User Ex Machina : Simulation as a Design Probe in Human-in-the-Loop Text Analytics
Paper and Code
Jan 06, 2021
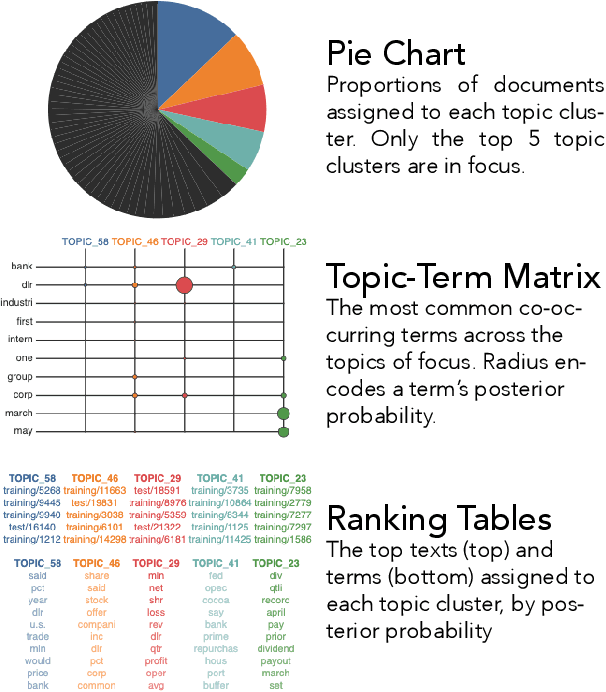
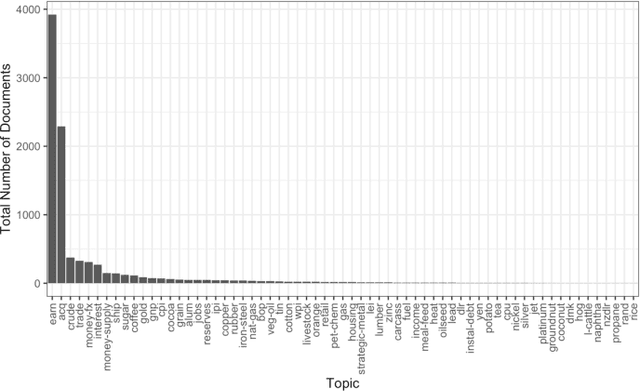
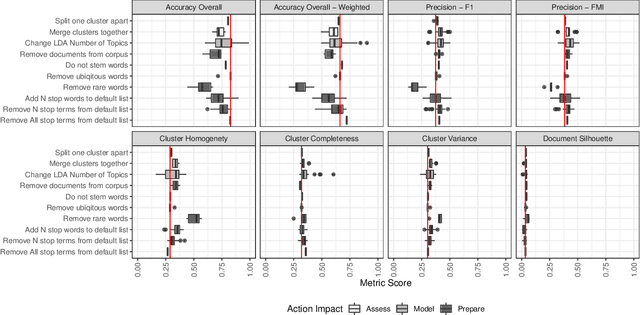
Topic models are widely used analysis techniques for clustering documents and surfacing thematic elements of text corpora. These models remain challenging to optimize and often require a "human-in-the-loop" approach where domain experts use their knowledge to steer and adjust. However, the fragility, incompleteness, and opacity of these models means even minor changes could induce large and potentially undesirable changes in resulting model. In this paper we conduct a simulation-based analysis of human-centered interactions with topic models, with the objective of measuring the sensitivity of topic models to common classes of user actions. We find that user interactions have impacts that differ in magnitude but often negatively affect the quality of the resulting modelling in a way that can be difficult for the user to evaluate. We suggest the incorporation of sensitivity and "multiverse" analyses to topic model interfaces to surface and overcome these deficiencies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge