Unsupervised classification of the spectrogram zeros
Paper and Code
Oct 11, 2022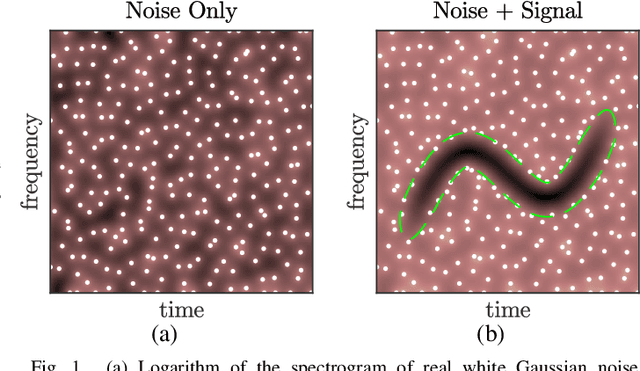
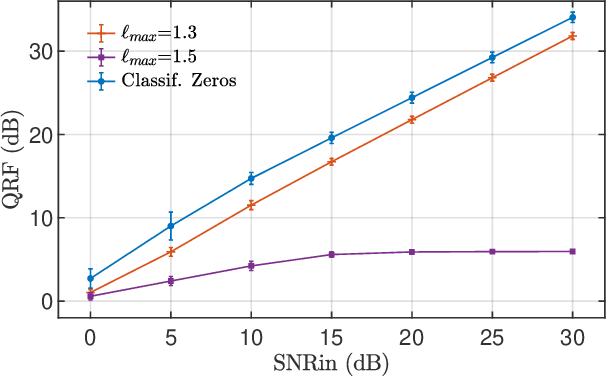
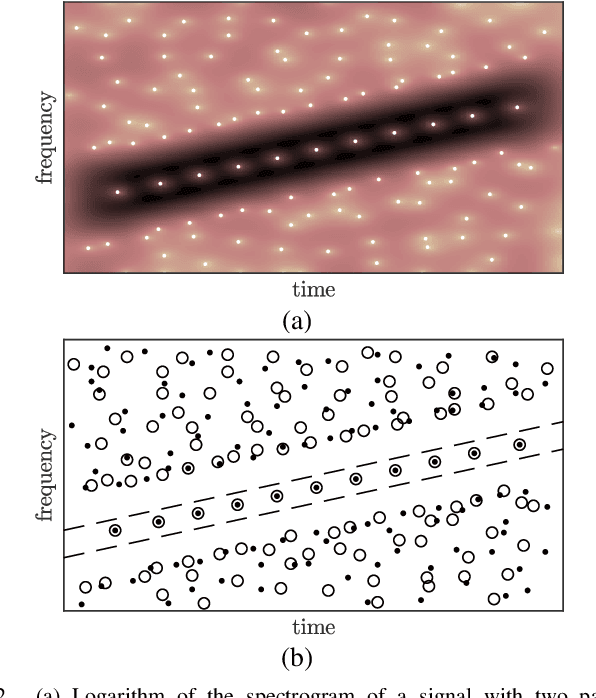

The zeros of the spectrogram have proven to be a relevant feature to describe the time-frequency structure of a signal, originated by the destructive interference between components in the time-frequency plane. In this work, a classification of these zeros in three types is introduced, based on the nature of the components that interfere to produce them. Echoing noise-assisted methods, a classification algorithm is proposed based on the addition of independent noise realizations to build a 2D histogram describing the stability of zeros. Features extracted from this histogram are later used to classify the zeros using a non-supervised clusterization algorithm. A denoising approach based on the classification of the spectrogram zeros is also introduced. Examples of the classification of zeros are given for synthetic and real signals, as well as a performance comparison of the proposed denoising algorithm with another zero-based approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge