What Color Scheme is More Effective in Assisting Readers to Locate Information in a Color-Coded Article?
Paper and Code
Aug 12, 2024
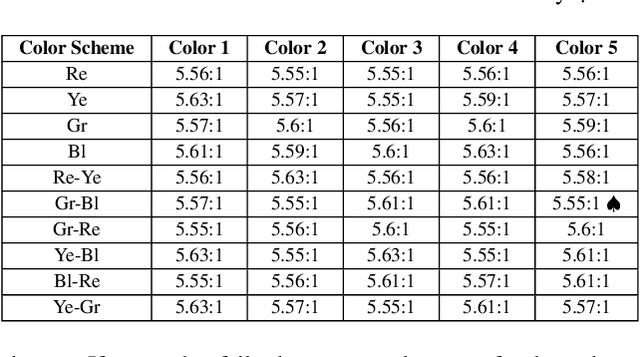
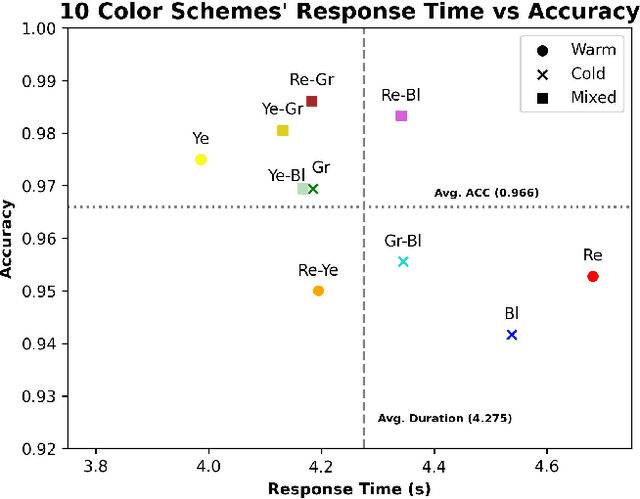
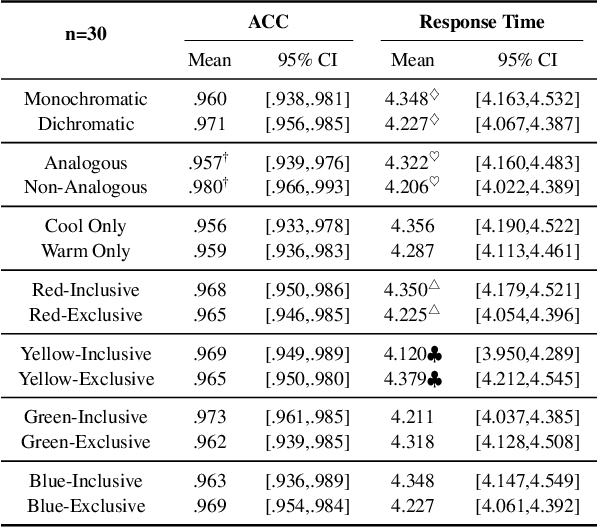
Color coding, a technique assigning specific colors to cluster information types, has proven advantages in aiding human cognitive activities, especially reading and comprehension. The rise of Large Language Models (LLMs) has streamlined document coding, enabling simple automatic text labeling with various schemes. This has the potential to make color-coding more accessible and benefit more users. However, the impact of color choice on information seeking is understudied. We conducted a user study assessing various color schemes' effectiveness in LLM-coded text documents, standardizing contrast ratios to approximately 5.55:1 across schemes. Participants performed timed information-seeking tasks in color-coded scholarly abstracts. Results showed non-analogous and yellow-inclusive color schemes improved performance, with the latter also being more preferred by participants. These findings can inform better color scheme choices for text annotation. As LLMs advance document coding, we advocate for more research focusing on the "color" aspect of color-coding techniques.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge