What and How Well You Performed? A Multitask Learning Approach to Action Quality Assessment
Paper and Code
Apr 08, 2019

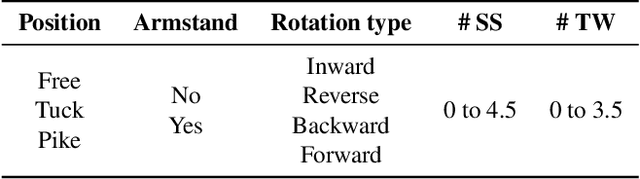

Can performance on the task of action quality assessment (AQA) be improved by exploiting a description of the action and its quality? Current AQA and skills assessment approaches propose to learn features that serve only one task - estimating the final score. In this paper, we propose to learn spatio-temporal features that explain three related tasks - fine-grained action recognition, commentary generation, and estimating the AQA score. A new multitask-AQA dataset, the largest to date, comprising of 1412 diving samples was collected to evaluate our approach (http://rtis.oit.unlv.edu/datasets.html). We show that our MTL approach outperforms STL approach using two different kinds of architectures: C3D-AVG and MSCADC. The C3D-AVG-MTL approach achieves the new state-of-the-art performance with a rank correlation of 90.44%. Detailed experiments were performed to show that MTL offers better generalization than STL, and representations from action recognition models are not sufficient for the AQA task and instead should be learned.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge