Wind Flow Estimation in Thermal Sky Images for Sun Occlusion Prediction
Paper and Code
Mar 03, 2021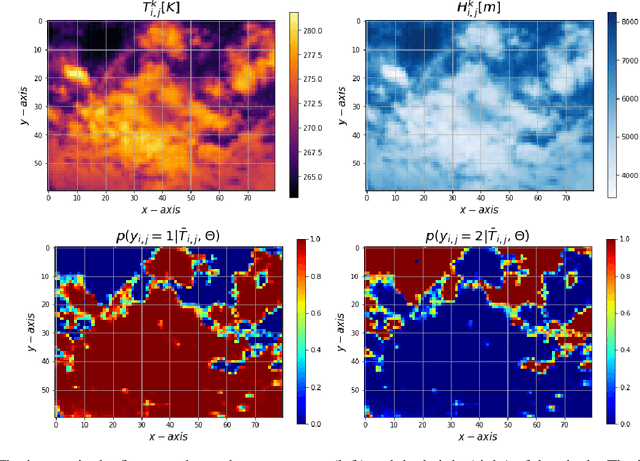
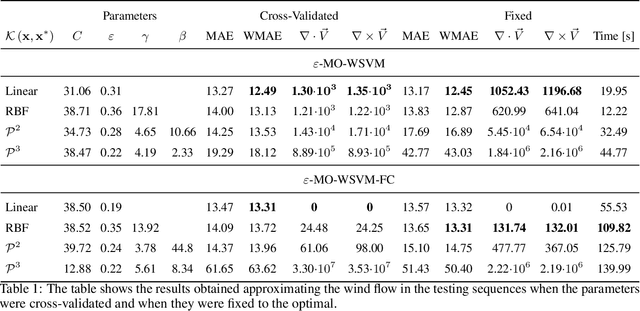
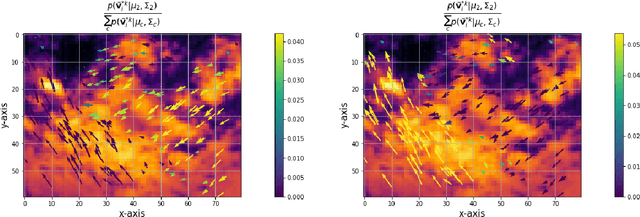

Moving clouds affect the global solar irradiance that reaches the surface of the Earth. As a consequence, the amount of resources available to meet the energy demand in a smart grid powered using Photovoltaic (PV) systems depends on the shadows projected by passing clouds. This research introduces an algorithm for tracking clouds to predict Sun occlusion. Using thermal images of clouds, the algorithm is capable of estimating multiple wind velocity fields with different altitudes, velocity magnitudes and directions.
* arXiv admin note: text overlap with arXiv:2012.02861
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge