Alan Inglis
Predicting Mycotoxin Contamination in Irish Oats Using Deep and Transfer Learning
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:Mycotoxin contamination poses a significant risk to cereal crop quality, food safety, and agricultural productivity. Accurate prediction of mycotoxin levels can support early intervention strategies and reduce economic losses. This study investigates the use of neural networks and transfer learning models to predict mycotoxin contamination in Irish oat crops as a multi-response prediction task. Our dataset comprises oat samples collected in Ireland, containing a mix of environmental, agronomic, and geographical predictors. Five modelling approaches were evaluated: a baseline multilayer perceptron (MLP), an MLP with pre-training, and three transfer learning models; TabPFN, TabNet, and FT-Transformer. Model performance was evaluated using regression (RMSE, $R^2$) and classification (AUC, F1) metrics, with results reported per toxin and on average. Additionally, permutation-based variable importance analysis was conducted to identify the most influential predictors across both prediction tasks. The transfer learning approach TabPFN provided the overall best performance, followed by the baseline MLP. Our variable importance analysis revealed that weather history patterns in the 90-day pre-harvest period were the most important predictors, alongside seed moisture content.
Machine Learning Applied to the Detection of Mycotoxin in Food: A Review
Apr 23, 2024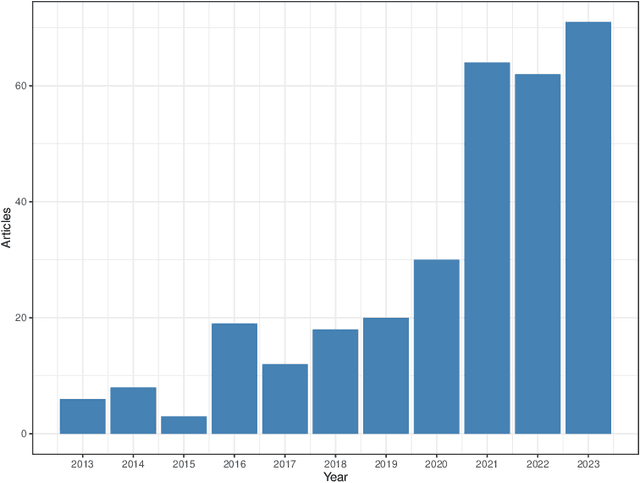
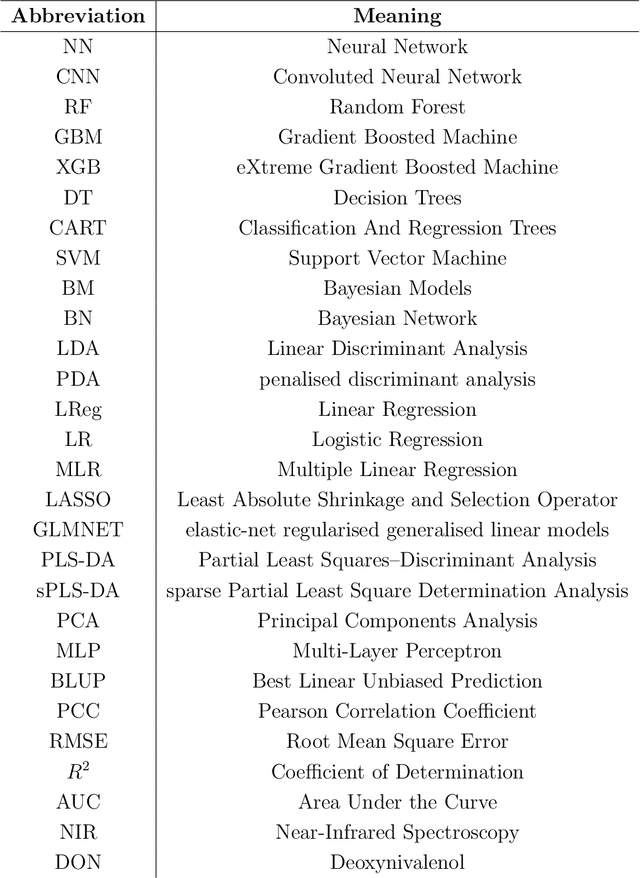
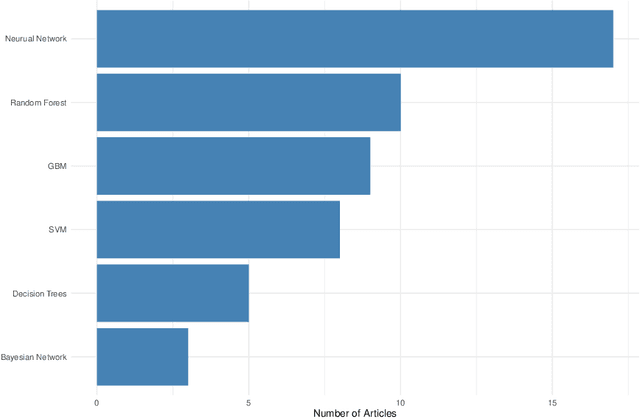
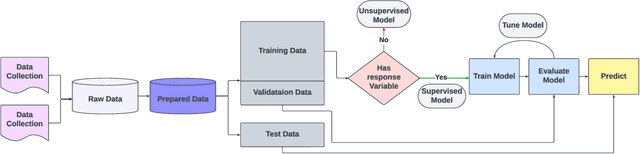
Abstract:Mycotoxins, toxic secondary metabolites produced by certain fungi, pose significant threats to global food safety and public health. These compounds can contaminate a variety of crops, leading to economic losses and health risks to both humans and animals. Traditional lab analysis methods for mycotoxin detection can be time-consuming and may not always be suitable for large-scale screenings. However, in recent years, machine learning (ML) methods have gained popularity for use in the detection of mycotoxins and in the food safety industry in general, due to their accurate and timely predictions. We provide a systematic review on some of the recent ML applications for detecting/predicting the presence of mycotoxin on a variety of food ingredients, highlighting their advantages, challenges, and potential for future advancements. We address the need for reproducibility and transparency in ML research through open access to data and code. An observation from our findings is the frequent lack of detailed reporting on hyperparameters in many studies as well as a lack of open source code, which raises concerns about the reproducibility and optimisation of the ML models used. The findings reveal that while the majority of studies predominantly utilised neural networks for mycotoxin detection, there was a notable diversity in the types of neural network architectures employed, with convolutional neural networks being the most popular.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge