Uncertainty Quantification and Propagation for Airline Disruption Management
Paper and Code
Feb 09, 2021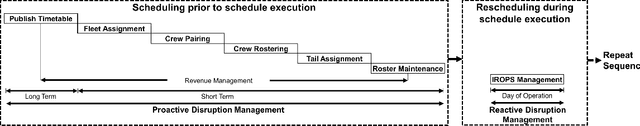
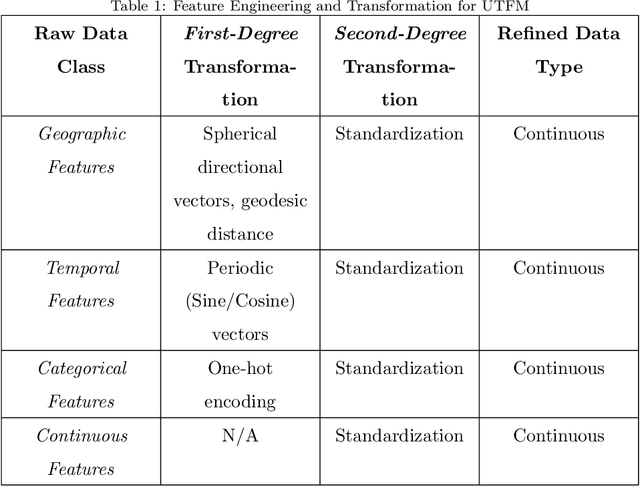
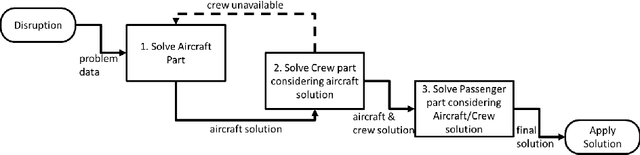
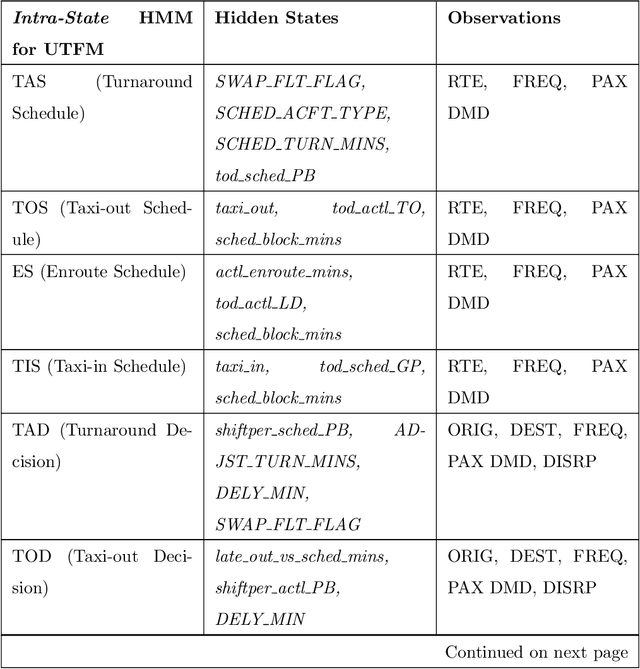
Disruption management during the airline scheduling process can be compartmentalized into proactive and reactive processes depending upon the time of schedule execution. The state of the art for decision-making in airline disruption management involves a heuristic human-centric approach that does not categorically study uncertainty in proactive and reactive processes for managing airline schedule disruptions. Hence, this paper introduces an uncertainty transfer function model (UTFM) framework that characterizes uncertainty for proactive airline disruption management before schedule execution, reactive airline disruption management during schedule execution, and proactive airline disruption management after schedule execution to enable the construction of quantitative tools that can allow an intelligent agent to rationalize complex interactions and procedures for robust airline disruption management. Specifically, we use historical scheduling and operations data from a major U.S. airline to facilitate the development and assessment of the UTFM, defined by hidden Markov models (a special class of probabilistic graphical models) that can efficiently perform pattern learning and inference on portions of large data sets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge