Akram Abderraouf Gharbi
Advancing Person Re-Identification: Tensor-based Feature Fusion and Multilinear Subspace Learning
Dec 24, 2023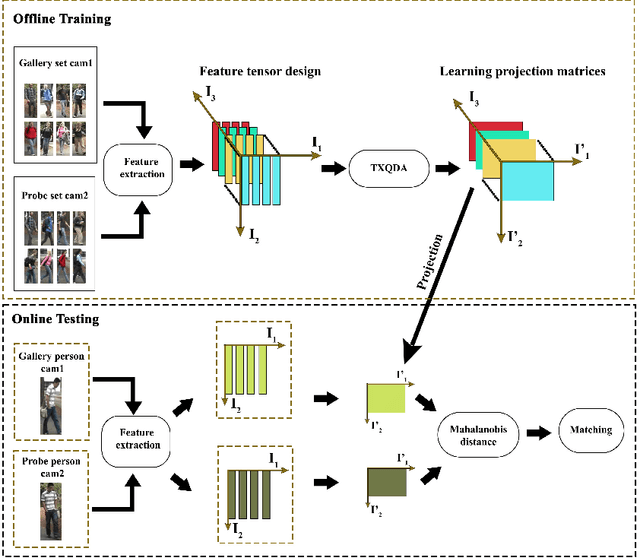
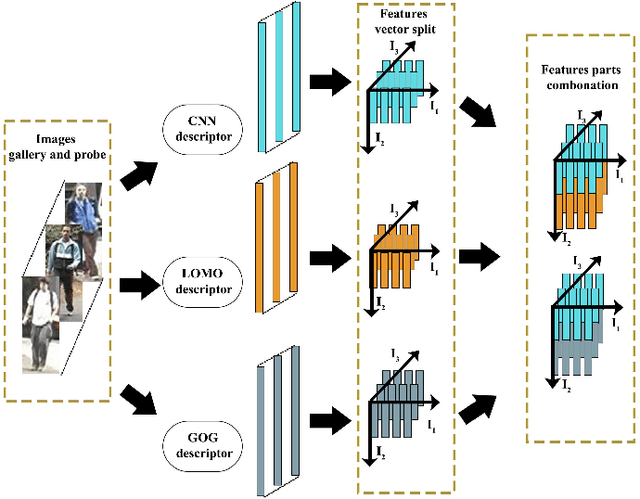
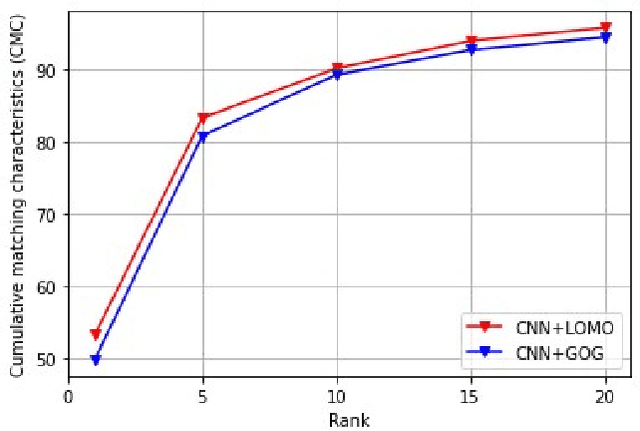
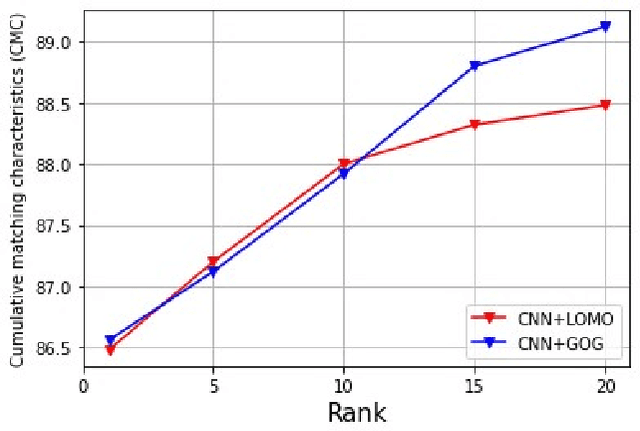
Abstract:Person re-identification (PRe-ID) is a computer vision issue, that has been a fertile research area in the last few years. It aims to identify persons across different non-overlapping camera views. In this paper, We propose a novel PRe-ID system that combines tensor feature representation and multilinear subspace learning. Our method exploits the power of pre-trained Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) as a strong deep feature extractor, along with two complementary descriptors, Local Maximal Occurrence (LOMO) and Gaussian Of Gaussian (GOG). Then, Tensor-based Cross-View Quadratic Discriminant Analysis (TXQDA) is used to learn a discriminative subspace that enhances the separability between different individuals. Mahalanobis distance is used to match and similarity computation between query and gallery samples. Finally, we evaluate our approach by conducting experiments on three datasets VIPeR, GRID, and PRID450s.
Enhancing Person Re-Identification through Tensor Feature Fusion
Dec 16, 2023Abstract:In this paper, we present a novel person reidentification (PRe-ID) system that based on tensor feature representation and multilinear subspace learning. Our approach utilizes pretrained CNNs for high-level feature extraction, along with Local Maximal Occurrence (LOMO) and Gaussian Of Gaussian (GOG ) descriptors. Additionally, Cross-View Quadratic Discriminant Analysis (TXQDA) algorithm is used for multilinear subspace learning, which models the data in a tensor framework to enhance discriminative capabilities. Similarity measure based on Mahalanobis distance is used for matching between training and test pedestrian images. Experimental evaluations on VIPeR and PRID450s datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our method.
Fusion of Deep and Shallow Features for Face Kinship Verification
Dec 16, 2023Abstract:Kinship verification from face images is a novel and formidable challenge in the realms of pattern recognition and computer vision. This work makes notable contributions by incorporating a preprocessing technique known as Multiscale Retinex (MSR), which enhances image quality. Our approach harnesses the strength of complementary deep (VGG16) and shallow texture descriptors (BSIF) by combining them at the score level using Logistic Regression (LR) technique. We assess the effectiveness of our approach by conducting comprehensive experiments on three challenging kinship datasets: Cornell Kin Face, UB Kin Face and TS Kin Face
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge