Uncertainty in Position Estimation Using Machine Learning
Paper and Code
Jun 04, 2021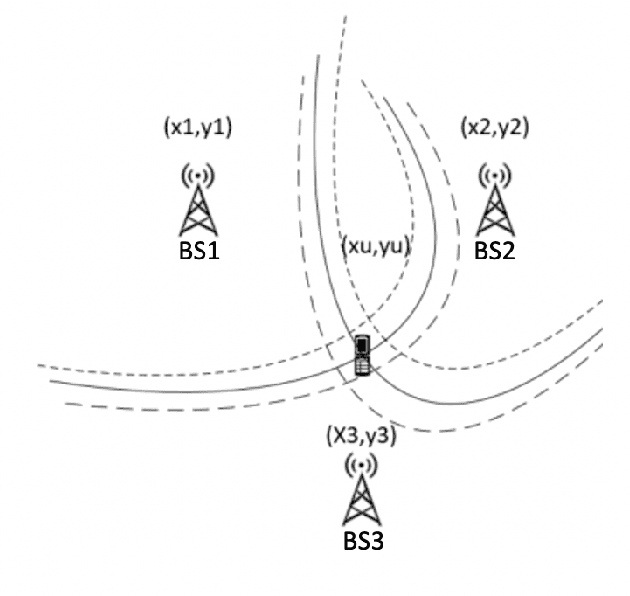
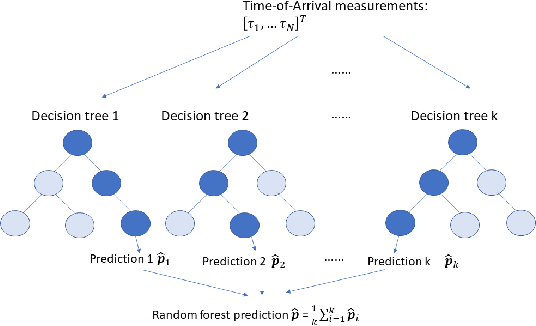
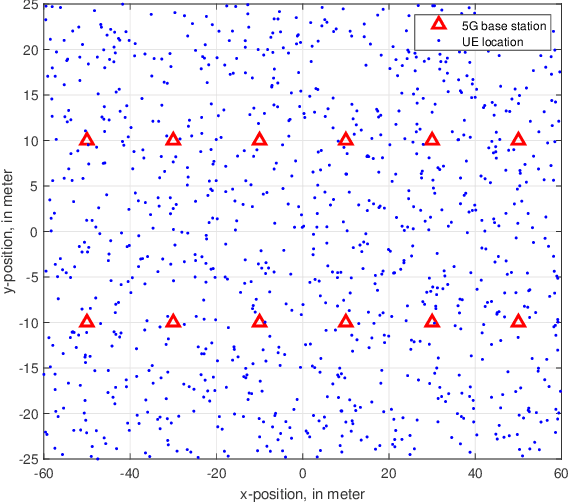
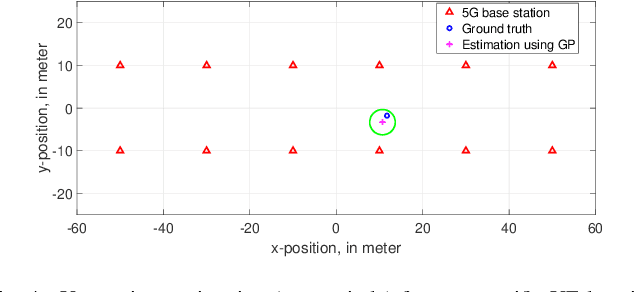
UE localization has proven its implications on multitude of use cases ranging from emergency call localization to new and emerging use cases in industrial IoT. To support plethora of use cases Radio Access Technology (RAT)-based positioning has been supported by 3GPP since Release 9 of its specifications that featured basic positioning methods based on Cell Identity (CID) and Enhanced-CID (E-CID). Since then, multiple positioning techniques and solutions are proposed and integrated in to the 3GPP specifications. When it comes to evaluating performance of the positioning techniques, achievable accuracy (2-Dimensional or 3-Dimensional) has, so far, been the primary metric. With the advent of Release 16 New Radio (NR) positioning, it is possible to configure Positioning Reference Signal (PRS) with wide bandwidth that naturally helps improving the positioning accuracy. However, the improvement is evident when the conditions are ideal for positioning. In practice where the conditions are non-ideal and the positioning accuracy is severely impacted, estimating the uncertainty in position estimation becomes important and can provide significant insight on how reliable a position estimation is. In order to determine the uncertainty in position estimation we resort to Machine Learning (ML) techniques that offer ways to determine the uncertainty/reliability of the predictions for a trained model. Hence, in this work we propose to combine ML methods such as Gaussian Process (GP) and Random Forest (RF) with RAT-based positioning measurements to predict the location of a UE and in the meantime also assess the uncertainty of the estimated position. The results show that both GP and RF not only achieve satisfactory positioning accuracy but also give a reliable uncertainty assessment of the predicted position of the UE.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge