Unsupervised Segmentation Algorithms for Infrared Cloud Images
Paper and Code
Mar 03, 2021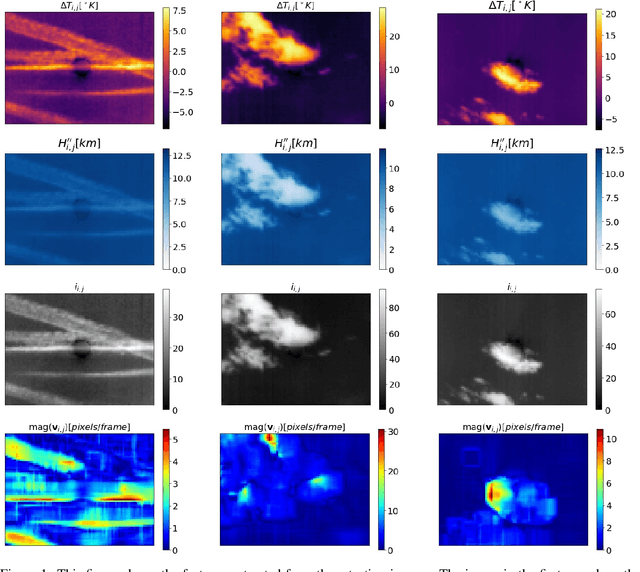
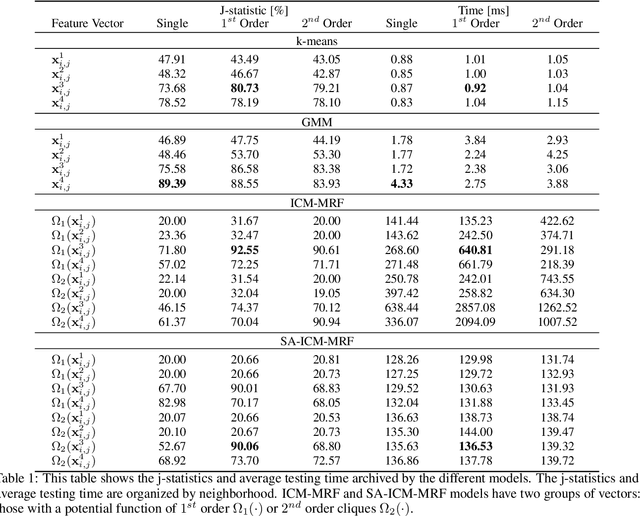

The increasing number of Photovoltaic (PV) systems connected to the power grids makes them vulnerable to the projection of shadows from moving clouds. Solar Global Irradiance (GSI) forecasting allows smart grids to optimize energy dispatch preventing cloud coverage shortages. This investigation compares the performances of unsupervised learning algorithms (not requiring labelled images for training) for real-time segmentation of clouds in a ground-base infrared sky-imaging system, which is commonly used to extract cloud features using only the pixels where clouds are detected.
* arXiv admin note: substantial text overlap with arXiv:2012.06930
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge