Ademola Okerinde
Self-Supervised Approach to Addressing Zero-Shot Learning Problem
Jan 21, 2022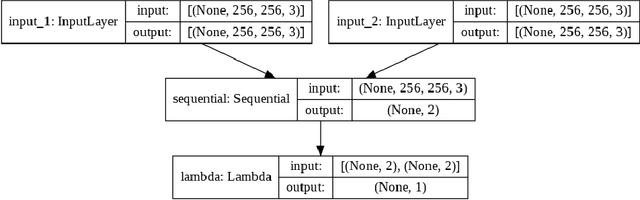
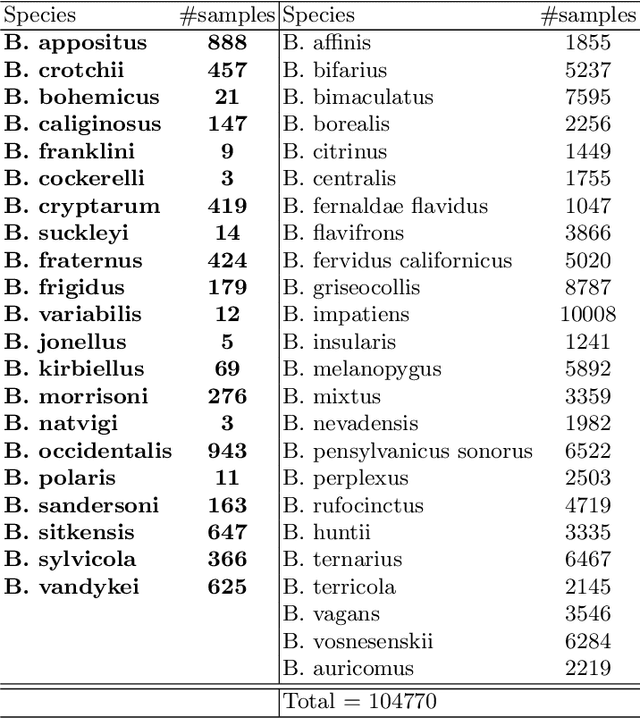
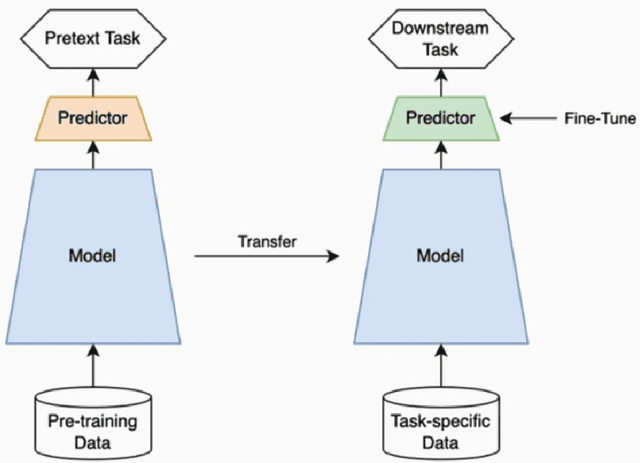
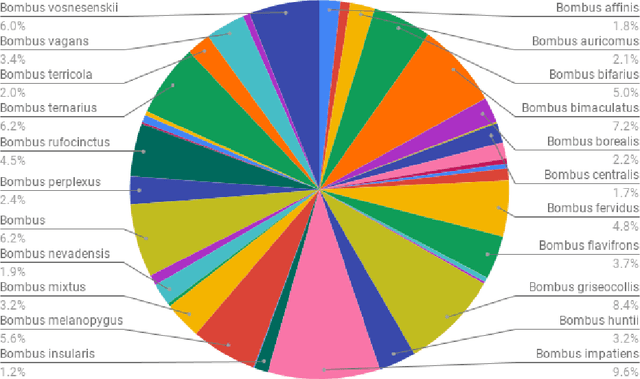
Abstract:In recent years, self-supervised learning has had significant success in applications involving computer vision and natural language processing. The type of pretext task is important to this boost in performance. One common pretext task is the measure of similarity and dissimilarity between pairs of images. In this scenario, the two images that make up the negative pair are visibly different to humans. However, in entomology, species are nearly indistinguishable and thus hard to differentiate. In this study, we explored the performance of a Siamese neural network using contrastive loss by learning to push apart embeddings of bumblebee species pair that are dissimilar, and pull together similar embeddings. Our experimental results show a 61% F1-score on zero-shot instances, a performance showing 11% improvement on samples of classes that share intersections with the training set.
eGAN: Unsupervised approach to class imbalance using transfer learning
Apr 09, 2021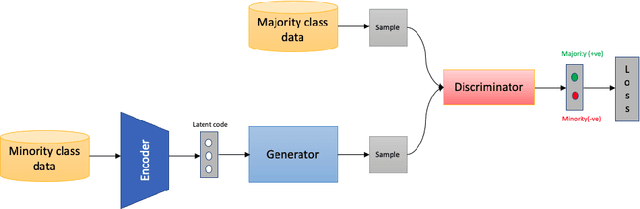


Abstract:Class imbalance is an inherent problem in many machine learning classification tasks. This often leads to trained models that are unusable for any practical purpose. In this study we explore an unsupervised approach to address these imbalances by leveraging transfer learning from pre-trained image classification models to encoder-based Generative Adversarial Network (eGAN). To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work to tackle this problem using GAN without needing to augment with synthesized fake images. In the proposed approach we use the discriminator network to output a negative or positive score. We classify as minority, test samples with negative scores and as majority those with positive scores. Our approach eliminates epistemic uncertainty in model predictions, as the P(minority) + P(majority) need not sum up to 1. The impact of transfer learning and combinations of different pre-trained image classification models at the generator and discriminator is also explored. Best result of 0.69 F1-score was obtained on CIFAR-10 classification task with imbalance ratio of 1:2500. Our approach also provides a mechanism of thresholding the specificity or sensitivity of our machine learning system. Keywords: Class imbalance, Transfer Learning, GAN, nash equilibrium
AdeNet: Deep learning architecture that identifies damaged electrical insulators in power lines
Mar 02, 2021
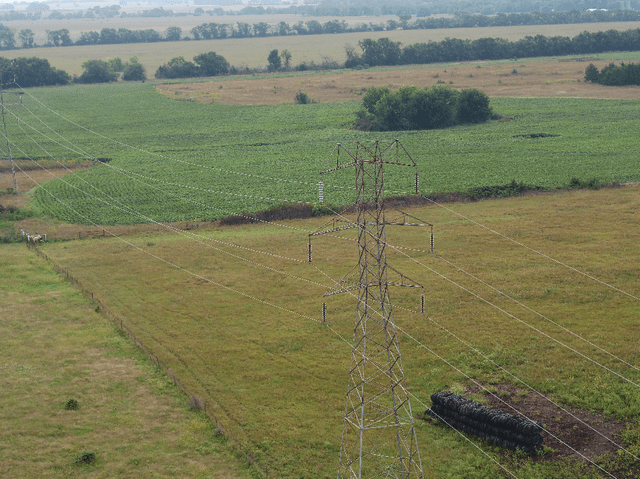



Abstract:Ceramic insulators are important to electronic systems, designed and installed to protect humans from the danger of high voltage electric current. However, insulators are not immortal, and natural deterioration can gradually damage them. Therefore, the condition of insulators must be continually monitored, which is normally done using UAVs. UAVs collect many images of insulators, and these images are then analyzed to identify those that are damaged. Here we describe AdeNet as a deep neural network designed to identify damaged insulators, and test multiple approaches to automatic analysis of the condition of insulators. Several deep neural networks were tested, as were shallow learning methods. The best results (88.8\%) were achieved using AdeNet without transfer learning. AdeNet also reduced the false negative rate to $\sim$7\%. While the method cannot fully replace human inspection, its high throughput can reduce the amount of labor required to monitor lines for damaged insulators and provide early warning to replace damaged insulators.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge