Akash Kumar Gautam
Discourse-Aware In-Context Learning for Temporal Expression Normalization
Apr 11, 2024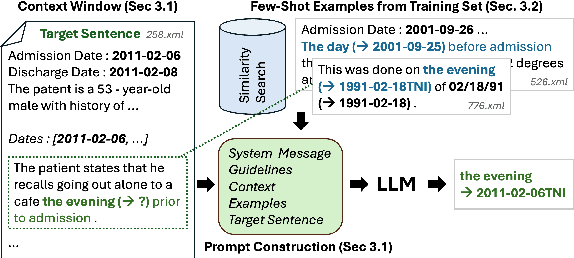



Abstract:Temporal expression (TE) normalization is a well-studied problem. However, the predominately used rule-based systems are highly restricted to specific settings, and upcoming machine learning approaches suffer from a lack of labeled data. In this work, we explore the feasibility of proprietary and open-source large language models (LLMs) for TE normalization using in-context learning to inject task, document, and example information into the model. We explore various sample selection strategies to retrieve the most relevant set of examples. By using a window-based prompt design approach, we can perform TE normalization across sentences, while leveraging the LLM knowledge without training the model. Our experiments show competitive results to models designed for this task. In particular, our method achieves large performance improvements for non-standard settings by dynamically including relevant examples during inference.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge