ZoDIAC: Zoneout Dropout Injection Attention Calculation
Paper and Code
Jun 28, 2022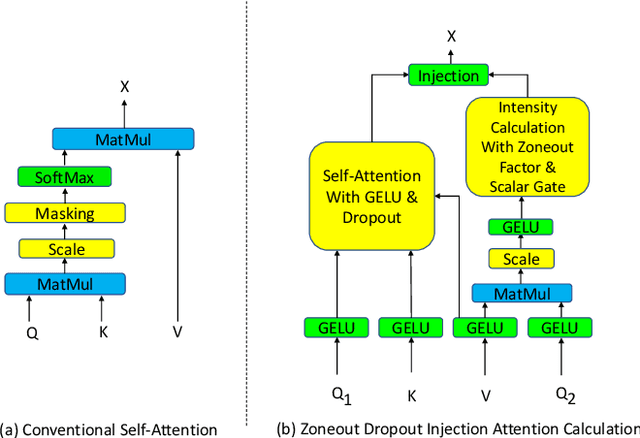
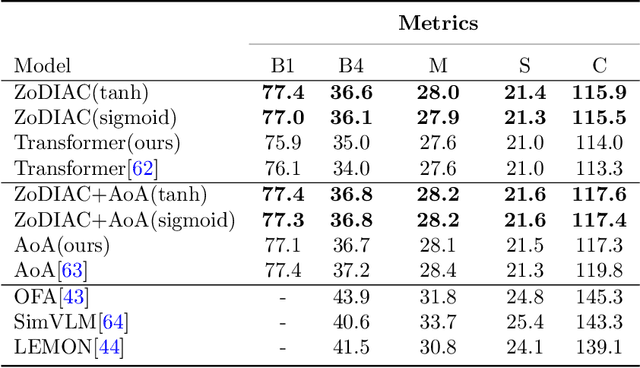
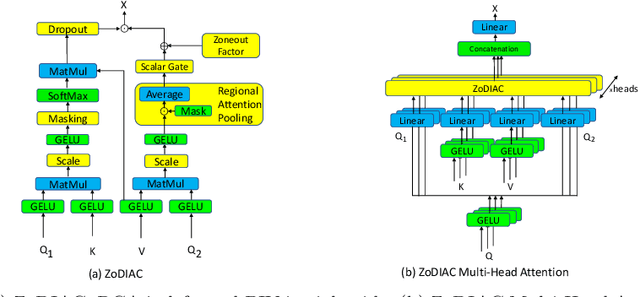
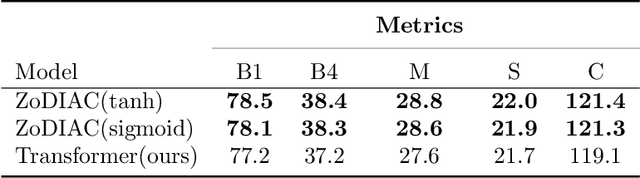
Recently the use of self-attention has yielded to state-of-the-art results in vision-language tasks such as image captioning as well as natural language understanding and generation (NLU and NLG) tasks and computer vision tasks such as image classification. This is since self-attention maps the internal interactions among the elements of input source and target sequences. Although self-attention successfully calculates the attention values and maps the relationships among the elements of input source and target sequence, yet there is no mechanism to control the intensity of attention. In real world, when communicating with each other face to face or vocally, we tend to express different visual and linguistic context with various amounts of intensity. Some words might carry (be spoken with) more stress and weight indicating the importance of that word in the context of the whole sentence. Based on this intuition, we propose Zoneout Dropout Injection Attention Calculation (ZoDIAC) in which the intensities of attention values in the elements of the input sequence are calculated with respect to the context of the elements of input sequence. The results of our experiments reveal that employing ZoDIAC leads to better performance in comparison with the self-attention module in the Transformer model. The ultimate goal is to find out if we could modify self-attention module in the Transformer model with a method that is potentially extensible to other models that leverage on self-attention at their core. Our findings suggest that this particular goal deserves further attention and investigation by the research community. The code for ZoDIAC is available on www.github.com/zanyarz/zodiac .
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge