UAV Corridor Coverage Analysis with Base Station Antenna Uptilt and Strongest Signal Association
Paper and Code
Mar 27, 2024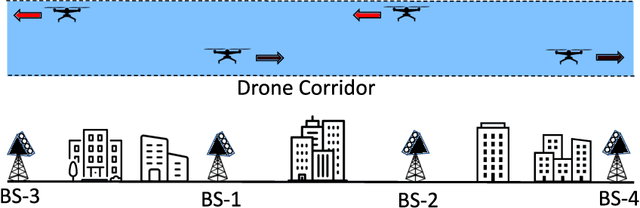
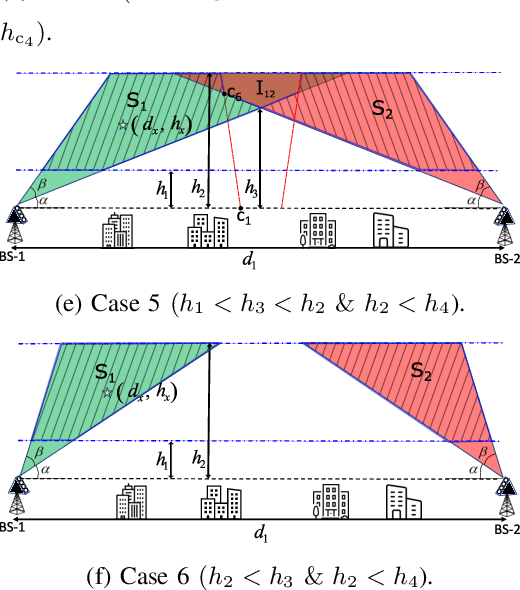
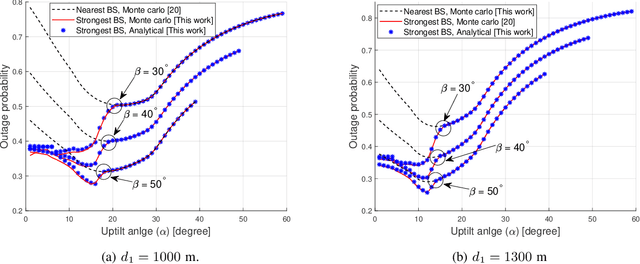
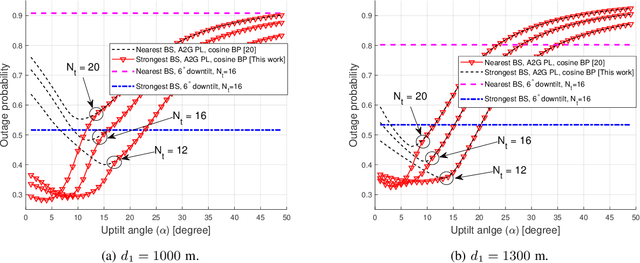
Unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) corridors are sky lanes where UAVs fly through safely between their origin and destination. To ensure the successful operation of UAV corridors, beyond visual line of sight (BVLOS) wireless connectivity within the corridor is crucial. One promising solution to support this is the use of cellular-connected UAV (C-UAV) networks, which offer long-range and seamless wireless coverage. However, conventional terrestrial base stations (BSs) that typically employ down-tilted sector antennas to serve ground users are not ideally suited to serve the aerial vehicles positioned above the BSs. In our previous work, we focused on studying the optimal uptilt angle of BS antennas to maximize the wireless coverage probability in UAV corridors. However, the association of BSs with UAVs was restricted to the nearest BS association, which limits the potential coverage benefits. In this paper, we address this limitation by considering the strongest BS signal association in UAV corridors, which enables enhanced coverage within the corridor compared to the nearest BS association. The strongest BS association allows UAVs to connect with the second nearest BSs while also accounting for interference from the third nearest BSs. Closed-form expression analysis and simulation results show that the strongest BSs association in UAV corridors yields a superior coverage probability when compared to the nearest BS association.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge