Voice Cloning: a Multi-Speaker Text-to-Speech Synthesis Approach based on Transfer Learning
Paper and Code
Feb 10, 2021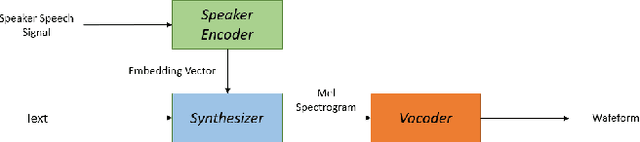
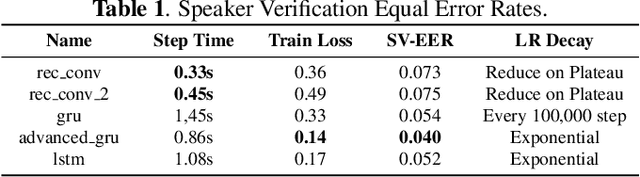
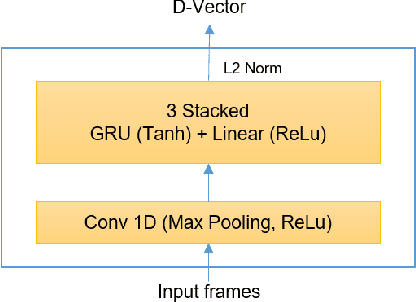
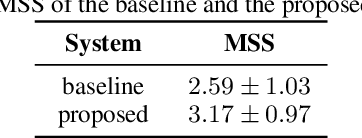
Deep learning models are becoming predominant in many fields of machine learning. Text-to-Speech (TTS), the process of synthesizing artificial speech from text, is no exception. To this end, a deep neural network is usually trained using a corpus of several hours of recorded speech from a single speaker. Trying to produce the voice of a speaker other than the one learned is expensive and requires large effort since it is necessary to record a new dataset and retrain the model. This is the main reason why the TTS models are usually single speaker. The proposed approach has the goal to overcome these limitations trying to obtain a system which is able to model a multi-speaker acoustic space. This allows the generation of speech audio similar to the voice of different target speakers, even if they were not observed during the training phase.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge