Ahmad Alhindi
Eating Garlic Prevents COVID-19 Infection: Detecting Misinformation on the Arabic Content of Twitter
Jan 09, 2021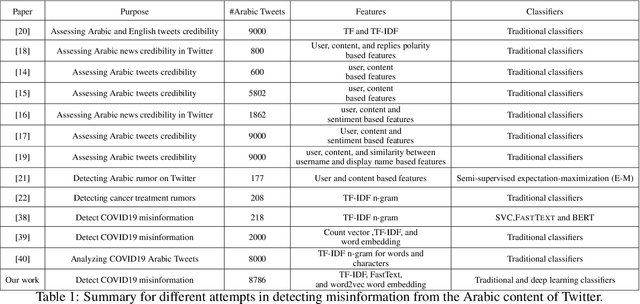
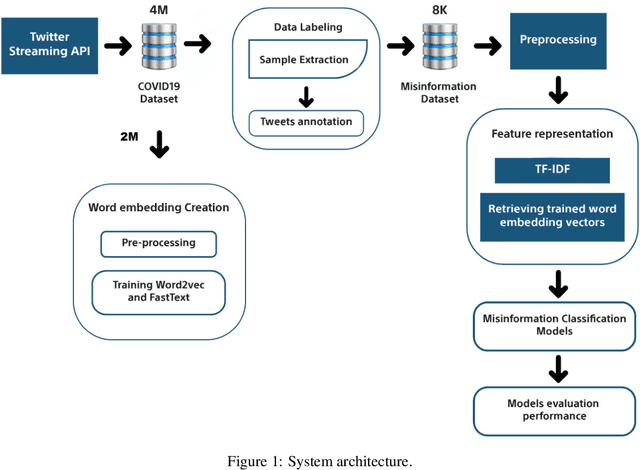

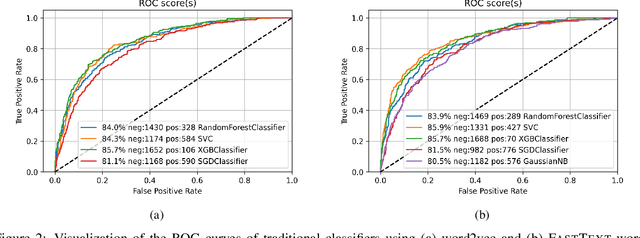
Abstract:The rapid growth of social media content during the current pandemic provides useful tools for disseminating information which has also become a root for misinformation. Therefore, there is an urgent need for fact-checking and effective techniques for detecting misinformation in social media. In this work, we study the misinformation in the Arabic content of Twitter. We construct a large Arabic dataset related to COVID-19 misinformation and gold-annotate the tweets into two categories: misinformation or not. Then, we apply eight different traditional and deep machine learning models, with different features including word embeddings and word frequency. The word embedding models (\textsc{FastText} and word2vec) exploit more than two million Arabic tweets related to COVID-19. Experiments show that optimizing the area under the curve (AUC) improves the models' performance and the Extreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost) presents the highest accuracy in detecting COVID-19 misinformation online.
Large Arabic Twitter Dataset on COVID-19
Apr 22, 2020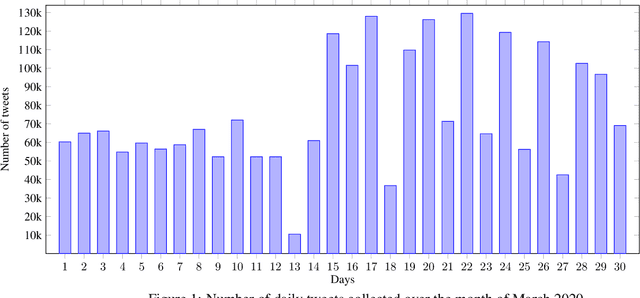

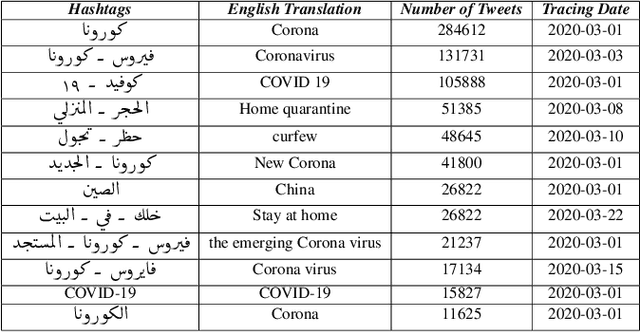

Abstract:The 2019 coronavirus disease (COVID-19), emerged late December 2019 in China, is now rapidly spreading across the globe. At the time of writing this paper, the number of global confirmed cases has passed two millions and half with over 180,000 fatalities. Many countries have enforced strict social distancing policies to contain the spread of the virus. This have changed the daily life of tens of millions of people, and urged people to turn their discussions online, e.g., via online social media sites like Twitter. In this work, we describe the first Arabic tweets dataset on COVID-19 that we have been collecting since January 1st, 2020. The dataset would help researchers and policy makers in studying different societal issues related to the pandemic. Many other tasks related to behavioral change, information sharing, misinformation and rumors spreading can also be analyzed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge