Akram Bayat
Improving Performance of Object Detection using the Mechanisms of Visual Recognition in Humans
Jan 23, 2023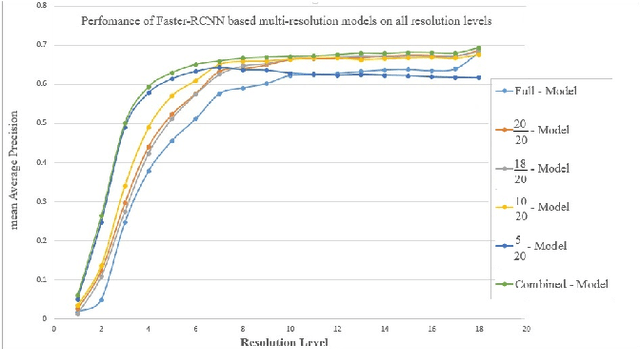
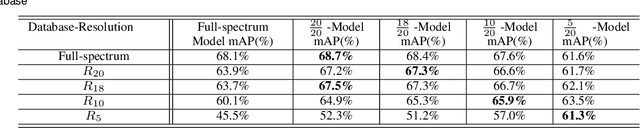

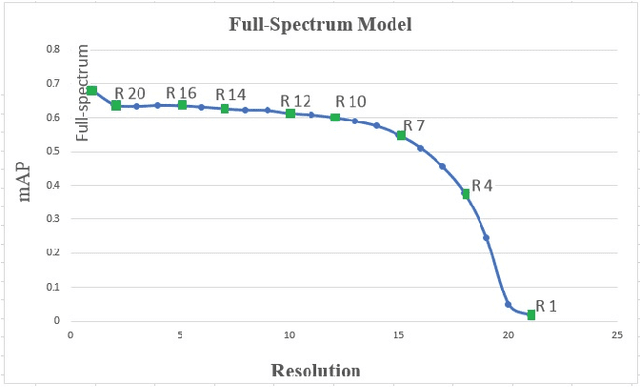
Abstract:Object recognition systems are usually trained and evaluated on high resolution images. However, in real world applications, it is common that the images have low resolutions or have small sizes. In this study, we first track the performance of the state-of-the-art deep object recognition network, Faster- RCNN, as a function of image resolution. The results reveals negative effects of low resolution images on recognition performance. They also show that different spatial frequencies convey different information about the objects in recognition process. It means multi-resolution recognition system can provides better insight into optimal selection of features that results in better recognition of objects. This is similar to the mechanisms of the human visual systems that are able to implement multi-scale representation of a visual scene simultaneously. Then, we propose a multi-resolution object recognition framework rather than a single-resolution network. The proposed framework is evaluated on the PASCAL VOC2007 database. The experimental results show the performance of our adapted multi-resolution Faster-RCNN framework outperforms the single-resolution Faster-RCNN on input images with various resolutions with an increase in the mean Average Precision (mAP) of 9.14% across all resolutions and 1.2% on the full-spectrum images. Furthermore, the proposed model yields robustness of the performance over a wide range of spatial frequencies.
Human Gait Database for Normal Walk Collected by Smart Phone Accelerometer
May 04, 2019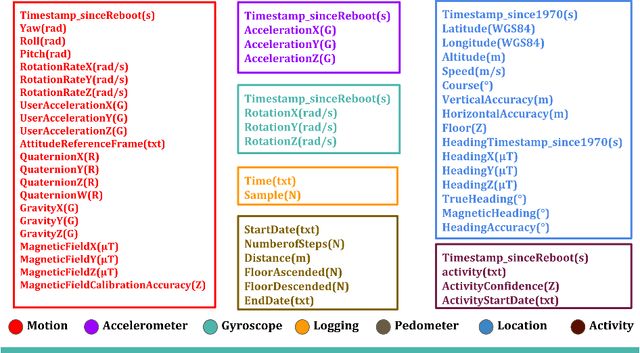
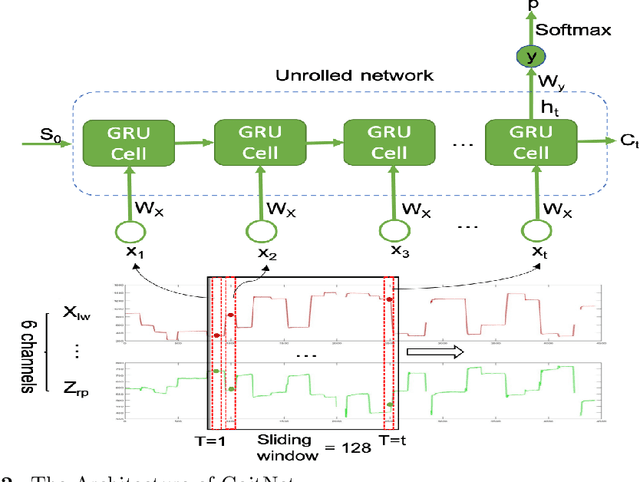
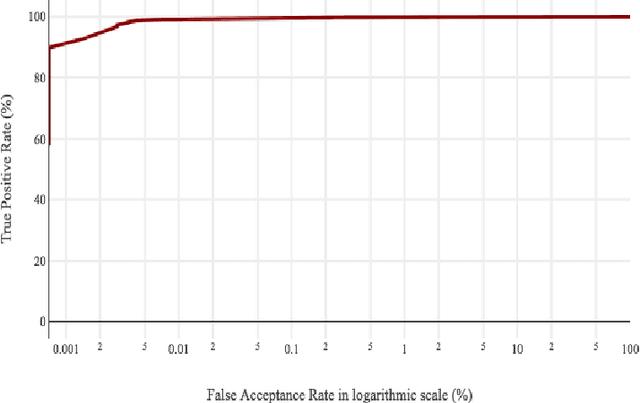
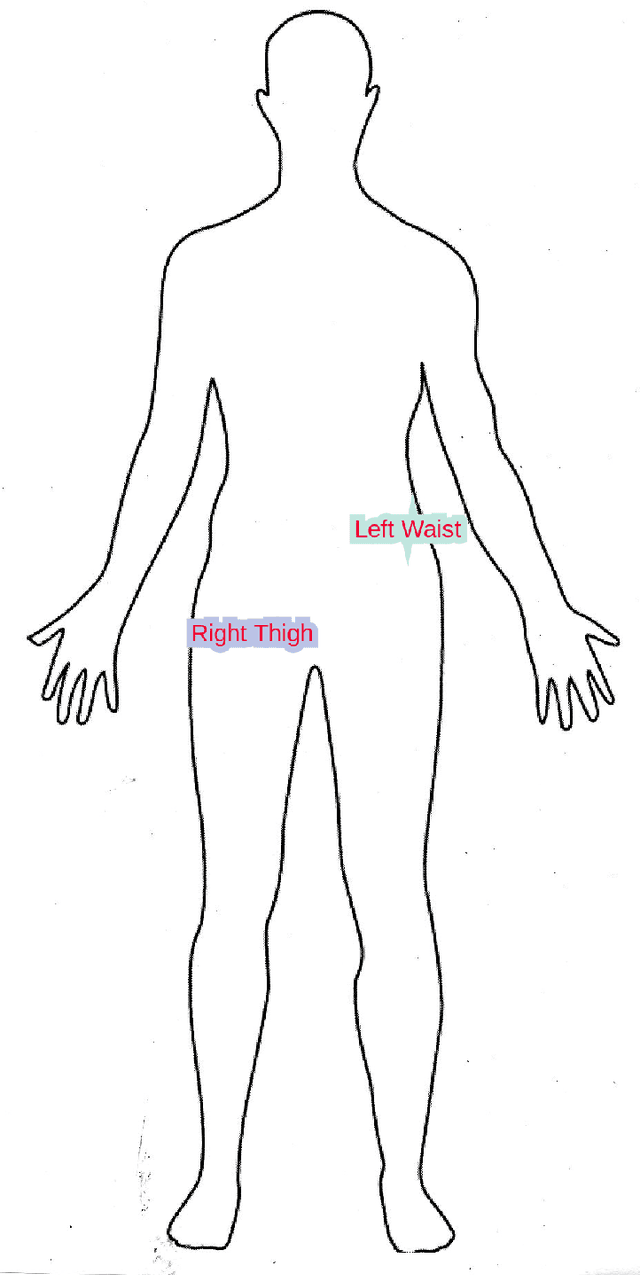
Abstract:The goal of this study is to introduce a comprehensive gait database of 93 human subjects who walked between two end points during two different sessions and record their gait data using two smart phones, one was attached to right thigh and another one on left side of waist. This data is collected with intention to be utilized by deep learning-based method which requires enough time points. The meta data including age, gender, smoking, daily exercise time, height, and weight of an individual is recorded. this data set is publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge