Underwater Acoustic Target Recognition based on Smoothness-inducing Regularization and Spectrogram-based Data Augmentation
Paper and Code
Jun 12, 2023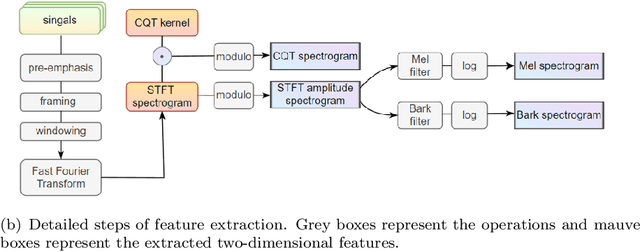
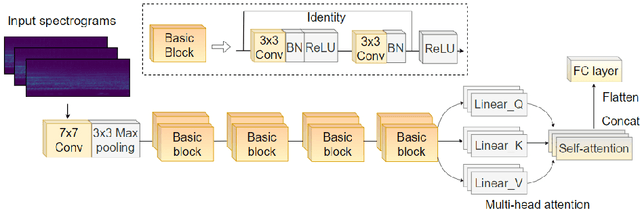

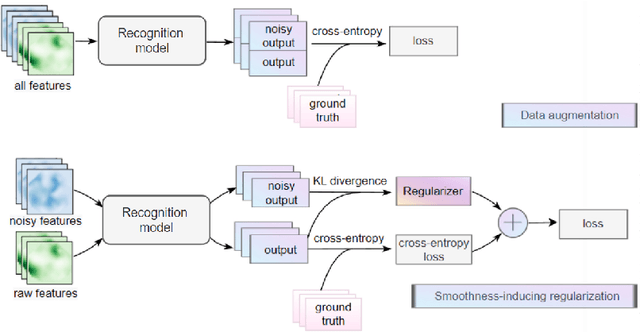
Underwater acoustic target recognition is a challenging task owing to the intricate underwater environments and limited data availability. Insufficient data can hinder the ability of recognition systems to support complex modeling, thus impeding their advancement. To improve the generalization capacity of recognition models, techniques such as data augmentation have been employed to simulate underwater signals and diversify data distribution. However, the complexity of underwater environments can cause the simulated signals to deviate from real scenarios, resulting in biased models that are misguided by non-true data. In this study, we propose two strategies to enhance the generalization ability of models in the case of limited data while avoiding the risk of performance degradation. First, as an alternative to traditional data augmentation, we utilize smoothness-inducing regularization, which only incorporates simulated signals in the regularization term. Additionally, we propose a specialized spectrogram-based data augmentation strategy, namely local masking and replicating (LMR), to capture inter-class relationships. Our experiments and visualization analysis demonstrate the superiority of our proposed strategies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge