Zero Shot Learning for Predicting Energy Usage of Buildings in Sustainable Design
Paper and Code
Feb 10, 2022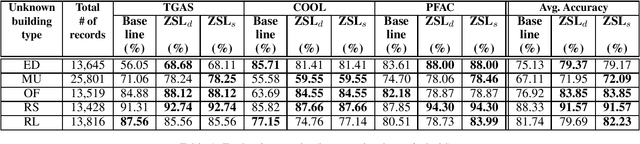
The 2030 Challenge is aimed at making all new buildings and major renovations carbon neutral by 2030. One of the potential solutions to meet this challenge is through innovative sustainable design strategies. For developing such strategies it is important to understand how the various building factors contribute to energy usage of a building, right at design time. The growth of artificial intelligence (AI) in recent years provides an unprecedented opportunity to advance sustainable design by learning complex relationships between building factors from available data. However, rich training datasets are needed for AI-based solutions to achieve good prediction accuracy. Unfortunately, obtaining training datasets are time consuming and expensive in many real-world applications. Motivated by these reasons, we address the problem of accurately predicting the energy usage of new or unknown building types, i.e., those building types that do not have any training data. We propose a novel approach based on zero-shot learning (ZSL) to solve this problem. Our approach uses side information from building energy modeling experts to predict the closest building types for a given new/unknown building type. We then obtain the predicted energy usage for the k-closest building types using the models learned during training and combine the predicted values using a weighted averaging function. We evaluated our approach on a dataset containing five building types generated using BuildSimHub, a popular platform for building energy modeling. Our approach achieved better average accuracy than a regression model (based on XGBoost) trained on the entire dataset of known building types.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge