Agnieszka Mensfelt
The Influence of Human-inspired Agentic Sophistication in LLM-driven Strategic Reasoners
May 14, 2025Abstract:The rapid rise of large language models (LLMs) has shifted artificial intelligence (AI) research toward agentic systems, motivating the use of weaker and more flexible notions of agency. However, this shift raises key questions about the extent to which LLM-based agents replicate human strategic reasoning, particularly in game-theoretic settings. In this context, we examine the role of agentic sophistication in shaping artificial reasoners' performance by evaluating three agent designs: a simple game-theoretic model, an unstructured LLM-as-agent model, and an LLM integrated into a traditional agentic framework. Using guessing games as a testbed, we benchmarked these agents against human participants across general reasoning patterns and individual role-based objectives. Furthermore, we introduced obfuscated game scenarios to assess agents' ability to generalise beyond training distributions. Our analysis, covering over 2000 reasoning samples across 25 agent configurations, shows that human-inspired cognitive structures can enhance LLM agents' alignment with human strategic behaviour. Still, the relationship between agentic design complexity and human-likeness is non-linear, highlighting a critical dependence on underlying LLM capabilities and suggesting limits to simple architectural augmentation.
Approximating Human Strategic Reasoning with LLM-Enhanced Recursive Reasoners Leveraging Multi-agent Hypergames
Feb 11, 2025Abstract:LLM-driven multi-agent-based simulations have been gaining traction with applications in game-theoretic and social simulations. While most implementations seek to exploit or evaluate LLM-agentic reasoning, they often do so with a weak notion of agency and simplified architectures. We implement a role-based multi-agent strategic interaction framework tailored to sophisticated recursive reasoners, providing the means for systematic in-depth development and evaluation of strategic reasoning. Our game environment is governed by the umpire responsible for facilitating games, from matchmaking through move validation to environment management. Players incorporate state-of-the-art LLMs in their decision mechanism, relying on a formal hypergame-based model of hierarchical beliefs. We use one-shot, 2-player beauty contests to evaluate the recursive reasoning capabilities of the latest LLMs, providing a comparison to an established baseline model from economics and data from human experiments. Furthermore, we introduce the foundations of an alternative semantic measure of reasoning to the k-level theory. Our experiments show that artificial reasoners can outperform the baseline model in terms of both approximating human behaviour and reaching the optimal solution.
Autoformalizing and Simulating Game-Theoretic Scenarios using LLM-augmented Agents
Dec 11, 2024



Abstract:Game-theoretic simulations are a versatile tool for exploring interactions of both natural and artificial agents. However, modelling real-world scenarios and developing simulations often require substantial human expertise and effort. To streamline this process, we present a framework that enables the autoformalization of game-theoretic scenarios using agents augmented by large language models (LLMs). In this approach, LLM-augmented agents translate natural language scenario descriptions into executable logic programs that define the rules of each game, validating these programs for syntactic accuracy. A tournament simulation is then conducted, during which the agents test the functionality of the generated games by playing them. When a ground truth payoff matrix is available, an exact semantic validation can also be performed. The validated games can then be used in further simulations to assess the effectiveness of different strategies. We evaluate our approach on a diverse set of 55 natural language descriptions across five well-known 2x2 simultaneous-move games, demonstrating 96% syntactic and 87% semantic correctness in the generated game rules. Additionally, we assess the LLM-augmented agents' capability to autoformalize strategies for gameplay.
Logic-Enhanced Language Model Agents for Trustworthy Social Simulations
Aug 28, 2024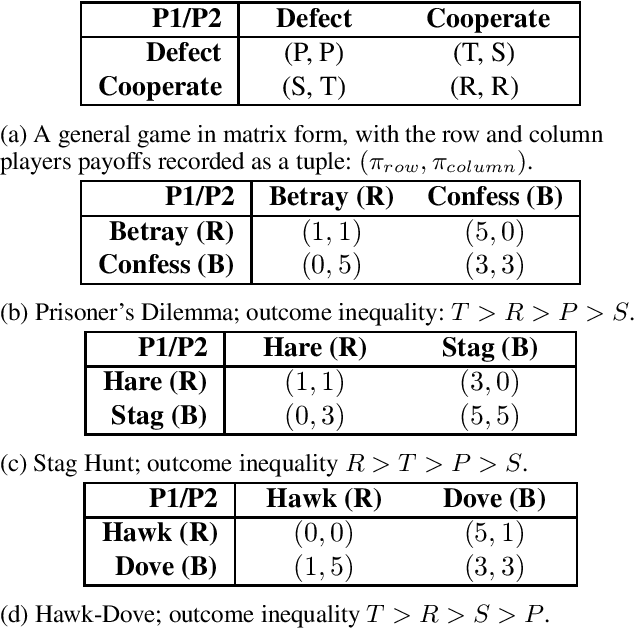


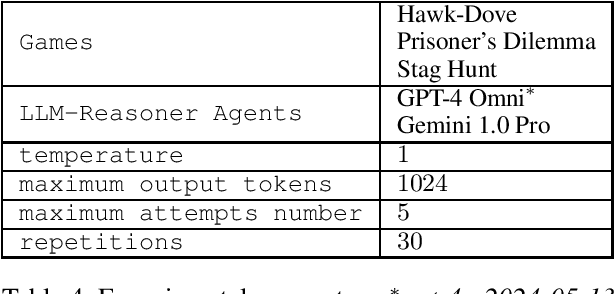
Abstract:We introduce the Logic-Enhanced Language Model Agents (LELMA) framework, a novel approach to enhance the trustworthiness of social simulations that utilize large language models (LLMs). While LLMs have gained attention as agents for simulating human behaviour, their applicability in this role is limited by issues such as inherent hallucinations and logical inconsistencies. LELMA addresses these challenges by integrating LLMs with symbolic AI, enabling logical verification of the reasoning generated by LLMs. This verification process provides corrective feedback, refining the reasoning output. The framework consists of three main components: an LLM-Reasoner for producing strategic reasoning, an LLM-Translator for mapping natural language reasoning to logic queries, and a Solver for evaluating these queries. This study focuses on decision-making in game-theoretic scenarios as a model of human interaction. Experiments involving the Hawk-Dove game, Prisoner's Dilemma, and Stag Hunt highlight the limitations of state-of-the-art LLMs, GPT-4 Omni and Gemini 1.0 Pro, in producing correct reasoning in these contexts. LELMA demonstrates high accuracy in error detection and improves the reasoning correctness of LLMs via self-refinement, particularly in GPT-4 Omni.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge