new method for discrimination of documents given in different scripts. The document is mapped into a uniformly coded text of numerical values. It is derived from the position of the letters in the text line, based on their typographical characteristics. Each code is considered as a gray level. Accordingly, the coded text determines a 1-D image, on which texture analysis by run-length statistics and local binary pattern is performed. It defines feature vectors representing the script content of the document. A modified clustering approach employed on document feature vector groups documents written in the same script. Experimentation performed on two custom oriented databases of historical documents in old Cyrillic, angular and round Glagolitic as well as Antiqua and Fraktur scripts demonstrates the superiority of the proposed method with respect to well-known methods in the state-of-the-art.
* 8 pages, 4 figures, 2 tables
An Approach to the Analysis of the South Slavic Medieval Labels Using Image Texture
Sep 07, 2015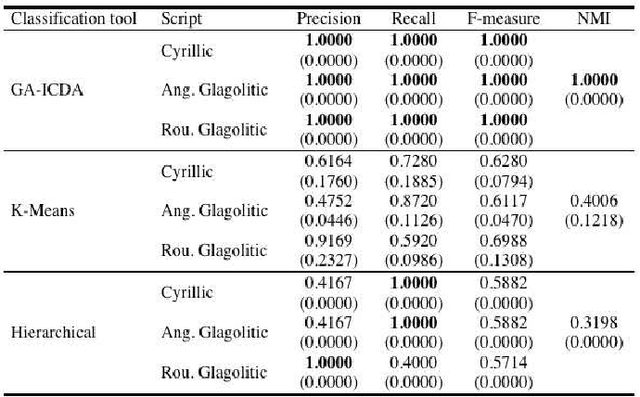
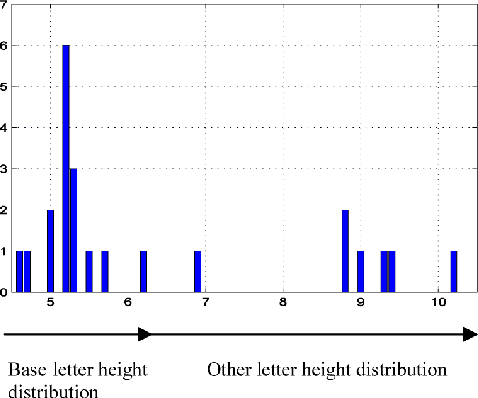
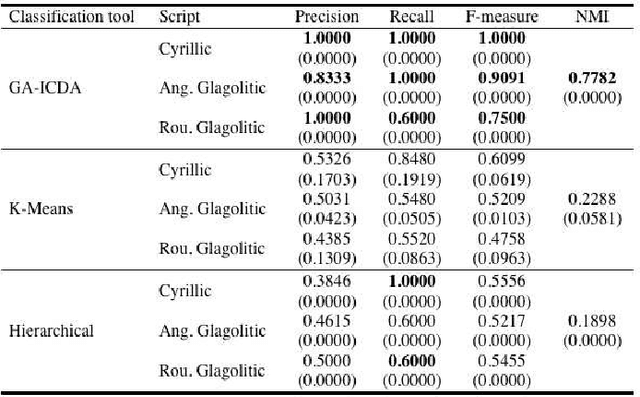

Abstract:The paper presents a new script classification method for the discrimination of the South Slavic medieval labels. It consists in the textural analysis of the script types. In the first step, each letter is coded by the equivalent script type, which is defined by its typographical features. Obtained coded text is subjected to the run-length statistical analysis and to the adjacent local binary pattern analysis in order to extract the features. The result shows a diversity between the extracted features of the scripts, which makes the feature classification more effective. It is the basis for the classification process of the script identification by using an extension of a state-of-the-art approach for document clustering. The proposed method is evaluated on an example of hand-engraved in stone and hand-printed in paper labels in old Cyrillic, angular and round Glagolitic. Experiments demonstrate very positive results, which prove the effectiveness of the proposed method.
Analysis of the South Slavic Scripts by Run-Length Features of the Image Texture
Jul 17, 2015
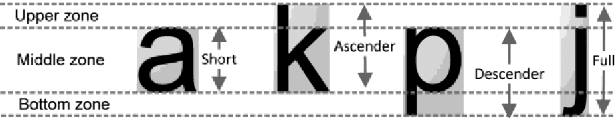
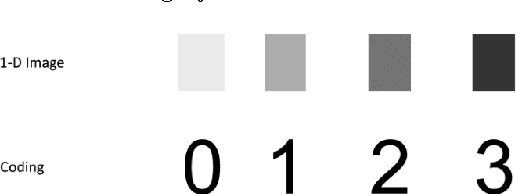
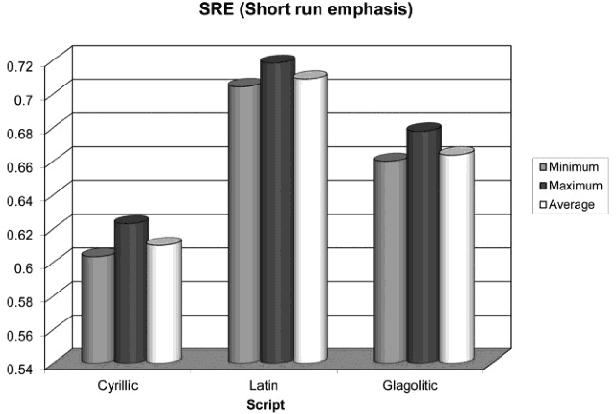
Abstract:The paper proposes an algorithm for the script recognition based on the texture characteristics. The image texture is achieved by coding each letter with the equivalent script type (number code) according to its position in the text line. Each code is transformed into equivalent gray level pixel creating an 1-D image. Then, the image texture is subjected to the run-length analysis. This analysis extracts the run-length features, which are classified to make a distinction between the scripts under consideration. In the experiment, a custom oriented database is subject to the proposed algorithm. The database consists of some text documents written in Cyrillic, Latin and Glagolitic scripts. Furthermore, it is divided into training and test parts. The results of the experiment show that 3 out of 5 run-length features can be used for effective differentiation between the analyzed South Slavic scripts.
* 9 pages, 9 figures, In Electronics 2015, Elektronika IR Elektrotechnika, ISSN 1392-1215 (in press)
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge