Aaron Key
Maximum Mean Discrepancy for Generalization in the Presence of Distribution and Missingness Shift
Nov 19, 2021



Abstract:Covariate shifts are a common problem in predictive modeling on real-world problems. This paper proposes addressing the covariate shift problem by minimizing Maximum Mean Discrepancy (MMD) statistics between the training and test sets in either feature input space, feature representation space, or both. We designed three techniques that we call MMD Representation, MMD Mask, and MMD Hybrid to deal with the scenarios where only a distribution shift exists, only a missingness shift exists, or both types of shift exist, respectively. We find that integrating an MMD loss component helps models use the best features for generalization and avoid dangerous extrapolation as much as possible for each test sample. Models treated with this MMD approach show better performance, calibration, and extrapolation on the test set.
Estimation of Corporate Greenhouse Gas Emissions via Machine Learning
Sep 09, 2021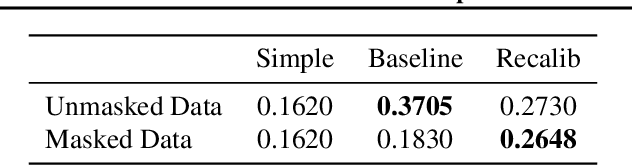
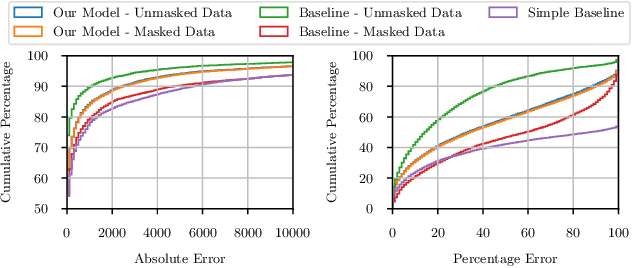
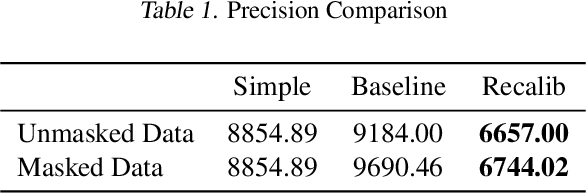

Abstract:As an important step to fulfill the Paris Agreement and achieve net-zero emissions by 2050, the European Commission adopted the most ambitious package of climate impact measures in April 2021 to improve the flow of capital towards sustainable activities. For these and other international measures to be successful, reliable data is key. The ability to see the carbon footprint of companies around the world will be critical for investors to comply with the measures. However, with only a small portion of companies volunteering to disclose their greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, it is nearly impossible for investors to align their investment strategies with the measures. By training a machine learning model on disclosed GHG emissions, we are able to estimate the emissions of other companies globally who do not disclose their emissions. In this paper, we show that our model provides accurate estimates of corporate GHG emissions to investors such that they are able to align their investments with the regulatory measures and achieve net-zero goals.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge