Utilizing Ensemble Learning for Performance and Power Modeling and Improvement of Parallel Cancer Deep Learning CANDLE Benchmarks
Paper and Code
Nov 12, 2020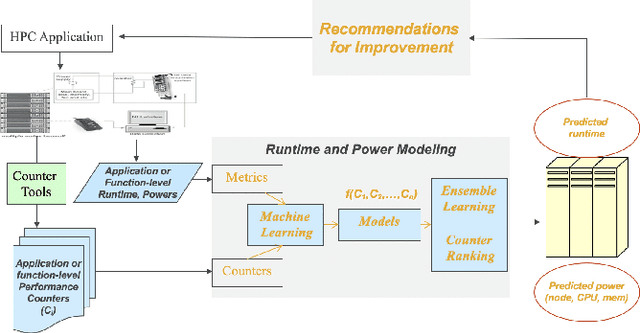
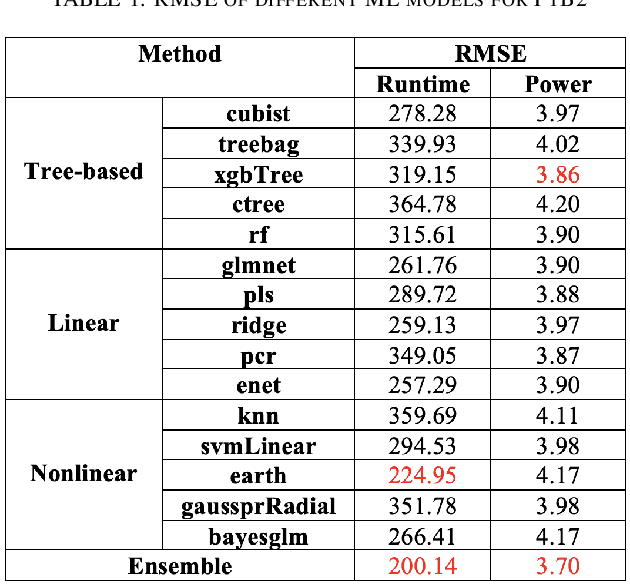
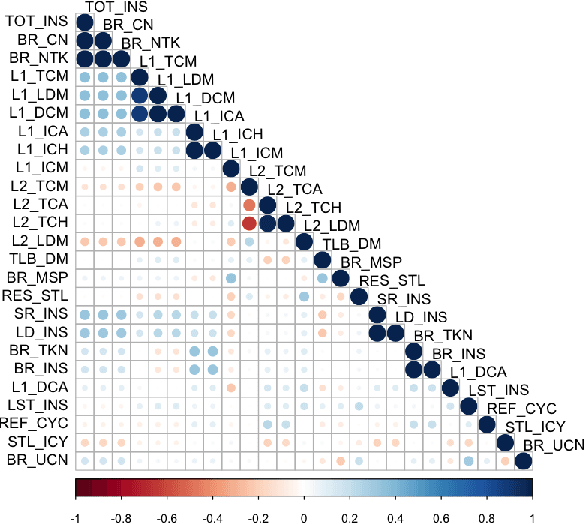
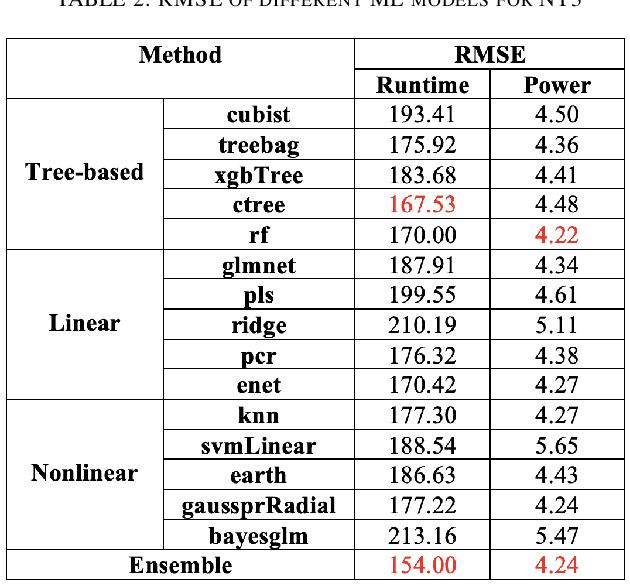
Machine learning (ML) continues to grow in importance across nearly all domains and is a natural tool in modeling to learn from data. Often a tradeoff exists between a model's ability to minimize bias and variance. In this paper, we utilize ensemble learning to combine linear, nonlinear, and tree-/rule-based ML methods to cope with the bias-variance tradeoff and result in more accurate models. Hardware performance counter values are correlated with properties of applications that impact performance and power on the underlying system. We use the datasets collected for two parallel cancer deep learning CANDLE benchmarks, NT3 (weak scaling) and P1B2 (strong scaling), to build performance and power models based on hardware performance counters using single-object and multiple-objects ensemble learning to identify the most important counters for improvement. Based on the insights from these models, we improve the performance and energy of P1B2 and NT3 by optimizing the deep learning environments TensorFlow, Keras, Horovod, and Python under the huge page size of 8 MB on the Cray XC40 Theta at Argonne National Laboratory. Experimental results show that ensemble learning not only produces more accurate models but also provides more robust performance counter ranking. We achieve up to 61.15% performance improvement and up to 62.58% energy saving for P1B2 and up to 55.81% performance improvement and up to 52.60% energy saving for NT3 on up to 24,576 cores.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge