Weakly-supervised diagnosis identification from Italian discharge letters
Paper and Code
Oct 19, 2024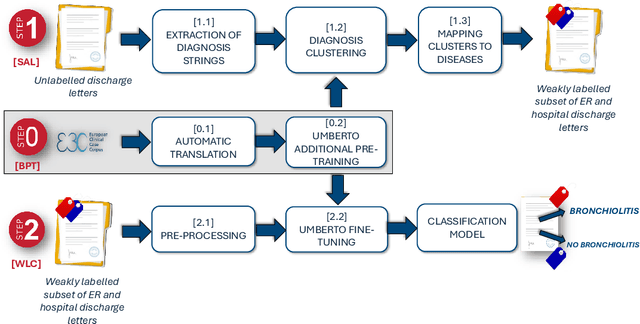
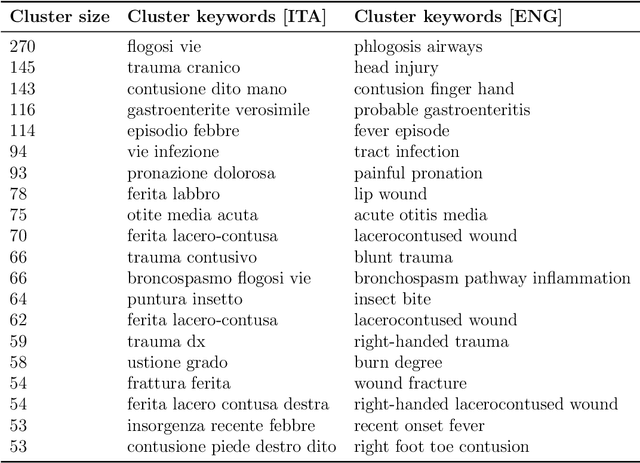
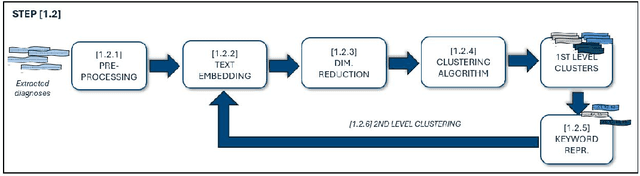

Objective: Recognizing diseases from discharge letters is crucial for cohort selection and epidemiological analyses, as this is the only type of data consistently produced across hospitals. This is a classic document classification problem, typically requiring supervised learning. However, manual annotation of large datasets of discharge letters is uncommon since it is extremely time-consuming. We propose a novel weakly-supervised pipeline to recognize diseases from Italian discharge letters. Methods: Our Natural Language Processing pipeline is based on a fine-tuned version of the Italian Umberto model. The pipeline extracts diagnosis-related sentences from a subset of letters and applies a two-level clustering using the embeddings generated by the fine-tuned Umberto model. These clusters are summarized and those mapped to the diseases of interest are selected as weak labels. Finally, the same BERT-based model is trained using these weak labels to detect the targeted diseases. Results: A case study related to the identification of bronchiolitis with 33'176 Italian discharge letters from 44 hospitals in the Veneto Region shows the potential of our method, with an AUC of 77.7 % and an F1-Score of 75.1 % on manually annotated labels, improving compared to other non-supervised methods and with a limited loss compared to fully supervised methods. Results are robust to the cluster selection and the identified clusters highlight the potential to recognize a variety of diseases. Conclusions: This study demonstrates the feasibility of diagnosis identification from Italian discharge letters in the absence of labelled data. Our pipeline showed strong performance and robustness, and its flexibility allows for easy adaptation to various diseases. This approach offers a scalable solution for clinical text classification, reducing the need for manual annotation while maintaining good accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge