UNBUS: Uncertainty-aware Deep Botnet Detection System in Presence of Perturbed Samples
Paper and Code
Apr 28, 2022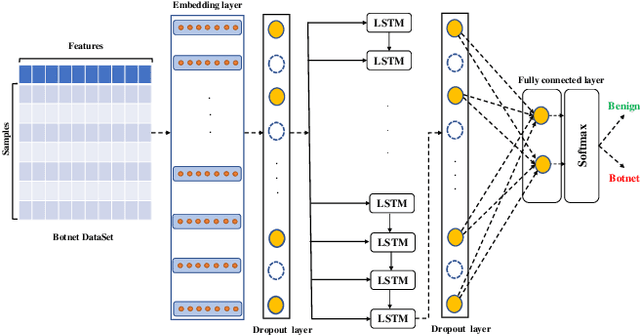
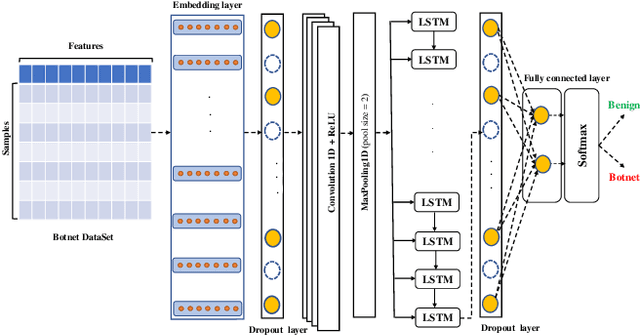
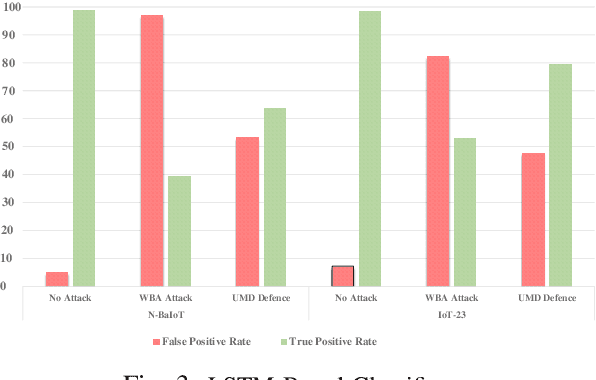
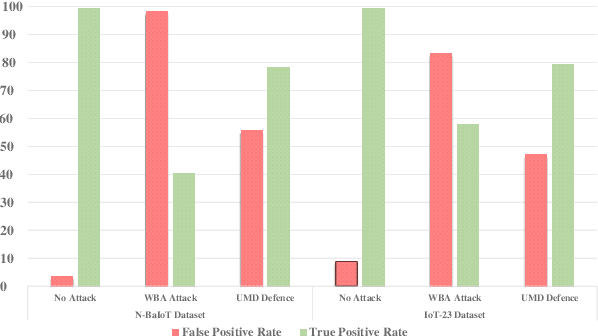
A rising number of botnet families have been successfully detected using deep learning architectures. While the variety of attacks increases, these architectures should become more robust against attacks. They have been proven to be very sensitive to small but well constructed perturbations in the input. Botnet detection requires extremely low false-positive rates (FPR), which are not commonly attainable in contemporary deep learning. Attackers try to increase the FPRs by making poisoned samples. The majority of recent research has focused on the use of model loss functions to build adversarial examples and robust models. In this paper, two LSTM-based classification algorithms for botnet classification with an accuracy higher than 98% are presented. Then, the adversarial attack is proposed, which reduces the accuracy to about 30%. Then, by examining the methods for computing the uncertainty, the defense method is proposed to increase the accuracy to about 70%. By using the deep ensemble and stochastic weight averaging quantification methods it has been investigated the uncertainty of the accuracy in the proposed methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge